Kernal Blas
GPU610/DPS915 | Student List | Group and Project Index | Student Resources | Glossary
Contents
[hide]Kernal Blas
Team Members
Progress
Assignment 1
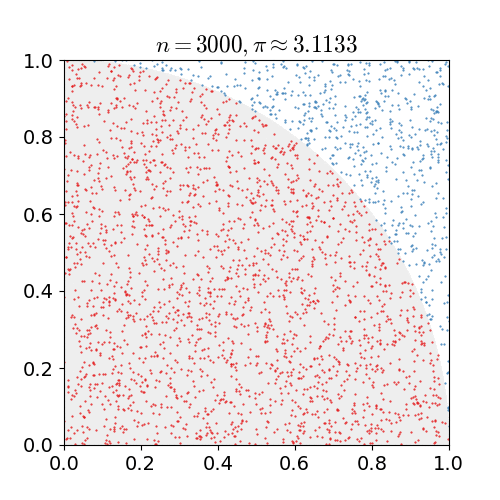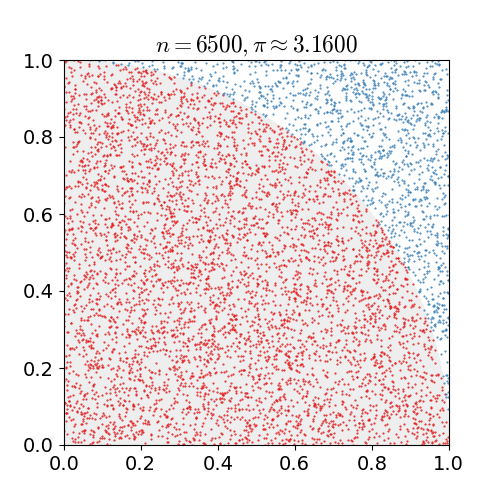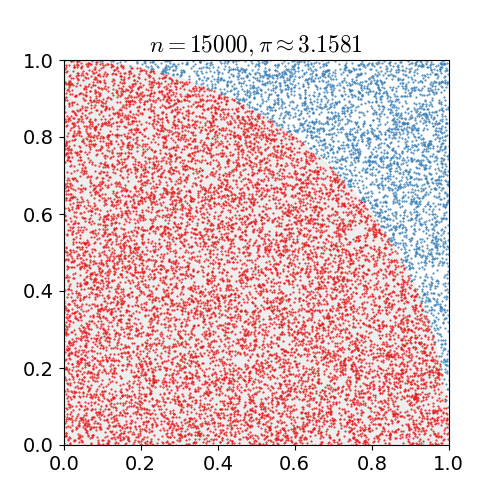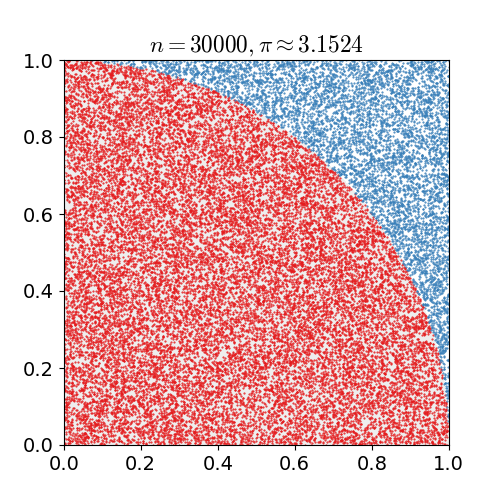
Calculation of Pi
For this assessment, we used code found at helloacm.com
In this version, the value of PI is calculated using the Monte Carlo method. This method states:
- A circle with radius r in a squre with side length 2r
- The area of the circle is πr2 and the area of the square is 4r2
- The ratio of the area of the circle to the area of the square is: πr2 / 4r2 = π / 4
- If you randomly generate N points inside the square, approximately N * π / 4 of those points (M) should fall inside the circle.
- π is then approximated as:
- N * π / 4 = M
- π / 4 = M / N
- π = 4 * M / N
In other words
π ≈ 4 * Ninner / Ntotal
For simplicity the radius of the circle is 1.
With this, we randomly generate points within the area and count the number of times each point falls within the circle, between 0 and 1.
We then calculate the ratio and
multiply by 4 which will give us the approximation of Π.
When we only have a small number of points, the estimation is not very accurate,
but when we have hundreds of thousands of points, we get much closer to the actual value.
When we run the program we see:
1st Run
1000 3.152 - took - 0 millisecs 10000 3.1328 - took - 0 millisecs 100000 3.14744 - took - 9 millisecs 1000000 3.141028 - took - 96 millisecs 10000000 3.1417368 - took - 998 millisecs 100000000 3.1419176 - took - 10035 millisecs The first column represents the number of points we are generating
With this method, we can see that the accuracy of the calculation is slightly off. This is due to the randomization of points within the circle. Running the program again will give us slightly different results.
2nd Run
1000 3.12 - took - 0 millisecs 10000 3.1428 - took - 0 millisecs 100000 3.13528 - took - 9 millisecs 1000000 3.143348 - took - 106 millisecs 10000000 3.1414228 - took - 1061 millisecs 100000000 3.14140056 - took - 8281 millisecs
The hotspot within the code lies in the loops. There iteration for the loops is O(n2)
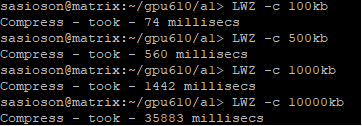
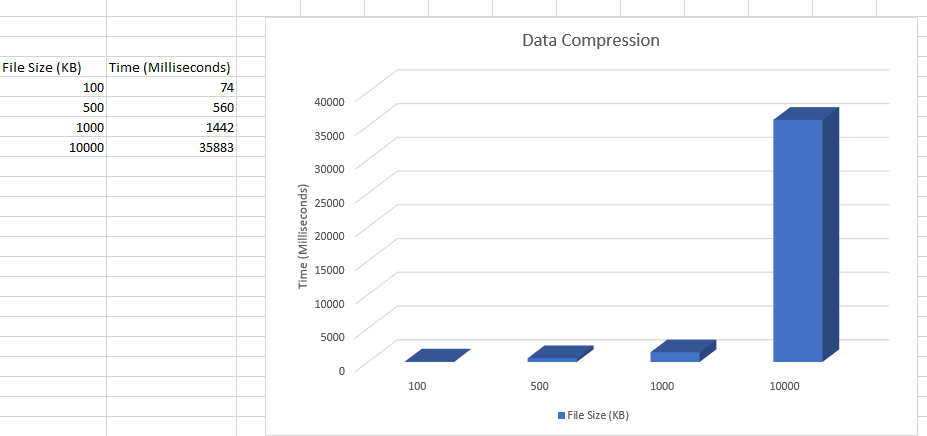
Data Compression
For this suggested project we used the LZW algorithm from one of the suggested projects.
The compress dictionary copies the file into a new file with a .LZW filetype which uses ASCII
The function that compresses the file initializing with ASCII
void compress(string input, int size, string filename) {
unordered_map<string, int> compress_dictionary(MAX_DEF);
//Dictionary initializing with ASCII
for (int unsigned i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
compress_dictionary[string(1, i)] = i;
}
string current_string;
unsigned int code;
unsigned int next_code = 256;
//Output file for compressed data
ofstream outputFile;
outputFile.open(filename + ".lzw");
for (char& c : input) {
current_string = current_string + c;
if (compress_dictionary.find(current_string) == compress_dictionary.end()) {
if (next_code <= MAX_DEF)
compress_dictionary.insert(make_pair(current_string, next_code++));
current_string.erase(current_string.size() - 1);
outputFile << convert_int_to_bin(compress_dictionary[current_string]);
current_string = c;
}
}
if (current_string.size())
outputFile << convert_int_to_bin(compress_dictionary[current_string]);
outputFile.close();
}
The results of the compression from:
Parallelizing
From one of the suggested improvements in the algorithm post link. A potential improvement is changing from char& c to a const char in the for loop
for (char& c : input) {since char& c is not being modified. Otherwise we did not see any way to parallelize compression.
Assignment 2
In order to parallelize the code from above, we decided to use a kernel to handle the calculations.
The logic largely remains the same, but we offload the CPU calculations to the GPU.
This code generates random points within the kernel and the calculations are also done in here.
Offloading to the GPU results in a pi calculation time to be reduced
Kernel code used
__global__ void calculate(float *d_pi, curandState *states, float n) {
unsigned int tid = threadIdx.x + blockDim.x * blockIdx.x;
float points = 0;
float x, y;
curand_init(1000, tid, 0, &states[tid]); // Initialize CURAND
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
x = curand_uniform(&states[tid]); //calls random float from 0.0 to 1.0
y = curand_uniform(&states[tid]);
points += (x*x + y*y <= 1.0f); // count if x & y is in the circle.
}
d_pi[tid] = 4.0f * points / n; // return estimate of pi
}
cuRAND documentation.
Results CPU vs GPU
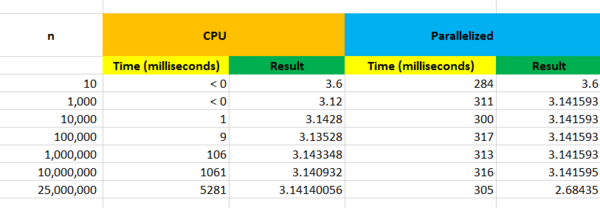
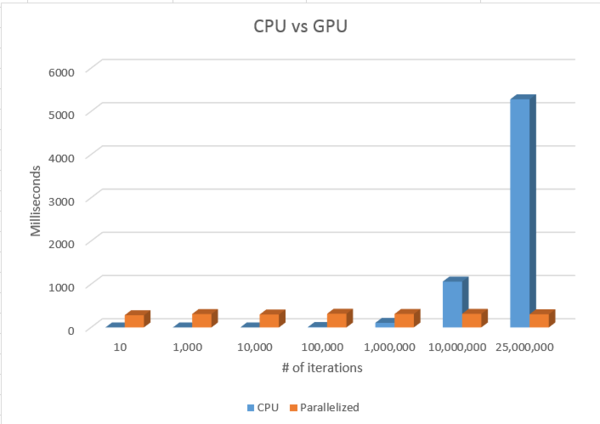
As we can see above, the more iterations, the more accurate the calculation of PI.
The CPU's results drastically change as we increase the iteration 10x.
However, the parallelized results seem to stay accurate throughout the iterations.
It seems as though the calculation time doesn't change much and stays consistent.
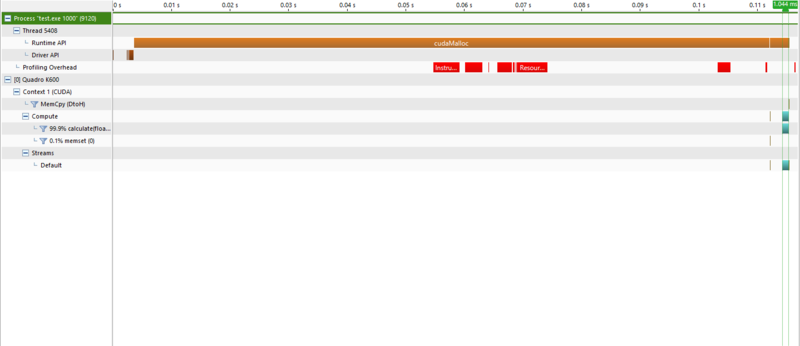
Profiling the code shows that memcpy takes up most of the time spent. Even when
there are 10 iterations, the time remains at 300 milliseconds.
As the iteration passes 25 million, we have a bit of memory leak which results in inaccurate results.
In order to optimize the code, we must find a way reduce the time memcpy takes.
Assignment 3
After realizing the cudaMemcpy was took quite a bit of time, we focused our efforts on optimizing it.
It was difficult to find a solution because the initial copy always takes a bit of time.
We tried using cudaMallocHost to see if we can allocate memory instead of using malloc.
cadaMallocHost will allocate pinned memory which is stored in RAM and can be accessed by the GPU's DMA directly.
We changed one part of our code
cudaMallocHost((void **)&host, size);
The error in PI estimation is how far it is from the known value of pi. PI = 3.1415926535
Here is where an error occurs and onward where we suspect that a memory leak causes the problem resulting in an error in pi calculation
The final results show that although cudaMallocHost should imporve the speed of memory transfer, if didn't make much
of a difference here. In conclusion, we can see that the GPU performance is significantly faster than the CPU's performance.