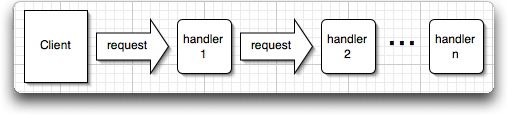
- The Chain of Responsibility pattern uses a chain of objects to handle a request, which is typically an event. Objects in the chain forward the request along the chain until one of the objects handles the event. Processing stops after an event is handled.
Purpose
- Avoid coupling the sender of a request to its receiver by giving more than one object a chance to handle the request. Chain the receiving objects and pass the request along the chain until an object handles it.
UML Diagram
The role of every class:
- Handler - defines an interface for handling requests
- RequestHandler:
- handles the requests it is responsible for
- If it can handle the request it does so, otherwise it sends the request to its successor
- Client - sends commands to the first object in the chain that may handle the command