OPS435 Online Lab1
Introduction to git, github.com, and Python
Contents
- 1 Lab Objectives
- 2 Overview
- 3 Reference
- 4 Glossary
- 5 Investigation 1 - git and github.com
- 6 Investigation 2 - Python on Matrix
- 7 LAB 1 SIGN-OFF Upload the following files individually to Blackboard
- 8 Lab Review
Lab Objectives
- Using the "git clone" command to clone a repository into a new directory
- Set up account on github.com for creating, tracking, and managing a repository
- configure and explore the Python interpreter on matrix.senecacollege.ca
Overview
- In this lab, you will create an account on github.com and follow the Github "Hello World guide" to create a new public repository on github to and explore the basic workflow of using github to track and manage revisions of software or other contents. The essential operations provided by Github includes
- creating new repository,
- creating a new branch,
- making changes to files,
- creating a pull request, and
- opening and merging a pull request.
- You will then use the git client (git clone) on matrix.senecacollege.ca to access and download the contents of the repository you created on github. Note: if you have your own Linux VM ready, you can also install and use the git client on your VM.
- You will also use the git client on matrix.senecacollege.ca to clone the repository on github.com which hosts the Python scripts for lab 1.
- Study and execute the Python scripts downloaded from the lab 1 repository
Reference
Glossary
- git - a distributed revision control system with rich command set that provides both high-level operations and full access to git's internals.
- github.com - a code hosting platform for version control and collaboration that lets people work together on software projects from anywhere.
Investigation 1 - git and github.com
Task 1: Create a Github.com account
- Start your web browser and go to github.com and use your own email (please note that Seneca's spam filter block email from github.com by default, if you use your Seneca email to sign up on github.com, you might have to re-configure your email spam filter to allow email from github.com in order to receive the confirmation message from github.com) to sign up for a new account if you don't already have one.
- Record your github.com user name on your lab logbook.
- email your github.com user name to your OPS435 professor from your Seneca email account.
Task 2: Create a project and make a pull request on GitHub
- Follow the Github "Hello World Guid" here to perform the following activities:
- Create a repository
- Create a branch
- Make and commit changes
- Open a pull request, and
- Merge your pull request
- Please make the following changes when following the guide:
- name the new repository using your Seneca user name instead of "hello-world".
- add your full name, and OPS435 section to the README file, do not post any other personal information there.
Task 3: Clone a Github.com repository into a new directory on a Linux system
- You can do the following steps either on matrix.senecacollege.ca or on your CentOS 7 vm:
- login to matrix.senecacollege.ca or your CentOS 7 vm
- create a directory named ops435/lab1 under your home directory
- change your working directory to ~/ops435/lab1
- run the following git command to clone the repository you created in Task 2 on github.com
git clone https://github.com/[your_github_user_name]/[your_seneca_user_name]
- for example, if your github user name is rc2030, and your seneca user name is rchan, the git command to clone the repository you created in Task 2 should be:
git clone https://github.com/rc2030/rchan
- change your working directory to your cloned git repository, which should be ~/ops435/lab1/[your_seneca_user_name]
- run the following two commands and capture their output to the named files:
git log > gitlog.txt
tree -a > repo_tree.txt
- Make sure that gitlog.txt and repo_tree.txt are not empty. Review and study the contents of gitlog.txt and repo_tree.txt
Investigation 2 - Python on Matrix
The Python Interpreter supports two mode of operations: script mode and interactive mode. In interactive mode, the Python interpreter allows us to run python code one statement at a time. Currently, there are two major versions of the Python interpreter available on matrix.senecacollege.ca: version 2 and version3. To start an interactive Python version 2 shell, type "python" at the command prompt. To start an interactive Python version 3 shell, type "python3" at the command prompt.
Task 1 - Setting up Python environment on Matrix for labs and assignments
Part I - Python Versions on Matrix
- Login to matrix.senecacollege.ca with you Seneca user name.
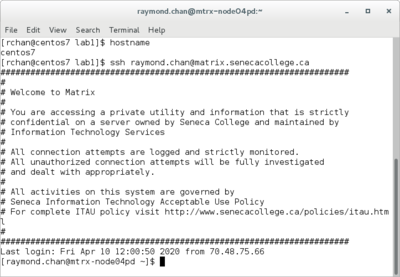
- Login from CentOS Linux (host or vm):
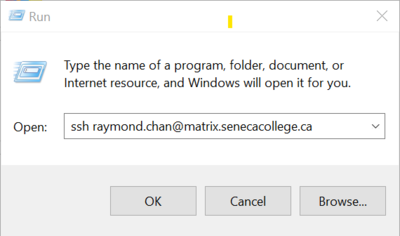
- Login from Windows 10:
- Login from CentOS Linux (host or vm):
- Python version
- Create subdirectories for labs and assignments
- Login to matrix.senecacollege.ca with you Seneca user name.
Task 2 - Testing your setup
- Download Checking script from github.com
- Exploring the sample script
- Running the sample script
Task 3 - exploring Python's built-in functions
- print() function
Task 4 - exploring Python's built-in data objects
- integer object
- string object
Task 5 - exploring on how to get Python to do maths
- Math operators
LAB 1 SIGN-OFF Upload the following files individually to Blackboard
- gitlog.txt: contains the output of the command "git log" from Task 3
- repo_tree.txt: contains the output of the command "tree -a" from Task 3
- lab1_check.txt: contains the output of the command "python3 ./checkLab1.py -f -v"
Lab Review
- What is a git repository?
- What kinds of data can be stored in a git repository?
- What is a git branch?
- What is the name of the definitive branch in a git repository?
- What is a "pull request" related to a branch in a git repository?