OPS235 Lab 6 - Fedora17
Revision as of 13:41, 2 March 2010 by Brian.gray (talk | contribs)
Contents
Configuring a Network Using Virtual Machines
Objectives
- Configure a virtual network for Virtual Machines
- Use the Fedora GUI program to configure network interfaces with static IP configuration and host name resolution
- Use the
findcommand to locate the configuration files modified by the GUI network configuration program - To examine some of the Linux's TCP/IP configuration files in the
/etc/directory - To configure a Fedora host with static network configuration without a GUI tool
- To use and interpret the
netstatcommand to troubleshoot and monitor network services - To configure the linux firewall
iptablesto allow/disallow/forward different types of network traffic using simple rules
Reference
- man pages for find, ifconfig, ping, netstat, NetworkManager, nslookup, iptables, arp
- Online reading material for week 8.
Required materials
- Fedora 12 Live CD or a classmate on the same pod
- USB flash drive, 64 MB or more in size (Warning: the contents of this drive will be erased)
- One SATA hard disk in a removable drive tray with Fedora host and 3 Fedora Virtual Machines installed
Current Configuration
Currently you should have the following network configuration:
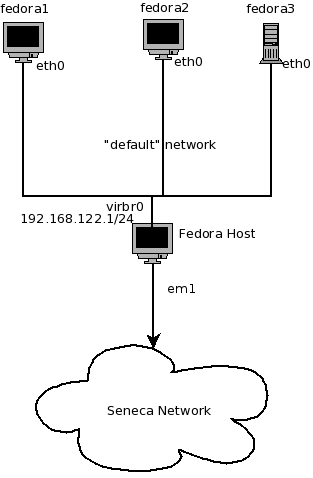
- Fedora host has 1 active network interface (probably
eth0)that receives IP configuration from the School's DHCP server. - Fedora host has 1 active network interface (
virbr0) that has a static default configuration of 192.168.122.1/255.255.255.0 - Fedora1 VM has 1 active interface (
eth0) that receives a dynamic configuration from your Fedora Host - Fedora2 VM has 1 active interface (
eth0) that receives a dynamic configuration from your Fedora Host - Fedora3 VM has 1 active interface (
eth0) that receives a dynamic configuration from your Fedora Host
Lab Preparation
Lab Investigations
Investigation 1: How do you create a new virtual network.
Before configuring our network we want to turn off dynamic network configuration for our Virtual Machines by turning off the "default" virtual network.
- On the fedora host start Virtual Machine Manager
- Under Edit->Host Details select the Virtual Networks tab
- Disable the default configuration from starting at boot by deselecting the "Autostart On Boot" checkbox.
- Stop the default network configuration by clicking on the stop button at the bottom of the window.
- Click on the add button to add a new network configuration.
- Give your new network a name (network1)
- Enter in the new network IP address space:
- 192.168.235.0/24
- Disable DHCP by deselecting the check box.
- Enable Network Forwarding by Selecting "Forwarding to physical network"
- The destination should be "Any physical device" and the mode should be "NAT"
- Now we need to add our new virtual network "network1" to the 3 VM's
- Select the fedora1 VM and edit the VM details
- Under View select Details
- In the left pane select the NIC and note that this NIC is on the "default" virtual network
- Click on the Remove button
- Click on "Add Hardware" and add a new network
- For the host device select "Virtual Network network1" : NAT
- Repeat these steps for fedora2 and fedora3 VM's
- Answer the Investigation 1 question in your lab log book.
Investigation 2: How do you create a new virtual network.
- Start fedora2 VM and login
- To configure a