Proxy
The Proxy pattern is used in software development to create a placeholder for an object. The object is not actually created until the information that the object holds is required. This extra layer of abstraction saves time when a program must access a database or a disk for the information.
If the information is never required, the database/disk will never be queried and the system will run more efficiently with less slowdowns for unnecessary materializations.
Proxy Design Pattern
When a request is made to a Proxy, the real object is then instantiated. From then on, any further requests are made to the real object. There are four common situations where a Proxy pattern is required:
- Remote Proxy - provides a local representative that is located in a different address space.
- Virtual Proxy - creates expensive objects only when that object's information is required.
- Protection Proxy - provides access controls for different clients to a specified target object.
- Smart Reference Proxy - performs additional actions when a specific object is referenced such as counting the number of references, loading an object into memory when first referenced, and checking that the object is locked before access so that no other object may change it.
There are several other Proxy pattern situations less common in design:
- Copy-on-Write Proxy
- Cache Proxy
- Firewall Proxy
- Synchronization Proxy
UML Diagram
Here is a UML depiction of the Proxy pattern:
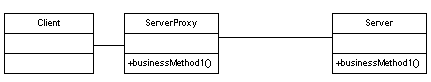
A more complete UML diagram of the Proxy pattern:
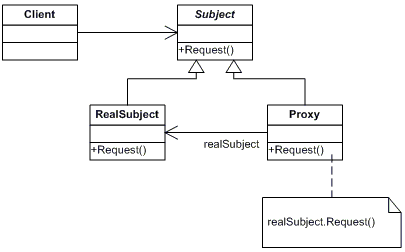
Here is a design class diagram using UML of how te Proxy pattern would be used in a system:
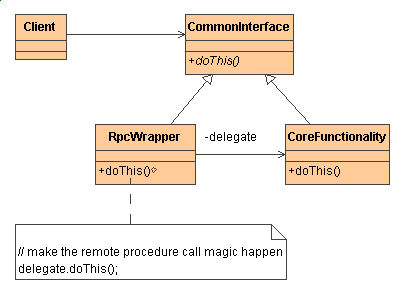
Code Samples
import Pyro.core, Pyro.naming, Pyro.constants import Pyro.EventService.Server from Pyro.errors import * # SUBSCRIBER: subscribes to certain events. class Subscriber(Pyro.core.CallbackObjBase): def __init__(self, ident=None): Pyro.core.ObjBase.__init__(self) Pyro.core.initServer() Pyro.core.initClient() daemon = Pyro.core.Daemon() locator = Pyro.naming.NameServerLocator(identification=ident) self.NS = locator.getNS(host=Pyro.config.PYRO_NS_HOSTNAME) daemon.useNameServer(self.NS) daemon.connect(self) # will also set self.daemon... uri = self.NS.resolve(Pyro.constants.EVENTSERVER_NAME) self.eventservice=Pyro.core.getProxyForURI(uri) self.eventservice._setIdentification(ident) self.abortListen=0 self.daemon=daemon # make sure daemon doesn't get garbage collected now def subscribe(self,subjects): # Subscribe to one or more subjects. # It is safe to call this multiple times. self.eventservice.subscribe(subjects, self.getProxy()) def subscribeMatch(self,subjectPatterns): # Subscribe to one or more subjects (by pattern) # It is safe to call this multiple times. self.eventservice.subscribeMatch(subjectPatterns, self.getProxy()) def unsubscribe(self, subjects): # Unsubscribe the subscriber for the given subject(s). self.eventservice.unsubscribe(subjects, self.getProxy()) def abort(self): self.abortListen=1 def setThreading(self, threaded): self.getDaemon().threaded=threaded def listen(self): self.getDaemon().requestLoop(lambda s=self: not s.abortListen) def event(self, event): # callback, override this! print event # PUBLISHER: publishes events. class Publisher: def __init__(self, ident=None): Pyro.core.initClient() locator = Pyro.naming.NameServerLocator(identification=ident) ns = locator.getNS(host=Pyro.config.PYRO_NS_HOSTNAME) uri = ns.resolve(Pyro.constants.EVENTSERVER_NAME) self.eventservice=Pyro.core.getProxyForURI(uri) self.eventservice._setIdentification(ident) def publish(self, subjects, msg): self.eventservice.publish(subjects,msg)
References
- Wikipedia article on the Proxy Pattern
- Design Patterns - Proxy UML Diagram
- Gamma, E., Helm, R., Johnson, R., Vlissides, J. (1995). Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software. Addison-Wesley. ISBN 0-201-63361-2
- Design Class Diagrams - Proxy UML Diagram
- Information on the Proxy Pattern with a UML Diagram
- Python Remote Method Invocation