Tutorial 8 - Links / Process Management
Content under development
Contents
LINKING FILES / MANAGING PROCESSES
Main Objectives of this Practice Tutorial
- Define the term i-node as it relates to the Unix/Linux File System
- Issue the ls -i command to view i-node (index) numbers associated with Unix/Linux files
- Define the terms Hard and Symbolic Links
- Issue the ln command to create hard and symbolic links
- Define term process as it relates to the Unix/ Linux operating system
- Run and terminate processes in the foreground and background
- Display and manipulate background and foreground processes
- Use alias and history commands in Unix/Linux
Tutorial Reference Material
| Course Notes |
Concepts / Commands | ||
| Course Notes:
|
Links
Managing Processes |
Linux Commands
| |
KEY CONCEPTS
i-node (index) ID Number of a File
An i-node is a database containing information (e.g. file type, owner, permissions, etc.) for all files that are created on the Unix/Linux filesystem.
The i-node number is like a finger-print, and is considered to be unique for each file on the Unix / Linux file system.
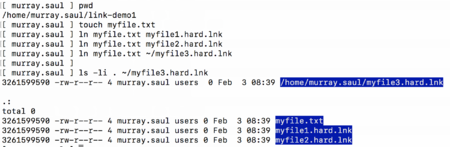
Referring to the diagram on the far right, issuing the ls command with the -i option displays the i-node number for each file. You can see that each file (whether it is a directory or regular file) has its own unique
i-node number.
Hard Links
(Image licensed under cc)
Image manipulated by author
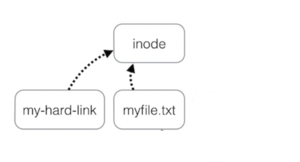
A Hard link is a reference to the physical data on a file system.
It does this by creating a file that shares the same i-node number with the original file.
Advantages: If only one hard link remains (even if original file has been removed), the data in that hard linked file is NOT lost. The data in hard linked files are automatically updated when original file are updated.
Disadvantages: Hard links take-up extra space, you cannot hard link directories,
and you cannot hard link files from other Unix/Linux servers (since the inode number may already be used by the other Unix/Linux server).
Examples:
ln myfile.txt myfile1.hard.lnk
ln myfile.txt ~/backups/myfile.hard.lnk
Symbolic Links
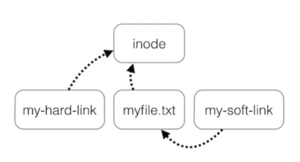
A Symbolic Link is an indirect pointer to a file and are also known as soft link or symlink. The symbolic link file contains the pathname to the original file.
Advantages: symbolic links are shortcuts to other files, where the symbolic link only contains the pathname to the original file, you can create symbolic links
on different Unix/Linux servers, and that you can create symbolic links for directories.
Disadvantages: Symbolic links are NOT good for backup purposes
since a symbolic link can point to a nonexistent file (referred to as a "broken link").
Examples:
ln -s otherfile.txt otherfile1.sym.lnk
ln -s otherfile.txt ~/backups/otherfile.sym.lnk
Managing Processes
All commands/programs (tasks) that are running on a Unix/Linux computer system are referred to as processes.
Characteristics of Processes:
- Each process has an owner
- Each process has a unique ID (PID)
- Processes keep their PID for their entire life.
- Usually a parent sleeps (suspends) when a child is running (the exception is when the child process is running in the background)
- UNIX / Linux processes are hierarchical. The process structure can have child processes, great grandchild processes, etc.
Users can manage processes to become more productive while working in the Unix / Linux Command-line environment.
Processes that run in the terminal are known as foreground processes. You can run or send processes currently running
in the foreground to the background to free-up your terminal (e.g. issue other Linux commands).
Below are a listing of common Linux commands and keyboard shortcuts to manage foreground and background processes:
| Linux Command / Key Combination | Purpose |
|---|---|
| ps | Displays snapshot information about processes. Examples: ps , ps -l , ps -ef , ps -u , ps aux |
| top | The top command provides a realtime status of running processes. NOTE: You can press ctrl-c to exit |
| ctrl-c | Terminates a process running in the foreground |
| ctrl-z | Sends a process running in the foreground into the background. |
| fg | Moves a background job from the current environment into the foreground. Example: fg %job-number |
| bg | Runs (starts) the most recent process that was placed into the background. Example: bg %job-number |
| jobs | The jobs utility displays the status of jobs that were started in the current shell environment. Example: jobs [1]+ Stopped vim a <-- Job #1 (+ most recent process / background) [2] Running sleep 200 & <-- Job #2 [3] Running sleep 300 & <-- Job #3 [4]- Running sleep 400 & <-- Job #4 (- second recent process / background) |
| kill | The kill command sends the specified signal to the specified processes or process groups. If no signal is specified, the TERM signal is sent. The default action for this signal is to terminate the process. Examples: kill PID , kill -9 PID , kill %job-number , kill -9 %job-number |
Aliases / Command History
Aliases:
An alias is a nickname to an existing command or group of commands.
An alias existing in system memory and will be lost when your current Linux session ends,
unless the alias is set in a start-up file (e.g. ~/.bashrc. You will learn about using start-up files later in this course.
Examples:
alias (Alias command without an argument will display all the aliases currently set)
alias dir=ls
alias ls='ls -al'
alias clearfile='cat /dev/null >'
unalias alias-name (removes alias from memory)
Command History:
The filename ~/.bash_history stores recently executed command lines
Examples of commands that use command history:
| up arrow or down arrow | move to previous command or next command within Bash shell prompt |
| fc -l | display last 16 commands |
| history | more | display all stored commands |
| !num | re-execute an issued command number by command number (determined from history command) |
| !xxx | re-run a most recent previously-issued command beginning with string "xxx" |
INVESTIGATION 1: LINKING FILES
ATTENTION: The due date for successfully completing this tutorial (i.e. tutorial 8) is by Friday, December 15 @ 11:59 PM (Week 14).
In this investigation, you will learn how to create hard links and symbolic links on your Matrix account,
and observe the advantages and limitations of using both types of links.
Perform the Following Steps:
- Login to your matrix account.
- Issue a Linux command to confirm you are located in your home directory.
NOTE: You will remain in your home directory to get practice using pathnames. - Issue the following Linux command to create a directory called ~/links:
mkdir ~/links - Issue the ls -ld command to confirm that the directory ~/links exists.
- Use a text editor to create a file called ~/links/data-file.txt
(i.e. without changing to the links directory). - Enter the following text displayed below:
This is line 1
This is line 2
This is line 3 - Save your editing session and exit your text editor.
- Issue the following Linux command:
ls -li ~/links/data-file.txt
View the i-node number for this file. What does this i-node number represent?
We will now create a hard link file to demonstrate how creating hard links are useful for back-ups. - Issue the following Linux command to create the following hard link in the same directory:
ln ~/links/data-file.txt ~/links/data-file.hard.lnk - Issue the following Linux command to display i-node ID numbers for both files:
ls -li ~/links/data-file.txt ~/links/data-file.hard.lnk
What do you notice about both of those file's i-node numbers? - Use a text editor to edit ~/links/data-file.txt
and add some lines of text to the bottom of that file. - Save your editing session and exit your text editor.
- Issue the following Linux command:
cat ~/links/data-file.hard.lnk
You should notice that the hard linked file also contains the additional line(s) that you added to the original file.
This is very useful for backing up your files without using the cp command! - Use a text editor to edit the hard-linked file ~/links/data-file.hard.lnk
and add some lines to the bottom of this file. - Save your editing session and exit your text editor.
- Issue the following Linux command:
cat ~/links/data-file.txt
What happened to this original file?</u> file?
What does this mean in terms of creating hard-linked files for back-ups? - Issue the following Linux command to create a hard-linked file in your home directory:
ln ~/links/data-file.txt ~/data-file.hard.lnk - Issue the following Linux command to compare all file's i-node numbers:
ls -li ~/links/data-file.txt ~/links/data-file.hard.lnk ~/data-file.hard.lnk
What do you notice about all of those file's i-node numbers? - Issue the following Linux command to check that you created those hard links:
~osl640/week8-check-1
If you encounter errors, then view the feedback to make corrections, and then re-run the checking script.
If you receive a congratulation message that there are no errors, then proceed with this tutorial. - Issue the following Linux command to remove the ~/links directory and its contents:
rm -rf ~/links - Issue a Linux command to confirm that the ~/links directory has been removed.
- Issue the following Linux command to view the contents of your linked file in your home directory:
cat ~/data-file.hard.lnk
What do you notice? What does this tell you about hard links?
We will now learn how to create symbolic links. - Issue the following Linux command to create a directory called ~/links2:
mkdir ~/links2
NOTE: You will remain in your home directory to get practice using pathnames. - Issue the ls -ld command to confirm that the directory called ~/links2 exists.
- Use a text editor to create a file called ~/links2/text-file.txt
(i.e. without changing to the links2 directory). - Enter the following text displayed below:
This is line one
This is line two
This is line three - Save your editing session and exit your text editor.
- Issue the following Linux command to create the following symbolic link in the same directory:
ln -s ~/links2/text-file.txt ~/links2/text-file.sym.lnk - Issue the following Linux command to display i-node numbers for both files:
ls -li ~/links2/text-file.txt ~/links2/text-file.sym.lnk
What do you notice about both of these file's i-node numbers?
What do you notice about the size of the file ~/links2/text-file.sym.lnk?
What pathname do you think this symbolic-linked file represents? - Issue the following Linux command to create the following symbolic link in your home directory:
ln -s ~/links2/text-file.txt ~/text-file.sym.lnk - Issue the following Linux command to display i-node numbers for all of those files:
ls -li ~/links2/text-file.txt ~/links2/text-file.sym.lnk ~/text-file.sym.lnk
What do you notice about all of those file's i-node numbers?
What is the file size of ~/text-file.sym.lnk?
What pathname do you think this symbolic-linked file contains? - Use a text editor to edit the symbolic link file called ~/links2/text-file.sym.lnk
and add some lines to the bottom of that file. - Save your editing session and exit your text editor.
- Issue the following Linux command to view the contents of the original file:
cat ~/links2/text-file.txt
What did you notice? This happened because when you edited the symbolic-linked file,
you were redirected (via pathname) to the original file. - Use a text editor to edit the original file called ~/links2/text-file.txt
and add some lines to the bottom of that file. - Save your editing session and exit your text editor.
- Issue the following Linux command to view the contents of the symbolic linked file:
cat ~/links2/text-file.sym.lnk
What did you notice? Again, when you view the contents of the symbolic-linked file,
you are redirected (via pathname) to the original file. - Issue the following Linux command to check that you created those symbolic links:
~osl640/week8-check-2
If you encounter errors, then view the feedback to make corrections, and then re-run the checking script.
If you receive a congratulation message that there are no errors, then proceed with this tutorial. - Issue the following Linux command to remove the ~/links2 directory:
rm -rf ~/links2 - Issue a Linux command to confirm that the ~/links2 directory has been removed.
- Issue the following Linux command to view the contents of the
original file called ~/links2/text-file.txt:
cat ~/text-file.sym.lnk
What happened? Why did does this happen? - Issue the following Linux command:
ls -l ~/text-file.sym.lnk
This output indicates a "broken link" and indicates this is not an effective method of backing up files. - Issue a command to delete the ~/text-file.sym.lnk file which is a broken link.
- Issue the following Linux command:
ln -s ~jason.carman/example t8example - Issue the following Linux command:
ls -ld t8example
What do you notice? Symbolic links are good for creating "short-cuts" to both regular files and directories.
- In the next investigation, you will learn how to manage processes on your Matrix server.
INVESTIGATION 2: MANAGING PROCESSES
In this investigation, you will learn how to manage processes on a Unix / Linux server.
Perform the Following Steps:
- Make certain that you are logged into your Matrix account.
- Issue a Linux command to confirm that you are located in your home directory.
The sleep command pauses for a specified number of seconds before returning to the shell prompt.
In this tutorial, we will be using this command to simulate the management of "long-running" processes. - Issue the following Linux command: sleep 700
Notice that this process will run for 700 seconds, and is forcing the user to wait until this process finishes.
A process that is running in the terminal is referred to as a foreground processes.
The Unix/Linux system is designed to allow users to send preemptive signals to manage those processes. - Press the following key combination to terminate the command running on the terminal: ctrl-c
You should notice that the process that was running in the foreground has been interrupted (i.e. terminated).
NOTE: The ctrl-c key combination sends SIGINT (Signal Interrupt - which is signal #2)
to terminate a process that is running on the terminal (i.e. a foreground process). - Reissue the Linux command: sleep 700
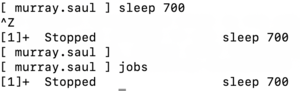
- Press the key combination: ctrl-z
- You should now see output similar to what is displayed below:
[1]+ Stopped sleep 700
NOTE: This indicates that this process has been placed into the background.
This is useful in order to "free-up" the terminal to run other Linux commands. - Issue the following Linux command: jobs
You should see the following output similar that was displayed above:
[1]+ Stopped sleep 700
This display indicates that this process (that is now in the background) has stopped.
In other words, the sleep command is NOT counting-down to zero to terminate.
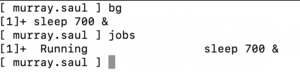
NOTE: You need to use the bg command to run that process that was sent into the background. - Issue the following Linux command: bg
NOTE: You can use the bg command WITHOUT arguments to run recent in the background. From the jobs command, the process that has a plus sign "+" indicates the most recent process placed into the background. - Issue the following Linux command: jobs
You should see the following output similar that was displayed above:
[1]+ sleep 700 &
This display indicates that this process in the background is running in the background
(indicated by the ampersand character "&"). Now this command has resume pausing until 700 seconds. - Issue the following Linux command: fg
You should notice that the sleep command is now running in the foreground.
- Press the key combination to terminate the process running in the foreground:
ctrl-c
You can issue Linux commands with ampersand "&" in your terminal to run processes automatically in the background without having to issue ctrl-z and bg short-cut keys.
- Issue the following Linux commands:
sleep 500 & sleep 600 & sleep 700 & - Issue the jobs command. What do you notice?
In the jobs command output, jobs that display a plus sign (+) indicates the most recent process
placed in to the background, and a minus sign (-) indicates the second most recent process
placed into the background.
The kill command issued to terminate processes that are running in the foreground or background.
Issuing the kill command without options would send the SIGTERM signal (eg. signal terminate - which is signal #15). - Issue the following Linux command to terminate the first job running in the background:
kill %1
NOTE: You can specify job number preceded by percent % with the
kill, bg, and fg commands to specify the processes' job number. - Issue the jobs command. What do you notice?
- Issue the following Linux commands:
kill %2
kill %3 - Issue the jobs command (you may have to issue the jobs command several times to get final result).
What do you notice? - Let's use grouping to run several commands in sequence within a single process.
- Issue the following Linux command:
(sleep 400; sleep 500; sleep 600) & - Issue the jobs command. What do you notice?
You should notice all commands are run in a group as just one process. - Issue the following Linux command to terminate the first job running in the background:
kill %1
NOTE: If issuing the kill command does not work, then you would need to send a STRONGER signal
to "kill" (not "SIGTERM - which is signal #15") the process. The SIGKILL signal (signal #9)
would be required to do this by issuing the kill command with the option: -9. - Issue the jobs command and make certain there are no processes that are running in the background.
You can also manipulate processes by their PID (process ID). Let's terminate our Matrix Bash shell process
by using the kill command using that processes' PID. - Issue the following Linux command: ps
- Note in the ps command output the PID of the process called bash.
You will be using that PID when issuing the next Linux command. - Issue the following Linux command (using the bash processes' PID number instead of "PID"):
kill PID
What did you notice?
FYI: If the command did NOT work, issue the following Linux command (using the bash processes' PID number instead of "PID"):
kill -9 PID
- In the next investigation, you will learn how to create aliases and view command history on your Matrix server.
INVESTIGATION 3: ALIASES / COMMAND HISTORY
= LINUX PRACTICE QUESTIONS =