Ghost Cells
GPU610/DPS915 | Student List | Group and Project Index | Student Resources | Glossary
Contents
[hide]Ghost Cells
Team Members
- Tony Sim, Issue Dumper
- Robert Dittrich, Issue Collector
- Inna Zhogova, Issue Resolver
Progress
Assignment 1
Tony
Subject: Jacobi's method for Poisson's equation
Source Code
| [Expand] poissan.h |
|---|
#ifndef POISSON_H
#define POISSON_H
#include <fstream>
namespace DPS{
class Poisson {
size_t nRowsTotal;
size_t nColumns;
float* data;
int bufferSide;
void update (size_t startRow, size_t endRow, const float wx, const float wy);
void bufferSwitch(){ bufferSide = 1 - bufferSide; };
public:
Poisson(std::ifstream& ifs);
Poisson(const size_t r, const size_t c, float* d);
~Poisson(){ delete[] data; };
float* operator()(const size_t iteration, const float wx, const float wy);
float* operator()(const size_t iteration){
return operator()(iteration,0.1,0.1);
}
void show(std::ostream& ofs) const;
};
}
#endif |
| [Expand] poissan.cpp |
|---|
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "poisson.h"
namespace DPS{
Poisson::Poisson(std::ifstream& ifs){
std::string line;
bufferSide = 0;
/* find number of columns */
std::getline(ifs,line);
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < line.size() ; i++){
if(line[i]==' ') nColumns++;
}
nColumns++;
/* find number of rows */
nRowsTotal++; /* already fetched one */
while(std::getline(ifs,line))
nRowsTotal++;
ifs.clear();
try{
data = new float[nColumns * nRowsTotal * 2];
}
catch (...){
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to Allocate Memory");
}
/* readin data */
ifs.seekg(0,ifs.beg);
std::cout << ifs.tellg() << std::endl;
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < nRowsTotal * nColumns ; i++) {
ifs >> data[i];
}
std::memset(data+nRowsTotal*nColumns,0,nRowsTotal*nColumns*sizeof(float));
}
Poisson::Poisson(const size_t r, const size_t c, float* d){
bufferSide = 0;
nRowsTotal = r;
nColumns = c;
try{
data = new float[r*c*2];
}
catch (...){
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to Allocate Memory");
}
std::memcpy(data,d,r*c*sizeof(float));
std::memset(data+r*c,0,r*c*sizeof(float));
}
void Poisson::update (size_t startRow, size_t endRow, const float wx, const float wy){
float* x_new = data + (1-bufferSide)*nRowsTotal*nColumns;
float* x_old = data + bufferSide*nRowsTotal*nColumns;
for (size_t i = startRow; i <= endRow; i++)
for (size_t j = 1; j < nColumns - 1; j++)
x_new[i * nColumns + j] = x_old[i * nColumns + j]
+ wx * (x_old[(i + 1) * nColumns + j] + x_old[(i - 1) * nColumns + j]
- 2.0f * x_old[i * nColumns + j])
+ wy * (x_old[i * nColumns + j + 1] + x_old[i * nColumns + j - 1]
- 2.0f * x_old[i * nColumns + j]);
}
float* Poisson::operator()(const size_t nIterations, const float wx, const float wy){
for (size_t i = 0; i < nIterations; i++) {
update(0, nRowsTotal-1, wx, wy);
bufferSwitch();
}
return data;
}
void Poisson::show(std::ostream& ofs) const{
ofs << std::fixed << std::setprecision(1);
for (size_t j = 0; j < nColumns ; j++) {
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < nRowsTotal ; i++)
ofs << std::setw(8) << data[ bufferSide*nColumns*nRowsTotal + i * nColumns + j];
ofs << std::endl;
}
}
} |
| [Expand] main.cpp |
|---|
// based on code from LLNL tutorial mpi_heat2d.c
// Master-Worker Programming Model
// Chris Szalwinski - 2018/11/13
// Adopted by Tony Sim - 2019/02/16
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <stdexcept>
#include "poisson.h"
// solution constants
const size_t NONE = 0;
const size_t MINPARTITIONS = 1;
const size_t MAXPARTITIONS = 7;
// weights
const float wx = 0.1f;
const float wy = 0.1f;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if (argc != 4) {
std::cerr << "*** Incorrect number of arguments ***\n";
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0]
<< " input_file output_file no_of_iterations\n";
return 1;
}
std::ifstream input(argv[1]);
std::ofstream output(argv[2]);
std::ofstream temp("init.csv");
if(!input.is_open()){
std::cerr << "Invalid Input File" << std::endl;
return 2;
}
if(!output.is_open()){
std::cerr << "Invalid Output File" << std::endl;
return 2;
}
DPS::Poisson* p = nullptr;
try{
p = new DPS::Poisson(input);
}
catch(std::exception& e){
std::cerr << "Error: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
p->show(temp);
size_t nIterations = std::atoi(argv[3]);
(*p)(nIterations);
// write results to file
p->show(output);
delete p;
} |
Introduction
The presented code simulates heat map using Jacobi's method for Poisson's equation. It is represented in a 2D array, and each element updates its value based on the adjacent elements at a given moment. Each iteration represent one instance in time. By repeating the calculation over the entire array through multiple iterations, we can estimate the state of the heat transfer after a given time interval.
Profiling
The profiling was conducted using a data set of 79 rows and 205 columns over 150000 iterations.
| [Expand] Flat profile |
|---|
|
Flat profile: Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls us/call us/call name 98.57 2.75 2.75 150000 18.33 18.33 DPS::Poisson::update(unsigned long, unsigned long, float, float) 0.00 2.75 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN3DPS7PoissonC2ERSt14basic_ifstreamIcSt11char_traitsIcEE 0.00 2.75 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I_main
|
| [Expand] Call graph |
|---|
Call graph
index % time self children called name 2.75 0.00 150000/150000 DPS::Poisson::operator()(unsigned long, float, float) [2] [1] 100.0 2.75 0.00 150000 DPS::Poisson::update(unsigned long, unsigned long, float, float) [1] <spontaneous> [2] 100.0 0.00 2.75 DPS::Poisson::operator()(unsigned long, float, float) [2] 2.75 0.00 150000/150000 DPS::Poisson::update(unsigned long, unsigned long, float, float) [1] 0.00 0.00 1/1 __libc_csu_init [21] [10] 0.0 0.00 0.00 1 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN3DPS7PoissonC2ERSt14basic_ifstreamIcSt11char_traitsIcEE [10] 0.00 0.00 1/1 __libc_csu_init [21] [11] 0.0 0.00 0.00 1 _GLOBAL__sub_I_main [11]
[10] _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN3DPS7PoissonC2ERSt14basic_ifstreamIcSt11char_traitsIcEE (poisson.cpp) [11] _GLOBAL__sub_I_main (main.cpp) [1] DPS::Poisson::update(unsigned long, unsigned long, float, float)
|
Analysis
given 98.57 percent of time is spent on the update() function, it is considered the hotspot. Total time taken was 2.75.
If we consider a GPU environment with 1000 cores, we can estimate the following speedup: S1000 = 1/(1-.9857 + .9857/1000) = 65.00 In fact, the speed will decrease from 2.75 seconds to 0.0450 seconds.
As each iteration depends on the product of the previous iteration, there is a dependency resolution that might hamper the parallel process. Consideration may also be extended to resolving ghost cells across different SMX while using the device global memory as the transfer pipeline.
Robert
Multi Sampling Anti Aliasing
Source Files
| [Expand] main.cpp |
|---|
#include <cstdint>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image.h"
#define STB_IMAGE_WRITE_IMPLEMENTATION
#include "stb_image_write.h"
#include "vec3.h"
struct Point {
int x;
int y;
};
uint8_t* msaa(const uint8_t* input, uint8_t* output, int width, int height, int channels, int samples) {
// directions is (samples * 2 + 1) ^ 2
int totalPoints = (samples * 2 + 1) * (samples * 2 + 1);
Point* directions = new Point[totalPoints];
size_t idx = 0;
for (int i = -samples; i <= samples; i++) {
for (int j = -samples; j <= samples; j++) {
directions[idx].x = i;
directions[idx].y = j;
idx++;
}
}
int x, y, cx, cy;
Vec3<int> average;
for (size_t i = 0; i < width*height; i++) {
x = i % width * channels;
y = i / width * channels;
for (size_t j = 0; j < totalPoints; j++) {
cx = x + directions[j].x * channels;
cy = y + directions[j].y * channels;
cx = std::clamp(cx, 0, width* channels);
cy = std::clamp(cy, 0, height* channels);
average.add(input[width * cy + cx], input[width * cy + cx + 1], input[width * cy + cx + 2]);
}
average.set(average.getX() / totalPoints, average.getY() / totalPoints, average.getZ() / totalPoints);
output[(width * y + x)] = average.getX();
output[(width * y + x) + 1] = average.getY();
output[(width * y + x) + 2] = average.getZ();
average.set(0, 0, 0);
}
delete[] directions;
return output;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if (argc != 5) {
std::cerr << argv[0] << ": invalid number of arguments\n";
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " input output sample_size passes \n";
system("pause");
return 1;
}
int width, height, channels;
uint8_t* rgb_read = stbi_load(argv[1], &width, &height, &channels, STBI_rgb);
if (channels != 3) {
std::cout << "Incorrect channels" << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 2;
}
int samples = std::atoi(argv[3]);
int passes = std::atoi(argv[4]);
uint8_t* rgb_write = new uint8_t[width*height*channels];
rgb_write = msaa(rgb_read, rgb_write, width, height, channels, samples);
for (int i = 1; i < passes; i++) {
rgb_write = msaa(rgb_write, rgb_write, width, height, channels, samples);
}
stbi_write_png(argv[2], width, height, channels, rgb_write, width*channels);
stbi_image_free(rgb_read);
delete[] rgb_write;
std::cout << "AA Done using " << samples << " sample size" << " over " << passes << " passes" << std::endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
} |
| [Expand] vec3.h |
|---|
#ifndef VEC3_H
#define VEC3_H
#include <iostream>
template <class T>
class Vec3 {
private:
T x;
T y;
T z;
public:
Vec3() {
x = 0;
y = 0;
z = 0;
};
Vec3(T x_, T y_, T z_) {
x = x_;
y = y_;
z = z_;
}
void set(const T &x_, const T &y_, const T &z_) {
x = x_;
y = y_;
z = z_;
}
void add(const T &x_, const T &y_, const T &z_) {
x += x_;
y += y_;
z += z_;
}
T getX() const { return x; }
T getY() const { return y; }
T getZ() const { return z; }
void setX(const T &x_) { x = x_; }
void setY(const T &y_) { y = y_; }
void setZ(const T &z_) { z = z_; }
static T dot(const Vec3& vec1, const Vec3& vec2) {
return vec1.x * vec2.x + vec1.y * vec2.y + vec1.z * vec2.z;
}
T dot(const Vec3 &vec) const {
return x * vec.x + y * vec.y + z * vec.z;
}
void display(std::ostream& os) {
os << "x: " << x << ", y: " << y << ", z: " << z << "\n";
}
};
#endif // !VEC3_H |
Introduction
For my selection I chose to do Anti Aliasing since I see it a lot in video games but I never really knew how it worked. There are other anti aliasing methods like FXAA which is fast approximate anti aliasing but it seemed a lot more complicated than MSAA. The way I approached this problem is by getting the color of the pixels around a pixel. In you can specify the distance it will search in the application flags. In my implementation you specify an input file, output file, the radius of pixels to sample and how many passes to take on the image. In my tests the command line options I used was an image I made in paint with 4 sample size and 4 passes.
| [Expand] Before |
|---|
| [Expand] After |
|---|
Profiling
| [Expand] Profiling |
|---|
Flat profile:
Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds.
% cumulative self self total
time seconds seconds calls ms/call ms/call name
85.72 0.18 0.18 msaa(unsigned char const*, unsigned char*, int, int, int, int)
14.29 0.21 0.03 1 30.00 30.00 stbi_zlib_compress
0.00 0.21 0.00 127820 0.00 0.00 stbiw__zlib_flushf(unsigned char*, unsigned int*, int*)
0.00 0.21 0.00 96904 0.00 0.00 stbiw__zhash(unsigned char*)
0.00 0.21 0.00 5189 0.00 0.00 stbi__fill_bits(stbi__zbuf*)
0.00 0.21 0.00 2100 0.00 0.00 stbiw__encode_png_line(unsigned char*, int, int, int, int, int, int, signed char*)
0.00 0.21 0.00 2014 0.00 0.00 stbiw__sbgrowf(void**, int, int) [clone .constprop.58]
0.00 0.21 0.00 38 0.00 0.00 stbi__get16be(stbi__context*)
0.00 0.21 0.00 19 0.00 0.00 stbi__get32be(stbi__context*)
0.00 0.21 0.00 3 0.00 0.00 stbi__skip(stbi__context*, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 3 0.00 0.00 stbiw__wpcrc(unsigned char**, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 3 0.00 0.00 stbi__stdio_read(void*, char*, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 3 0.00 0.00 stbi__zbuild_huffman(stbi__zhuffman*, unsigned char const*, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 stbi__mad3sizes_valid(int, int, int, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I_stbi_failure_reason
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi__getn(stbi__context*, unsigned char*, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi__readval(stbi__context*, int, unsigned char*)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi__load_main(stbi__context*, int*, int*, int*, int, stbi__result_info*, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi__parse_zlib(stbi__zbuf*, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi__malloc_mad3(int, int, int, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi__parse_png_file(stbi__png*, int, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi__start_callbacks(stbi__context*, stbi_io_callbacks*, void*)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi__decode_jpeg_header(stbi__jpeg*, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi__compute_huffman_codes(stbi__zbuf*)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi__load_and_postprocess_8bit(stbi__context*, int*, int*, int*, int)
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi_load_from_file
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 30.00 stbi_write_png_to_mem
0.00 0.21 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 stbi_zlib_decode_malloc_guesssize_headerflag |
Conclusion
Since the msaa function I wrote is a hotspot of the program I would suggest offloading part of it to a GPU, more specifically the part that finds the average of colors of the nearby pixels. That part also does not depend on previous iterations to finish so it is a prime candidate for parallelization.
Inna
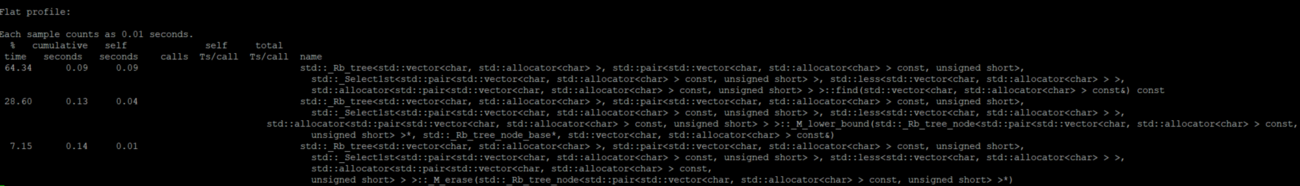
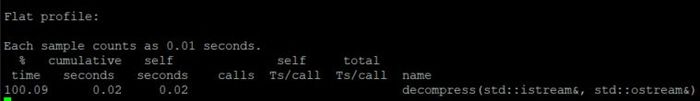
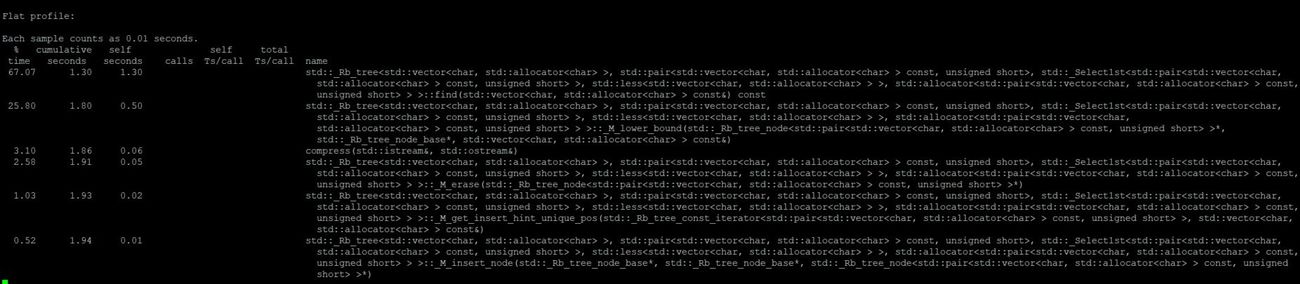
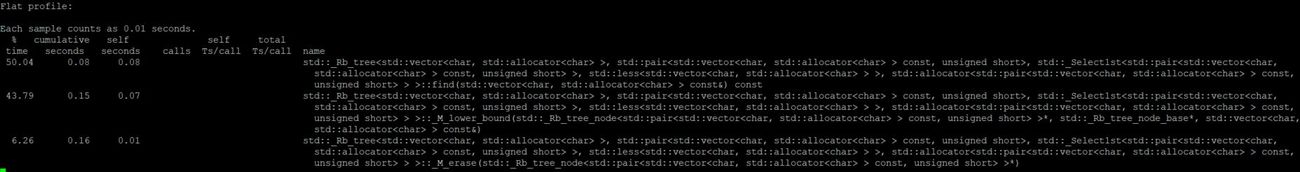
Subject: Data compression - LWZ algorithm.
Source: http://www.cplusplus.com/articles/iL18T05o/#Version1
I tested the following source code for a compression and decompression of .txt files and a gif.
| [Expand] lwz.cpp( ... ) |
|---|
///
/// @file
/// @author Julius Pettersson
/// @copyright MIT/Expat License.
/// @brief LZW file compressor
/// @version 1
///
/// This is the C++11 implementation of a Lempel-Ziv-Welch single-file command-line compressor.
/// It uses the simpler fixed-width code compression method.
/// It was written with Doxygen comments.
///
/// @see http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lempel%E2%80%93Ziv%E2%80%93Welch
/// @see http://marknelson.us/2011/11/08/lzw-revisited/
/// @see http://www.cs.duke.edu/csed/curious/compression/lzw.html
/// @see http://warp.povusers.org/EfficientLZW/index.html
/// @see http://en.cppreference.com/
/// @see http://www.doxygen.org/
///
#include <cstdint>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <exception>
#include <fstream>
#include <ios>
#include <iostream>
#include <istream>
#include <limits>
#include <map>
#include <ostream>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
/// Type used to store and retrieve codes.
using CodeType = std::uint16_t;
namespace globals {
/// Dictionary Maximum Size (when reached, the dictionary will be reset)
const CodeType dms {std::numeric_limits<CodeType>::max()};
} // namespace globals
///
/// @brief Helper operator intended to simplify code.
/// @param vc original vector
/// @param c element to be appended
/// @returns vector resulting from appending `c` to `vc`
///
std::vector<char> operator + (std::vector<char> vc, char c)
{
vc.push_back(c);
return vc;
}
///
/// @brief Compresses the contents of `is` and writes the result to `os`.
/// @param [in] is input stream
/// @param [out] os output stream
///
void compress(std::istream &is, std::ostream &os)
{
std::map<std::vector<char>, CodeType> dictionary;
// "named" lambda function, used to reset the dictionary to its initial contents
const auto reset_dictionary = [&dictionary] {
dictionary.clear();
const long int minc = std::numeric_limits<char>::min();
const long int maxc = std::numeric_limits<char>::max();
for (long int c = minc; c <= maxc; ++c)
{
// to prevent Undefined Behavior, resulting from reading and modifying
// the dictionary object at the same time
const CodeType dictionary_size = dictionary.size();
dictionary[{static_cast<char> (c)}] = dictionary_size;
}
};
reset_dictionary();
std::vector<char> s; // String
char c;
while (is.get(c))
{
// dictionary's maximum size was reached
if (dictionary.size() == globals::dms)
reset_dictionary();
s.push_back(c);
if (dictionary.count(s) == 0)
{
// to prevent Undefined Behavior, resulting from reading and modifying
// the dictionary object at the same time
const CodeType dictionary_size = dictionary.size();
dictionary[s] = dictionary_size;
s.pop_back();
os.write(reinterpret_cast<const char *> (&dictionary.at(s)), sizeof (CodeType));
s = {c};
}
}
if (!s.empty())
os.write(reinterpret_cast<const char *> (&dictionary.at(s)), sizeof (CodeType));
}
///
/// @brief Decompresses the contents of `is` and writes the result to `os`.
/// @param [in] is input stream
/// @param [out] os output stream
///
void decompress(std::istream &is, std::ostream &os)
{
std::vector<std::vector<char>> dictionary;
// "named" lambda function, used to reset the dictionary to its initial contents
const auto reset_dictionary = [&dictionary] {
dictionary.clear();
dictionary.reserve(globals::dms);
const long int minc = std::numeric_limits<char>::min();
const long int maxc = std::numeric_limits<char>::max();
for (long int c = minc; c <= maxc; ++c)
dictionary.push_back({static_cast<char> (c)});
};
reset_dictionary();
std::vector<char> s; // String
CodeType k; // Key
while (is.read(reinterpret_cast<char *> (&k), sizeof (CodeType)))
{
// dictionary's maximum size was reached
if (dictionary.size() == globals::dms)
reset_dictionary();
if (k > dictionary.size())
throw std::runtime_error("invalid compressed code");
if (k == dictionary.size())
dictionary.push_back(s + s.front());
else
if (!s.empty())
dictionary.push_back(s + dictionary.at(k).front());
os.write(&dictionary.at(k).front(), dictionary.at(k).size());
s = dictionary.at(k);
}
if (!is.eof() || is.gcount() != 0)
throw std::runtime_error("corrupted compressed file");
}
///
/// @brief Prints usage information and a custom error message.
/// @param s custom error message to be printed
/// @param su Show Usage information
///
void print_usage(const std::string &s = "", bool su = true)
{
if (!s.empty())
std::cerr << "\nERROR: " << s << '\n';
if (su)
{
std::cerr << "\nUsage:\n";
std::cerr << "\tprogram -flag input_file output_file\n\n";
std::cerr << "Where `flag' is either `c' for compressing, or `d' for decompressing, and\n";
std::cerr << "`input_file' and `output_file' are distinct files.\n\n";
std::cerr << "Examples:\n";
std::cerr << "\tlzw_v1.exe -c license.txt license.lzw\n";
std::cerr << "\tlzw_v1.exe -d license.lzw new_license.txt\n";
}
std::cerr << std::endl;
}
///
/// @brief Actual program entry point.
/// @param argc number of command line arguments
/// @param [in] argv array of command line arguments
/// @retval EXIT_FAILURE for failed operation
/// @retval EXIT_SUCCESS for successful operation
///
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 4)
{
print_usage("Wrong number of arguments.");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
enum class Mode {
Compress,
Decompress
};
Mode m;
if (std::string(argv[1]) == "-c")
m = Mode::Compress;
else
if (std::string(argv[1]) == "-d")
m = Mode::Decompress;
else
{
print_usage(std::string("flag `") + argv[1] + "' is not recognized.");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
std::ifstream input_file(argv[2], std::ios_base::binary);
if (!input_file.is_open())
{
print_usage(std::string("input_file `") + argv[2] + "' could not be opened.");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
std::ofstream output_file(argv[3], std::ios_base::binary);
if (!output_file.is_open())
{
print_usage(std::string("output_file `") + argv[3] + "' could not be opened.");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
try
{
input_file.exceptions(std::ios_base::badbit);
output_file.exceptions(std::ios_base::badbit | std::ios_base::failbit);
if (m == Mode::Compress)
compress(input_file, output_file);
else
if (m == Mode::Decompress)
decompress(input_file, output_file);
}
catch (const std::ios_base::failure &f)
{
print_usage(std::string("File input/output failure: ") + f.what() + '.', false);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
catch (const std::exception &e)
{
print_usage(std::string("Caught exception: ") + e.what() + '.', false);
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
} |
Tested data
1. book.txt - a 343 kilobyte text file.
2. words.txt - a 4.7 megabyte text file.
3. fire.gif - a 309 kilobyte graphical image.
Flat Profiles
Book
Flat profile for compression:
Flat profile for decompression:
Text
Flat profile for compression:
Flat profile for decompression:
GIF
Flat profile for compression:
Flat profile for decompression:
Assignment 2
Source Files
| [Expand] poisson-pcie.cu |
|---|
/*
* Poisson Method using two arrays.
* Non-Ghost Cells Method
* Multiple PCIe Calls made, once per iteration
* by Tony Sim
*/
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include "poisson.cuh"
namespace DPS{
Poisson::Poisson(std::ifstream& ifs) {
std::string line;
nColumns = 0;
bufferSide = 0;
nRowsTotal = 0;
/* find number of columns */
std::getline(ifs,line);
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < line.size() ; i++){
if(line[i]==' ') nColumns++;
}
nColumns++;
/* find number of rows */
nRowsTotal++; /* already fetched one */
while(std::getline(ifs,line))
nRowsTotal++;
ifs.clear();
try{
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++)
h_data[i] = new float[ (nColumns+2) * (nRowsTotal+2)]; /* add edge buffers */
}
catch (...){
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to Allocate Memory");
}
/* readin data */
std::cout <<"Reading in data"<<std::endl;
ifs.seekg(0,ifs.beg);
/* allocate memory to all but the edge buffer, index 0 and max for each row and column */
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < nRowsTotal+2 ; i++){
for (size_t j = 0 ; j < nColumns+2 ; j++){
float val = 0;
if(!(i == 0 || i == nRowsTotal + 1 || j == 0 || j == nColumns + 1))
ifs >> val;
h_data[0][i*(nColumns+2)+j] = val;
}
}
std::cout <<"Setting buffer"<<std::endl;
std::memset(h_data[1],0,(nRowsTotal+2)*(nColumns+2)*sizeof(float));
bool state = devMemSet();
}
Poisson::Poisson(const size_t r, const size_t c, float* d) {
bufferSide = 0;
nRowsTotal = r;
nColumns = c;
try{
h_data[0] = new float[(r+2)*(c+2)];
h_data[1] = new float[(r+2)*(c+2)];
}
catch (...){
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to Allocate Memory");
}
std::memcpy(h_data[0],d,(r+2)*(c+2)*sizeof(float));
std::memset(h_data[1],0,(r+2)*(c+2)*sizeof(float));
devMemSet();
}
Poisson::~Poisson(){
for( size_t i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++){
delete [] h_data[i];
cudaFree(d_data[i]);
}
}
bool Poisson::devMemSet(){
for(size_t i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++){
cudaMalloc(&d_data[i],(nColumns+2)*(nRowsTotal+2)*sizeof(float));
if(d_data[i] != nullptr){
cudaError_t state = cudaMemcpy((void*)d_data[i],(const void*)h_data[i],(nColumns+2)*(nRowsTotal+2)*sizeof(float),cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if(state != cudaSuccess)
std::cerr << "ERROR on devMemSet for : " << i <<" with : " << cudaGetErrorString(state)<< std::endl;
}
}
return d_data[0]&&d_data[1];
}
float* Poisson::operator()(const size_t nIterations, const float wx, const float wy){
/* calculate the grid, block, where block has 1024 threads total */
unsigned int blockx = 32;
unsigned int blocky = 32;
unsigned int gridx = ((nRowsTotal+2)+blockx-1)/blockx;
unsigned int gridy = ((nRowsTotal+2)+blocky-1)/blocky;
/* create dim3 */
dim3 dBlock= {blockx,blocky};
dim3 dGrid = {gridx,gridy};
/* run iterations */
for (size_t i = 0; i < nIterations; i++) {
update<<<dGrid,dBlock>>>(d_data[1-bufferSide],d_data[bufferSide],nColumns, nRowsTotal, wx, wy);
bufferSwitch();
}
/* DEBUG */ h_data[bufferSide][1*(nColumns+2) + 1] = 100.0f;
/* output results from device to host */
cudaError_t state = cudaMemcpy(h_data[bufferSide],d_data[bufferSide],(nColumns+2)*(nRowsTotal+2)*sizeof(float),cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if(state != cudaSuccess)
std::cout << "ERROR on () when copying data back to host" <<" with : " << cudaGetErrorString(state)<< std::endl;
return h_data[bufferSide];
}
void Poisson::show(std::ostream& ofs) const{
ofs << std::fixed << std::setprecision(1);
for (size_t j = 1; j <= nColumns ; j++) {
for (size_t i = 1 ; i <= nRowsTotal ; i++)
ofs << std::setw(8) << h_data[bufferSide][i * (nColumns+2) + j]<<",";
ofs << std::endl;
}
}
__global__ void update (float* newD, const float* currD, int nCol, int nRow, const float wx, const float wy){
size_t i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x + 1; /* for x axis */
size_t j = blockDim.y * blockIdx.y + threadIdx.y + 1; /* for y axis */
newD[i*(nCol+2)+j] = currD[i * (nCol+2) +j] + wx*(currD[(i+1) * (nCol+2) +j] + currD[(i-1) * (nCol+2) +j] - 2.0f * currD[i * (nCol+2) +j] ) + wy*( currD[i * (nCol+2) +j+1] + currD[i * (nCol+2) +j-1] - 2.0f * currD[i * (nCol+2) +j]) ;
__syncthreads();
}
} |
| [Expand] poisson-alt.cu |
|---|
/*
* Poisson Method using two arrays.
* Non-Ghost Cells Method
* One PCIe Call made, iterations done in kernel
* by Tony Sim
*/
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include "poisson-alt.cuh"
namespace DPS{
Poisson::Poisson(std::ifstream& ifs) {
blockx = 32;
blocky = 32;
std::string line;
nColumns = 0;
bufferSide = 0;
nRowsTotal = 0;
/* find number of columns */
std::getline(ifs,line);
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < line.size() ; i++){
if(line[i]==' ') nColumns++;
}
nColumns++;
/* find number of rows */
nRowsTotal++; /* already fetched one */
while(std::getline(ifs,line))
nRowsTotal++;
ifs.clear();
int sizeX = ((nColumns + 2 + blockx + 2 - 1)/(blockx+2))*(blockx+2);
int sizeY = ((nRowsTotal + 2 + blocky + 2 - 1)/(blocky+2))*(blocky+2);
bufferSize = sizeX * sizeY;
std::cout << "Allocate initial memory" << std::endl;
try{
h_data = new float[ bufferSize ]; /* add edge buffers */
}
catch (...){
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to Allocate Memory");
}
/* readin data */
std::cout <<"Reading in data"<<std::endl;
ifs.seekg(0,ifs.beg);
/* allocate memory to all but the edge buffer, index 0 and max for each row and column */
std::memset(h_data,0,bufferSize);
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < nRowsTotal+2 ; i++){
for (size_t j = 0 ; j < nColumns+2 ; j++){
float val = 0;
if(!(i == 0 || i == nRowsTotal + 1 || j == 0 || j == nColumns + 1))
ifs >> val;
h_data[i*(nColumns+2)+j] = val;
}
}
std::cout <<"Setting buffer"<<std::endl;
bool state = devMemSet();
}
Poisson::Poisson(const size_t r, const size_t c, float* d) {
bufferSide = 0;
nRowsTotal = r;
nColumns = c;
try{
h_data = new float[(r+2)*(c+2)];
}
catch (...){
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to Allocate Memory");
}
std::memcpy(h_data,d,(r+2)*(c+2)*sizeof(float));
devMemSet();
}
Poisson::~Poisson(){
delete [] h_data;
cudaFree(d_data);
cudaDeviceReset();
}
bool Poisson::devMemSet(){
/* create double buffer */
cudaMalloc(&d_data,2* bufferSize * sizeof(float));
if(d_data != nullptr){
/* copy the initial information to the first buffer */
cudaError_t state = cudaMemcpy((void*)d_data,(const void*)h_data, bufferSize * sizeof(float),cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if(state != cudaSuccess)
std::cerr << "ERROR on devMemSet at cudaMemcpy : " << cudaGetErrorString(state)<< std::endl;
/* set the second buffer to zero */
state = cudaMemset( d_data + bufferSize , 0, bufferSize * sizeof(float));
if(state != cudaSuccess)
std::cerr << "ERROR on devMemSet at cudaMemset : " << cudaGetErrorString(state)<< std::endl;
}
return d_data;
}
float* Poisson::operator()(const size_t nIterations, const float wx, const float wy){
/* calculate the grid, block, where block has 1024 threads total */
unsigned int gridx = ((nRowsTotal+2)+blockx-1)/blockx;
unsigned int gridy = ((nRowsTotal+2)+blocky-1)/blocky;
/* create dim3 */
dim3 dBlock= {blockx,blocky};
dim3 dGrid = {gridx,gridy};
/* run iterations */
update<<<dGrid,dBlock>>>(d_data,nColumns, nRowsTotal, wx, wy,nIterations,bufferSize);
/*DEBUG */ h_data[2*(nColumns+2)+2] = 100.0f;
/* output results from device to host */
cudaError_t state = cudaMemcpy(h_data,d_data,(nColumns+2)*(nRowsTotal+2)*sizeof(float),cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if(state != cudaSuccess)
std::cout << "ERROR on () when copying data back to host with : " << cudaGetErrorString(state)<< std::endl;
return h_data;
}
void Poisson::show(std::ostream& ofs) const{
ofs << std::fixed << std::setprecision(1);
for (size_t j = 1; j <= nColumns ; j++) {
for (size_t i = 1 ; i <= nRowsTotal ; i++)
ofs << std::setw(8) << h_data[i * (nColumns+2) + j]<<",";
ofs << std::endl;
}
}
__global__ void update (float* data, int nCol, int nRow, const float wx, const float wy, unsigned int nIterations, unsigned int bufferSize){
size_t i = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x + 1; /* for x axis */
size_t j = blockDim.y * blockIdx.y + threadIdx.y + 1; /* for y axis */
unsigned int buffer = 0;
/* run iterations */
for (unsigned int n = 0 ; n < nIterations; n++){
/* Calculate and store into the other buffer */
data[(1-buffer)*bufferSize + i*(nCol+2)+j] = data[buffer*bufferSize + i * (nCol+2)+ j]
+ wx * (data[buffer*bufferSize + (i+1) * (nCol+2) +j] + data[buffer*bufferSize + (i-1) * (nCol+2) + j] - 2.0f * data[buffer*bufferSize + i * (nCol+2)+ j])
+ wy * (data[buffer*bufferSize + i * (nCol+2) + j + 1] + data[buffer*bufferSize + i * (nCol+2) + j - 1] - 2.0f * data[buffer*bufferSize + i * (nCol+2)+ j]);
__syncthreads();
/* flip buffer */
buffer = 1-buffer;
}
/* copy the output back into global memory */
data[i*(nCol+2)+j] = data[buffer * bufferSize + i * (nCol+2) + j ];
__syncthreads();
}
} |
Profiles
| [Expand] Poisson PCIe Profile |
|---|
Reading in data
Setting buffer
==6484== NVPROF is profiling process 6484, command: .\pcie.exe .\test3.csv .\output3.csv 1000
==6484== Profiling application: .\pcie.exe .\test3.csv .\output3.csv 1000
==6484== Warning: 43 API trace records have same start and end timestamps.
This can happen because of short execution duration of CUDA APIs and low timer resolution on the underlying operating sy
stem.
==6484== Profiling result:
Type Time(%) Time Calls Avg Min Max Name
GPU activities: 99.86% 29.120ms 1000 29.119us 24.158us 30.589us DPS::update(float*, float const *, int, int
, float, float)
0.09% 26.269us 2 13.134us 12.990us 13.279us [CUDA memcpy HtoD]
0.04% 13.119us 1 13.119us 13.119us 13.119us [CUDA memcpy DtoH]
API calls: 71.59% 183.43ms 2 91.713ms 10.265us 183.42ms cudaMalloc
15.25% 39.069ms 1 39.069ms 39.069ms 39.069ms cuDevicePrimaryCtxRelease
8.04% 20.601ms 3 6.8671ms 81.478us 20.424ms cudaMemcpy
3.76% 9.6313ms 1000 9.6310us 6.7360us 335.53us cudaLaunchKernel
1.26% 3.2196ms 96 33.537us 0ns 1.6234ms cuDeviceGetAttribute
0.05% 127.03us 1 127.03us 127.03us 127.03us cuModuleUnload
0.04% 107.78us 2 53.890us 22.454us 85.327us cudaFree
0.00% 10.265us 1 10.265us 10.265us 10.265us cuDeviceTotalMem
0.00% 9.6230us 1 9.6230us 9.6230us 9.6230us cuDeviceGetPCIBusId
0.00% 1.2820us 2 641ns 320ns 962ns cuDeviceGet
0.00% 962ns 3 320ns 0ns 641ns cuDeviceGetCount
0.00% 962ns 1 962ns 962ns 962ns cuDeviceGetName
0.00% 321ns 1 321ns 321ns 321ns cuDeviceGetUuid
0.00% 321ns 1 321ns 321ns 321ns cuDeviceGetLuid |
| [Expand] Poisson AltProfile |
|---|
Allocate initial memory
Reading in data
Setting buffer
==2720== NVPROF is profiling process 2720, command: .\alt.exe .\test3.csv .\output3.csv 1000
==2720== Profiling application: .\alt.exe .\test3.csv .\output3.csv 1000
==2720== Warning: 50 API trace records have same start and end timestamps.
This can happen because of short execution duration of CUDA APIs and low timer resolution on the underlying operating sy
stem.
==2720== Profiling result:
Type Time(%) Time Calls Avg Min Max Name
GPU activities: 99.88% 25.679ms 1 25.679ms 25.679ms 25.679ms DPS::update(float*, int, int, float, float,
unsigned int, unsigned int)
0.06% 16.670us 1 16.670us 16.670us 16.670us [CUDA memcpy HtoD]
0.05% 12.575us 1 12.575us 12.575us 12.575us [CUDA memcpy DtoH]
0.00% 576ns 1 576ns 576ns 576ns [CUDA memset]
API calls: 70.46% 158.87ms 1 158.87ms 158.87ms 158.87ms cudaMalloc
16.71% 37.678ms 1 37.678ms 37.678ms 37.678ms cudaDeviceReset
11.48% 25.877ms 2 12.938ms 60.947us 25.816ms cudaMemcpy
1.25% 2.8161ms 96 29.334us 0ns 1.3867ms cuDeviceGetAttribute
0.06% 133.12us 1 133.12us 133.12us 133.12us cudaFree
0.02% 47.475us 1 47.475us 47.475us 47.475us cudaMemset
0.01% 18.605us 1 18.605us 18.605us 18.605us cudaLaunchKernel
0.01% 11.548us 1 11.548us 11.548us 11.548us cuDeviceTotalMem
0.00% 9.9440us 1 9.9440us 9.9440us 9.9440us cuDeviceGetPCIBusId
0.00% 1.2830us 1 1.2830us 1.2830us 1.2830us cuDeviceGetName
0.00% 963ns 3 321ns 0ns 642ns cuDeviceGetCount
0.00% 642ns 1 642ns 642ns 642ns cuDeviceGetLuid
0.00% 641ns 2 320ns 0ns 641ns cuDeviceGet
0.00% 0ns 1 0ns 0ns 0ns cuDeviceGetUuid |
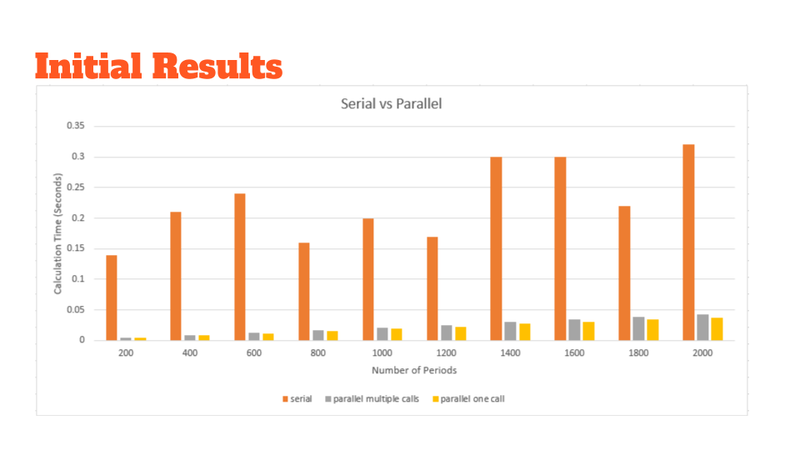
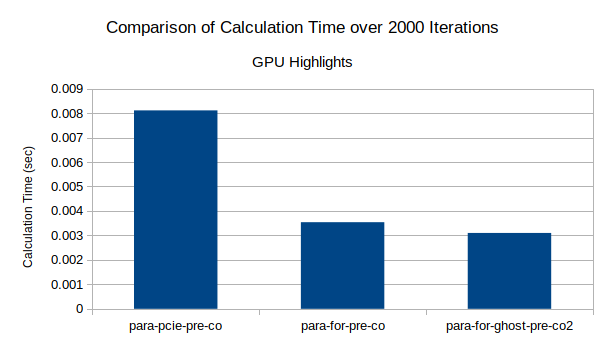
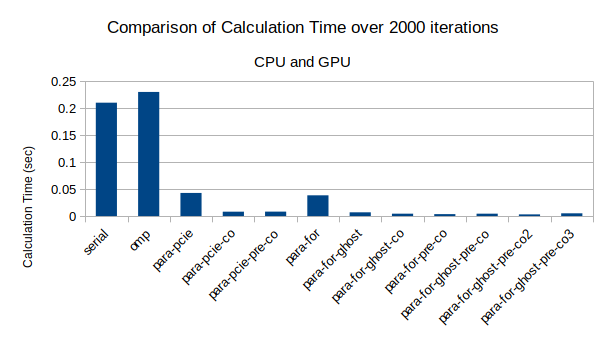
GPU Offload Vs CPU
Assignment 3
Source Codes
| [Expand] PCIe Optimization |
|---|
/*
* Poisson Method using two arrays.
* Non-Ghost Cells Method
* Multiple PCIe Calls made, once per iteration
* by Tony Sim
*/
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include "poisson.cuh"
namespace DPS{
Poisson::Poisson(std::ifstream& ifs) {
std::string line;
nColumns = 0;
bufferSide = 0;
nRowsTotal = 0;
/* find number of columns */
std::getline(ifs,line);
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < line.size() ; i++){
if(line[i]==' ') nColumns++;
}
nColumns++;
/* find number of rows */
nRowsTotal++; /* already fetched one */
while(std::getline(ifs,line))
nRowsTotal++;
ifs.clear();
try{
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++)
h_data[i] = new float[ (nColumns+2) * (nRowsTotal+2)]; /* add edge buffers */
}
catch (...){
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to Allocate Memory");
}
/* readin data */
std::cout <<"Reading in data"<<std::endl;
ifs.seekg(0,ifs.beg);
/* allocate memory to all but the edge buffer, index 0 and max for each row and column */
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < nRowsTotal+2 ; i++){
for (size_t j = 0 ; j < nColumns+2 ; j++){
float val = 0;
if(!(i == 0 || i == nRowsTotal + 1 || j == 0 || j == nColumns + 1))
ifs >> val;
h_data[0][i*(nColumns+2)+j] = val;
}
}
std::cout <<"Setting buffer"<<std::endl;
std::memset(h_data[1],0,(nRowsTotal+2)*(nColumns+2)*sizeof(float));
bool state = devMemSet();
/* DEBUG */ std::cout << state << std::endl;
}
Poisson::Poisson(const size_t r, const size_t c, float* d) {
bufferSide = 0;
nRowsTotal = r;
nColumns = c;
try{
h_data[0] = new float[(r+2)*(c+2)];
h_data[1] = new float[(r+2)*(c+2)];
}
catch (...){
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to Allocate Memory");
}
std::memcpy(h_data[0],d,(r+2)*(c+2)*sizeof(float));
std::memset(h_data[1],0,(r+2)*(c+2)*sizeof(float));
devMemSet();
}
Poisson::~Poisson(){
for( size_t i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++){
delete [] h_data[i];
cudaFree(d_data[i]);
}
}
bool Poisson::devMemSet(){
for(size_t i = 0 ; i < 2 ; i++){
cudaMalloc(&d_data[i],(nColumns+2)*(nRowsTotal+2)*sizeof(float));
if(d_data[i] != nullptr){
cudaError_t state = cudaMemcpy((void*)d_data[i],(const void*)h_data[i],(nColumns+2)*(nRowsTotal+2)*sizeof(float),cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if(state != cudaSuccess)
std::cerr << "ERROR on devMemSet for : " << i <<" with : " << cudaGetErrorString(state)<< std::endl;
}
}
return d_data[0]&&d_data[1];
}
float* Poisson::operator()(const size_t nIterations, const float wx, const float wy){
/* calculate the grid, block, where block has 1024 threads total */
unsigned int blockx = 32;
unsigned int blocky = 32;
unsigned int gridx = ((nRowsTotal+2)+blockx-1)/blockx;
unsigned int gridy = ((nRowsTotal+2)+blocky-1)/blocky;
/* create dim3 */
dim3 dBlock= {blockx,blocky};
dim3 dGrid = {gridx,gridy};
/* run iterations */
for (size_t i = 0; i < nIterations; i++) {
update<<<dGrid,dBlock>>>(d_data[1-bufferSide],d_data[bufferSide],nColumns, nRowsTotal, wx, wy);
bufferSwitch();
}
/* DEBUG */ h_data[bufferSide][1*(nColumns+2) + 1] = 100.0f;
/* output results from device to host */
cudaError_t state = cudaMemcpy(h_data[bufferSide],d_data[bufferSide],(nColumns+2)*(nRowsTotal+2)*sizeof(float),cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if(state != cudaSuccess)
std::cout << "ERROR on () when copying data back to host" <<" with : " << cudaGetErrorString(state)<< std::endl;
return h_data[bufferSide];
}
void Poisson::show(std::ostream& ofs) const{
ofs << std::fixed << std::setprecision(1);
for (size_t j = 1; j <= nColumns ; j++) {
for (size_t i = 1 ; i <= nRowsTotal ; i++)
ofs << std::setw(8) << h_data[bufferSide][i * (nColumns+2) + j]<<",";
ofs << std::endl;
}
}
__global__ void update (float* newD, const float* currD, int nCol, int nRow, const float wx, const float wy){
size_t j = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x + 1; /* for x axis */
size_t i = blockDim.y * blockIdx.y + threadIdx.y + 1; /* for y axis */
float curr = currD[i * (nCol+2)+ j];
float dir1 = currD[(i+1) * (nCol+2) +j];
float dir2 = currD[(i-1) * (nCol+2) +j];
float dir3 = currD[i * (nCol+2) +j+1];
float dir4 = currD[i * (nCol+2) +j-1];
newD[i*(nCol+2)+j] = curr + wx * (dir1+dir2-2.0f*curr) + wy * (dir3+dir4-2.0f*curr);
__syncthreads();
}
} |
| [Expand] For-loop Optimization |
|---|
/*
* Poisson Method using two arrays.
* Non-Ghost Cells Method
* Multiple PCIe Calls made, once per iteration
* by Tony Sim
*/
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iomanip>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include "poisson-alt-ghost2.cuh"
namespace DPS{
Poisson::Poisson(std::ifstream& ifs) {
blockx = 32;
blocky = 32;
std::string line;
nColumns = 0;
bufferSide = 0;
nRowsTotal = 0;
/* find number of columns */
std::getline(ifs,line);
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < line.size() ; i++){
if(line[i]==' ') nColumns++;
}
nColumns++;
/* find number of rows */
nRowsTotal++; /* already fetched one */
while(std::getline(ifs,line))
nRowsTotal++;
ifs.clear();
int sizeX = ((nColumns + 2 + blockx + 2 - 1)/(blockx+2))*(blockx+2);
int sizeY = ((nRowsTotal + 2 + blocky + 2 - 1)/(blocky+2))*(blocky+2);
bufferSize = sizeX * sizeY;
std::cout << "Allocate initial memory" << std::endl;
try{
h_data = new float[ bufferSize ]; /* add edge buffers */
}
catch (...){
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to Allocate Memory");
}
/* readin data */
std::cout <<"Reading in data"<<std::endl;
ifs.seekg(0,ifs.beg);
/* allocate memory to all but the edge buffer, index 0 and max for each row and column */
std::memset(h_data,0,bufferSize);
for (size_t i = 0 ; i < nRowsTotal+2 ; i++){
for (size_t j = 0 ; j < nColumns+2 ; j++){
float val = 0;
if(!(i == 0 || i == nRowsTotal + 1 || j == 0 || j == nColumns + 1))
ifs >> val;
h_data[i*(nColumns+2)+j] = val;
}
}
std::cout <<"Setting buffer"<<std::endl;
bool state = devMemSet();
}
Poisson::Poisson(const size_t r, const size_t c, float* d) {
bufferSide = 0;
nRowsTotal = r;
nColumns = c;
try{
h_data = new float[(r+2)*(c+2)];
}
catch (...){
throw std::runtime_error("Failed to Allocate Memory");
}
std::memcpy(h_data,d,(r+2)*(c+2)*sizeof(float));
devMemSet();
}
Poisson::~Poisson(){
delete [] h_data;
cudaFree(d_data);
cudaDeviceReset();
}
bool Poisson::devMemSet(){
/* create double buffer */
cudaMalloc(&d_data, bufferSize * sizeof(float));
if(d_data != nullptr){
/* copy the initial information to the first buffer */
cudaError_t state = cudaMemcpy((void*)d_data,(const void*)h_data, bufferSize * sizeof(float),cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if(state != cudaSuccess)
std::cerr << "ERROR on devMemSet at cudaMemcpy : " << cudaGetErrorString(state)<< std::endl;
}
return d_data;
}
float* Poisson::operator()(const size_t nIterations, const float wx, const float wy){
/* calculate the grid, block, where block has 1024 threads total */
unsigned int gridx = ((nRowsTotal+2)+blockx-1)/blockx;
unsigned int gridy = ((nRowsTotal+2)+blocky-1)/blocky;
/* create dim3 */
dim3 dBlock= {blockx,blocky};
dim3 dGrid = {gridx,gridy};
/* generate shared memory map that will control ghost cell sharing */
char* hmap = new char[(blockx+2)*(blocky+2)*3];
int stride = 3;
for(int i = 0 ; i < (blockx+2);i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < (blocky+2);j++){
char val = 0;
char x = 0;
char y = 0;
if(i==1){
val = 1;
x=-1;
y=0;
}
if(j==1){
val = 1;
x=0;
y=-1;
}
if(i==blockx) {
val = 1;
x=1;
y=0;
}
if(j==blocky){
val = 1;
x=0;
y=1;
}
if(i==2 || j==2 || i==31 || j==31)
val = 2;
hmap[(i * (blockx+2) + j)*stride] = val;
hmap[(i * (blockx+2) + j)*stride+1] = x;
hmap[(i * (blockx+2) + j)*stride+2] = y;
}
}
/* transfer to device */
char* dmap = nullptr;
cudaMalloc(&dmap,(blockx+2)*(blocky+2)*sizeof(char)*3);
cudaMemcpy(dmap,hmap,(blockx+2)*(blocky+2)*sizeof(char)*3,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
/* run iterations */
update<<<dGrid,dBlock>>>(d_data,dmap,nColumns, nRowsTotal, wx, wy,nIterations);
/*DEBUG */ h_data[2*(nColumns+2)+2] = 100.0f;
/* output results from device to host */
cudaError_t state = cudaMemcpy(h_data,d_data,(nColumns+2)*(nRowsTotal+2)*sizeof(float),cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if(state != cudaSuccess)
std::cout << "ERROR on () when copying data back to host with : " << cudaGetErrorString(state)<< std::endl;
return h_data;
}
void Poisson::show(std::ostream& ofs) const{
ofs << std::fixed << std::setprecision(1);
for (size_t j = 1; j <= nColumns ; j++) {
for (size_t i = 1 ; i <= nRowsTotal ; i++)
ofs << std::setw(8) << h_data[i * (nColumns+2) + j]<<",";
ofs << std::endl;
}
}
__global__ void update (float* data, char* dmap, int nCol, int nRow, const float wx, const float wy, unsigned int nIterations){
size_t j = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x + 1; /* for x axis */
size_t i = blockDim.y * blockIdx.y + threadIdx.y + 1; /* for y axis */
size_t y = threadIdx.x+1;
size_t x = threadIdx.y+1;
const unsigned int bufferSize = (32+2)*(32+2);
__shared__ float localBuffer[ 2 * bufferSize ]; /* double local buffer with ghost cells */
// __shared__ char lmap[bufferSize];
unsigned int buffer = 0;
float prefetch = 0.0f;
/* copy information into first of the local buffer */
localBuffer[x*(32+2)+y] = data[i*(nCol+2)+j];
__syncthreads();
const char lmap = dmap[(x*(32+2)+y)*3];
const char addx = dmap[(x*(32+2)+y)*3+1];
const char addy = dmap[(x*(32+2)+y)*3+2];
/* prefetch */
if(lmap)
prefetch = data[(i+addx)*(nCol+2)+j+addy] ;
/* run iterations */
for (unsigned int n = 0 ; n < nIterations; n++){
if(lmap)
localBuffer[buffer * bufferSize + (x+addx)*(32+2) + y+addy] = prefetch;
/* Calculate and store into the other buffer */
float curr = localBuffer[buffer*bufferSize + x * (32+2)+ y];
float dir1 = localBuffer[buffer*bufferSize + (x+1) * (32+2) +y];
float dir2 = localBuffer[buffer*bufferSize + (x-1) * (32+2) +y];
float dir3 = localBuffer[buffer*bufferSize + x * (32+2) + y + 1];
float dir4 = localBuffer[buffer*bufferSize + x * (32+2) + y - 1];
localBuffer[(1-buffer)*bufferSize + x*(32+2)+y] = curr + wx*(dir1+dir2-2.0f*curr) + wy*(dir3+dir4-2.0f*curr);
/* flip buffer */
buffer = 1-buffer;
/* for threads in charge of edges, share and obtain ghost cells */
if(lmap){
/* Copy over edges to global memory to be shared with neighboring blocks */
data[i*(nCol+2)+j] = localBuffer[buffer * bufferSize + x * (32+2) + y ];
}
__syncthreads();
if(lmap){
/* Copy back buffers from global memory */
prefetch = data[(i+addx)*(nCol+2)+j+addy] ;
}
}
/* copy the output back into global memory */
data[i*(nCol+2)+j] = localBuffer[buffer * bufferSize + x * (32+2) + y ];
__syncthreads();
}
} |
| [Expand] For-loop Optimization - poissant-alt-ghost2.cuh |
|---|
/*
* Poisson Method using two arrays.
* Non-Ghost Cells Method
* Multiple PCIe Calls made, once per iteration
* by Tony Sim
*/
#ifndef POISSON_H
#define POISSON_H
#include <fstream>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
namespace DPS{
class Poisson {
unsigned int blockx;
unsigned int blocky;
unsigned int nRowsTotal;
unsigned int nColumns;
unsigned int bufferSize;
float* h_data;
float* d_data;
int bufferSide;
void bufferSwitch(){ bufferSide = 1 - bufferSide; };
bool devMemSet();
public:
Poisson() = delete;
Poisson(std::ifstream& ifs);
Poisson(const size_t r, const size_t c, float* d);
~Poisson();
float* operator()(const size_t iteration, const float wx, const float wy);
float* operator()(const size_t iteration){
return operator()(iteration,0.1,0.1);
}
void show(std::ostream& ofs) const;
};
__global__ void update (float* data, char* dmap, int nCol, int nRow, const float wx, const float wy, unsigned int nIterations);
}
#endif |
Optimization Details
PCIe Version
- Coalesced Memory - Large performance boost.
- Prefetch - this had minor to no effect on the performance.
For-loop Version
- Shared Memory - Small boost. Used technique called Ghost Cells where updated information is shared over global memory as needed to perform the next iteration.
- Prefetch - Small boost. Information are fetched first into register in the previous iteration to be copied in the current iteration prior to calculation.
- Coalesed Memory - Large boost.
- Logic change - To minimize the number of condition calls, a predefined map of instruction was created on the host based on the block dimension information. Using this information, the if statement had been cut down to almost 1/4, showing noticeable performance increase.
Result
POST Presentation Results Contrary to the presentation's conclusion, the ghost-cell method proved to be more effective with some changes to the logic than simpler global-memory-based counterpart. It does require some preparation in the host machine. The gain is small.