HeadCrab
GPU621/DPS921 | Participants | Groups and Projects | Resources | Glossary
Contents
[hide]Intel Math Kernel Library (MKL)
Team Member
Intro
For this assignment I will be focusing on the Linear Algebra routines. I will use workshop six to demonstrate how BLAS can be used to significantly speed up the calculations and compare them to other parallelization methods.
Compared to
- Serial
- Cilk
- Cilk with array notation and reduction
- Cilk with SIMD and reduction
- MKL CBLAS level 3
- CUDA CUBLAS level 3
- TBB
- OpenMP
Intel Math Kernel Library
MKL provides highly vectorized and threaded Linear Algebra, Fast Fourier Transforms, Vector Math and Statistics functions. Intel MKL uses industry standard APIs. This means that developers would have to make minor changes to their programs when switching to MKL.
Intel MKL gives the developer control over the necessary trade-offs
- Result consistency vs performance
- Accuracy vs performance
Intel MKL is also compatible with your choice of compilers, languages, operating systems, linking and threading models. One library solution across multiple environments means only one library to learn and manage.
Linear Algebra
Intel MKL provides highly optimized BLAS routines
- BLAS Level 1 vector-vector
- BLAS Level 2 matrix-vector
- BLAS Level 3 matrix-matrix
How to enable Intel MKL
#include <mkl.h>
Command line
- -mkl
- -mkl=parallel to link with standard threaded Intel MKL.
- -mkl=sequential to link with sequential version of Intel MKL.
- -mkl=cluster to link with Intel MKL cluster components (sequential) that use Intel MPI.
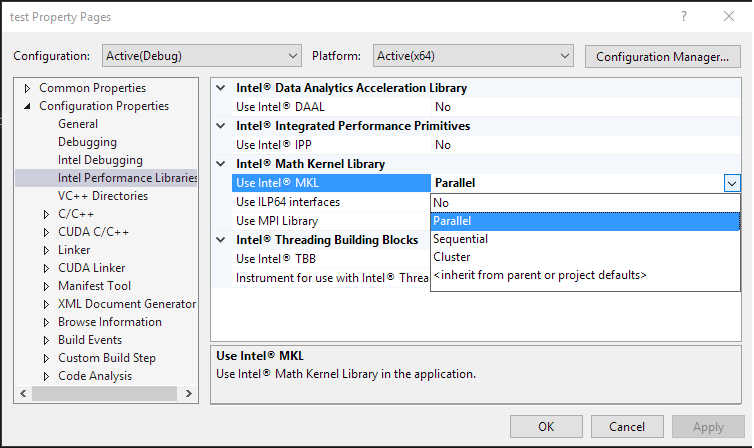
Microsoft Visual Studio
project properties->Intel Performance Libraries->Intel Math Kernel Library
Fig 1 - Enable MKL
Source code
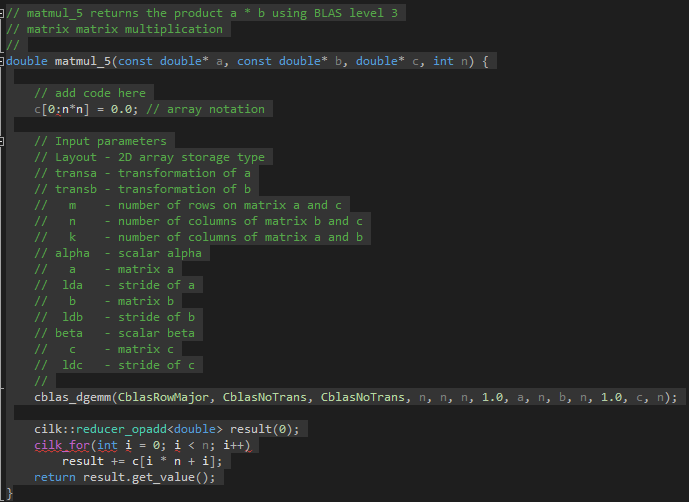
Fig 2 - MKL
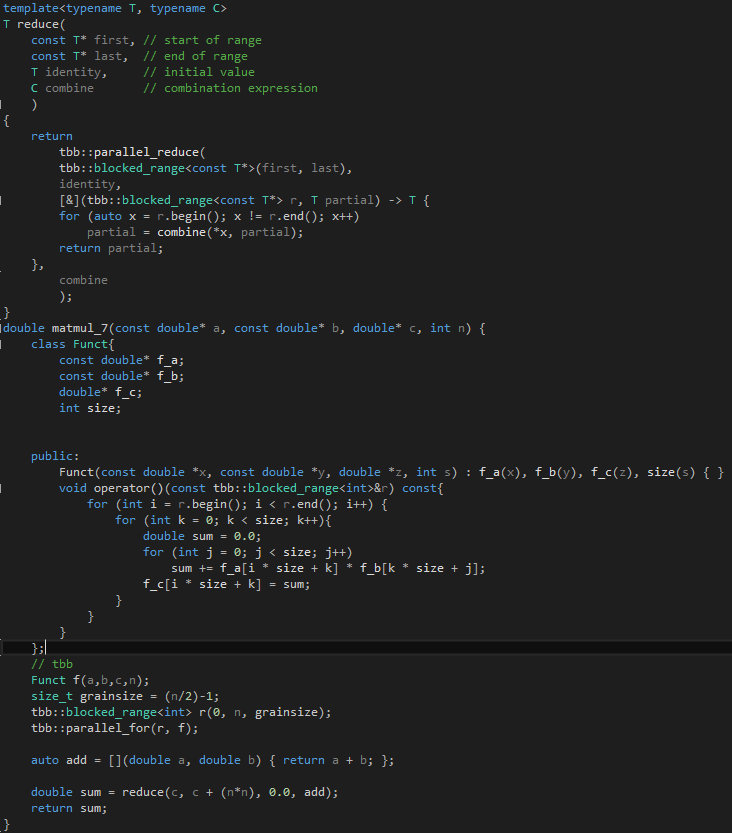
Fig 3 - TBB
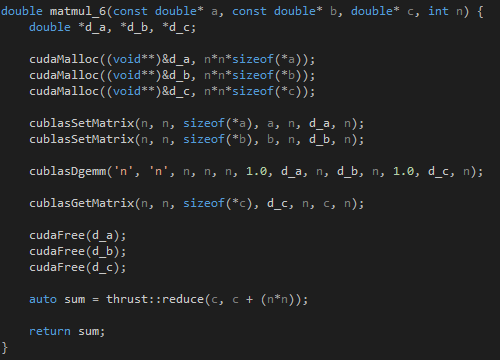
Fig 4 - CUDA
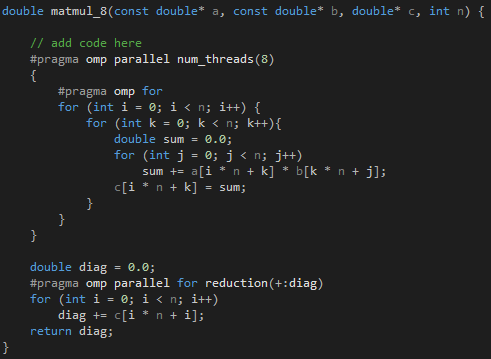
Fig 5 - OpenMP
Useful Link
- https://software.intel.com/en-us/intel-mkl/details
- https://software.intel.com/en-us/node/468380
- https://software.intel.com/sites/default/files/managed/4a/d6/mkl_11.2.1_lnx_userguide.pdf
Progress
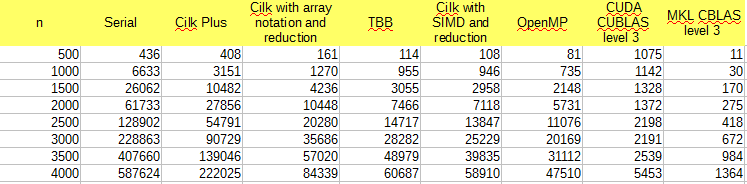
Fig 6 - Recorded times
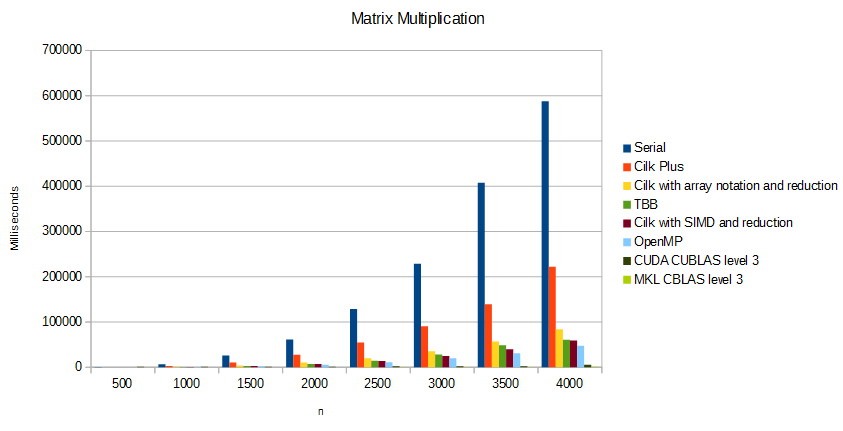
Fig 7 - Graph of times