A-Team
Contents
Back Propagation Acceleration
Team Members
- Sebastian Djurovic, Team Lead and Developer
- Henry Leung, Developer and Quality Control
- ...
Progress
Assignment 1
Our group decided to profile a couple of different solutions, the first being a simple neural network and ray tracing solution, in order to determine the best project to generate a solution for.
Neural Network
Sebastian's findings
I found a simple neural network that takes a MNIST data set and preforms training on batches of the data. For a quick illustration MNIST is a numerical data set that contains many written numbers --in a gray scale format at 28 x 28 pixels in size. As well as the corresponding numerical values; between 0 and 9. The reason for this data set is to train networks such that they will be able to recognize written numbers when they confront them.
Initial Profile
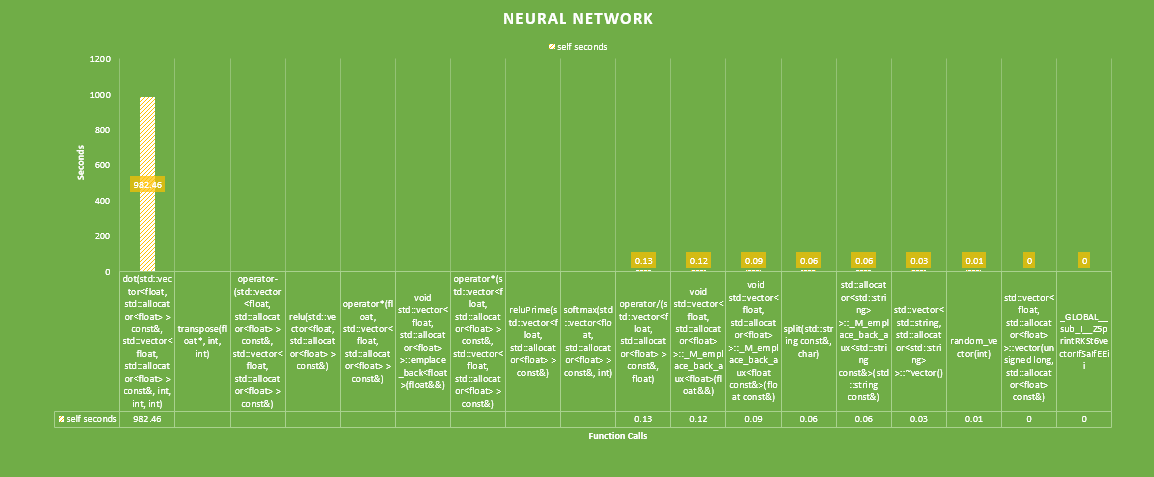
Flat profile: Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls ns/call ns/call name 97.94 982.46 982.46 dot(std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&, std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&, int, int, int) 1.45 997.05 14.58 transpose(float*, int, int) 0.15 998.56 1.51 operator-(std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&, std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&) 0.15 1000.06 1.50 relu(std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&) 0.15 1001.55 1.49 operator*(float, std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&) 0.07 1002.27 0.72 519195026 1.39 1.39 void std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> >::emplace_back<float>(float&&) 0.06 1002.91 0.63 operator*(std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&, std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&) 0.05 1003.37 0.46 reluPrime(std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&) 0.02 1003.62 0.25 softmax(std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&, int) 0.01 1003.75 0.13 operator/(std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> > const&, float) 0.01 1003.87 0.12 442679 271.35 271.35 void std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> >::_M_emplace_back_aux<float>(float&&) 0.01 1003.96 0.09 13107321 6.87 6.87 void std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> >::_M_emplace_back_aux<float const&>(float const&) 0.01 1004.02 0.06 split(std::string const&, char) 0.01 1004.08 0.06 462000 130.00 130.00 void std::vector<std::string, std::allocator<std::string> >::_M_emplace_back_aux<std::string const&>(std::string const&) 0.00 1004.11 0.03 std::vector<std::string, std::allocator<std::string> >::~vector() 0.00 1004.12 0.01 random_vector(int) 0.00 1004.12 0.00 3 0.00 0.00 std::vector<float, std::allocator<float> >::vector(unsigned long, std::allocator<float> const&) 0.00 1004.12 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__Z5printRKSt6vectorIfSaIfEEii
After the initial profile it is obvious that the dot product function consumes 97.94% of our run time. Additionally, the transpose function also consumes 1.45% which seems messily, however during back propagation transpose is also called, as well as two rectifiers(activation functions), reluPrime and relu. Where reluPrime is a binary activation function.
Relu = f(x) = {0 for x > 0, x otherwise}
ReluPrime = f(x) = {0 for x > 0, 1 otherwise}
// Back propagation
vector<float> dyhat = (yhat - b_y);
// dW3 = a2.T * dyhat
vector<float> dW3 = dot(transpose( &a2[0], BATCH_SIZE, 64 ), dyhat, 64, BATCH_SIZE, 10);
// dz2 = dyhat * W3.T * relu'(a2)
vector<float> dz2 = dot(dyhat, transpose( &W3[0], 64, 10 ), BATCH_SIZE, 10, 64) * reluPrime(a2);
// dW2 = a1.T * dz2
vector<float> dW2 = dot(transpose( &a1[0], BATCH_SIZE, 128 ), dz2, 128, BATCH_SIZE, 64);
// dz1 = dz2 * W2.T * relu'(a1)
vector<float> dz1 = dot(dz2, transpose( &W2[0], 128, 64 ), BATCH_SIZE, 64, 128) * reluPrime(a1);
// dW1 = X.T * dz1
vector<float> dW1 = dot(transpose( &b_X[0], BATCH_SIZE, 784 ), dz1, 784, BATCH_SIZE, 128);
vector <float> dot (const vector <float>& m1, const vector <float>& m2, const int m1_rows, const int m1_columns, const int m2_columns) {
vector <float> output (m1_rows*m2_columns);
for( int row = 0; row != m1_rows; ++row ) {
for( int col = 0; col != m2_columns; ++col ) {
output[ row * m2_columns + col ] = 0.f;
for( int k = 0; k != m1_columns; ++k ) {
output[ row * m2_columns + col ] += m1[ row * m1_columns + k ] * m2[ k * m2_columns + col ];
}
}
}
return output;
}
//
// nn.cpp // // To compile: g++ -o nn nn.cpp -std=c++11 // To run: ./nn // Created by Sergei Bugrov on 4/20/18. // Copyright © 2017 Sergei Bugrov. All rights reserved. // Download dataset from: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1OdtwXHf_-2T0aS9HLBnxU3o-72mklCZY/view?usp=sharing
- include <iostream>
- include <vector>
- include <math.h>
- include <fstream>
- include <sstream>
- include <string>
- include <random>
using namespace std;
void print ( const vector <float>& m, int n_rows, int n_columns ) {
/* "Couts" the input vector as n_rows x n_columns matrix.
Inputs:
m: vector, matrix of size n_rows x n_columns
n_rows: int, number of rows in the left matrix m1
n_columns: int, number of columns in the left matrix m1
*/
for( int i = 0; i != n_rows; ++i ) {
for( int j = 0; j != n_columns; ++j ) {
cout << m[ i * n_columns + j ] << " ";
}
cout << '\n';
}
cout << endl;
}
int argmax ( const vector <float>& m ) {
return distance(m.begin(), max_element(m.begin(), m.end()));
}
vector <float> relu(const vector <float>& z){
int size = z.size();
vector <float> output;
for( int i = 0; i < size; ++i ) {
if (z[i] < 0){
output.push_back(0.0);
}
else output.push_back(z[i]);
}
return output;
}
vector <float> reluPrime (const vector <float>& z) {
int size = z.size();
vector <float> output;
for( int i = 0; i < size; ++i ) {
if (z[i] <= 0){
output.push_back(0.0);
}
else output.push_back(1.0);
}
return output;
}
static vector<float> random_vector(const int size) {
random_device rd; mt19937 gen(rd()); uniform_real_distribution<> distribution(0.0, 0.05); static default_random_engine generator;
vector<float> data(size);
generate(data.begin(), data.end(), [&]() { return distribution(generator); });
return data;
}
vector <float> softmax (const vector <float>& z, const int dim) {
const int zsize = static_cast<int>(z.size());
vector <float> out;
for (unsigned i = 0; i != zsize; i += dim) {
vector <float> foo;
for (unsigned j = 0; j != dim; ++j) {
foo.push_back(z[i + j]);
}
float max_foo = *max_element(foo.begin(), foo.end());
for (unsigned j = 0; j != dim; ++j) {
foo[j] = exp(foo[j] - max_foo);
}
float sum_of_elems = 0.0;
for (unsigned j = 0; j != dim; ++j) {
sum_of_elems = sum_of_elems + foo[j];
}
for (unsigned j = 0; j != dim; ++j) {
out.push_back(foo[j]/sum_of_elems);
}
}
return out;
}
vector <float> sigmoid_d (const vector <float>& m1) {
/* Returns the value of the sigmoid function derivative f'(x) = f(x)(1 - f(x)),
where f(x) is sigmoid function.
Input: m1, a vector.
Output: x(1 - x) for every element of the input matrix m1.
*/
const unsigned long VECTOR_SIZE = m1.size();
vector <float> output (VECTOR_SIZE);
for( unsigned i = 0; i != VECTOR_SIZE; ++i ) {
output[ i ] = m1[ i ] * (1 - m1[ i ]);
}
return output;
}
vector <float> sigmoid (const vector <float>& m1) {
/* Returns the value of the sigmoid function f(x) = 1/(1 + e^-x).
Input: m1, a vector.
Output: 1/(1 + e^-x) for every element of the input matrix m1.
*/
const unsigned long VECTOR_SIZE = m1.size();
vector <float> output (VECTOR_SIZE);
for( unsigned i = 0; i != VECTOR_SIZE; ++i ) {
output[ i ] = 1 / (1 + exp(-m1[ i ]));
}
return output;
}
vector <float> operator+(const vector <float>& m1, const vector <float>& m2){
/* Returns the elementwise sum of two vectors.
Inputs:
m1: a vector
m2: a vector
Output: a vector, sum of the vectors m1 and m2.
*/
const unsigned long VECTOR_SIZE = m1.size();
vector <float> sum (VECTOR_SIZE);
for (unsigned i = 0; i != VECTOR_SIZE; ++i){
sum[i] = m1[i] + m2[i];
};
return sum;
}
vector <float> operator-(const vector <float>& m1, const vector <float>& m2){
/* Returns the difference between two vectors.
Inputs:
m1: vector
m2: vector
Output: vector, m1 - m2, difference between two vectors m1 and m2.
*/
const unsigned long VECTOR_SIZE = m1.size();
vector <float> difference (VECTOR_SIZE);
for (unsigned i = 0; i != VECTOR_SIZE; ++i){
difference[i] = m1[i] - m2[i];
};
return difference;
}
vector <float> operator*(const vector <float>& m1, const vector <float>& m2){
/* Returns the product of two vectors (elementwise multiplication).
Inputs:
m1: vector
m2: vector
Output: vector, m1 * m2, product of two vectors m1 and m2
*/
const unsigned long VECTOR_SIZE = m1.size();
vector <float> product (VECTOR_SIZE);
for (unsigned i = 0; i != VECTOR_SIZE; ++i){
product[i] = m1[i] * m2[i];
};
return product;
}
vector <float> operator*(const float m1, const vector <float>& m2){
/* Returns the product of a float and a vectors (elementwise multiplication).
Inputs:
m1: float
m2: vector
Output: vector, m1 * m2, product of two vectors m1 and m2
*/
const unsigned long VECTOR_SIZE = m2.size();
vector <float> product (VECTOR_SIZE);
for (unsigned i = 0; i != VECTOR_SIZE; ++i){
product[i] = m1 * m2[i];
};
return product;
}
vector <float> operator/(const vector <float>& m2, const float m1){
/* Returns the product of a float and a vectors (elementwise multiplication).
Inputs:
m1: float
m2: vector
Output: vector, m1 * m2, product of two vectors m1 and m2
*/
const unsigned long VECTOR_SIZE = m2.size();
vector <float> product (VECTOR_SIZE);
for (unsigned i = 0; i != VECTOR_SIZE; ++i){
product[i] = m2[i] / m1;
};
return product;
}
vector <float> transpose (float *m, const int C, const int R) {
/* Returns a transpose matrix of input matrix.
Inputs:
m: vector, input matrix
C: int, number of columns in the input matrix
R: int, number of rows in the input matrix
Output: vector, transpose matrix mT of input matrix m
*/
vector <float> mT (C*R);
for(unsigned n = 0; n != C*R; n++) {
unsigned i = n/C;
unsigned j = n%C;
mT[n] = m[R*j + i];
}
return mT;
}
vector <float> dot (const vector <float>& m1, const vector <float>& m2, const int m1_rows, const int m1_columns, const int m2_columns) {
/* Returns the product of two matrices: m1 x m2.
Inputs:
m1: vector, left matrix of size m1_rows x m1_columns
m2: vector, right matrix of size m1_columns x m2_columns (the number of rows in the right matrix
must be equal to the number of the columns in the left one)
m1_rows: int, number of rows in the left matrix m1
m1_columns: int, number of columns in the left matrix m1
m2_columns: int, number of columns in the right matrix m2
Output: vector, m1 * m2, product of two vectors m1 and m2, a matrix of size m1_rows x m2_columns
*/
vector <float> output (m1_rows*m2_columns);
for( int row = 0; row != m1_rows; ++row ) {
for( int col = 0; col != m2_columns; ++col ) {
output[ row * m2_columns + col ] = 0.f;
for( int k = 0; k != m1_columns; ++k ) {
output[ row * m2_columns + col ] += m1[ row * m1_columns + k ] * m2[ k * m2_columns + col ];
}
}
}
return output;
}
vector<string> split(const string &s, char delim) {
stringstream ss(s);
string item;
vector<string> tokens;
while (getline(ss, item, delim)) {
tokens.push_back(item);
}
return tokens;
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
string line; vector<string> line_v;
cout << "Loading data ...\n";
vector<float> X_train;
vector<float> y_train;
ifstream myfile ("train.txt");
if (myfile.is_open())
{
while ( getline (myfile,line) )
{
line_v = split(line, '\t');
int digit = strtof((line_v[0]).c_str(),0);
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10; ++i) {
if (i == digit)
{
y_train.push_back(1.);
}
else y_train.push_back(0.);
}
int size = static_cast<int>(line_v.size());
for (unsigned i = 1; i < size; ++i) {
X_train.push_back(strtof((line_v[i]).c_str(),0));
}
}
X_train = X_train/255.0;
myfile.close();
}
else cout << "Unable to open file" << '\n';
int xsize = static_cast<int>(X_train.size());
int ysize = static_cast<int>(y_train.size());
// Some hyperparameters for the NN
int BATCH_SIZE = 256;
float lr = .01/BATCH_SIZE;
// Random initialization of the weights vector <float> W1 = random_vector(784*128); vector <float> W2 = random_vector(128*64); vector <float> W3 = random_vector(64*10);
cout << "Training the model ...\n";
for (unsigned i = 0; i < 10000; ++i) {
// Building batches of input variables (X) and labels (y)
int randindx = rand() % (42000-BATCH_SIZE);
vector<float> b_X;
vector<float> b_y;
for (unsigned j = randindx*784; j < (randindx+BATCH_SIZE)*784; ++j){
b_X.push_back(X_train[j]);
}
for (unsigned k = randindx*10; k < (randindx+BATCH_SIZE)*10; ++k){
b_y.push_back(y_train[k]);
}
// Feed forward
vector<float> a1 = relu(dot( b_X, W1, BATCH_SIZE, 784, 128 ));
vector<float> a2 = relu(dot( a1, W2, BATCH_SIZE, 128, 64 ));
vector<float> yhat = softmax(dot( a2, W3, BATCH_SIZE, 64, 10 ), 10);
// Back propagation
vector<float> dyhat = (yhat - b_y);
// dW3 = a2.T * dyhat
vector<float> dW3 = dot(transpose( &a2[0], BATCH_SIZE, 64 ), dyhat, 64, BATCH_SIZE, 10);
// dz2 = dyhat * W3.T * relu'(a2)
vector<float> dz2 = dot(dyhat, transpose( &W3[0], 64, 10 ), BATCH_SIZE, 10, 64) * reluPrime(a2);
// dW2 = a1.T * dz2
vector<float> dW2 = dot(transpose( &a1[0], BATCH_SIZE, 128 ), dz2, 128, BATCH_SIZE, 64);
// dz1 = dz2 * W2.T * relu'(a1)
vector<float> dz1 = dot(dz2, transpose( &W2[0], 128, 64 ), BATCH_SIZE, 64, 128) * reluPrime(a1);
// dW1 = X.T * dz1
vector<float> dW1 = dot(transpose( &b_X[0], BATCH_SIZE, 784 ), dz1, 784, BATCH_SIZE, 128);
// Updating the parameters
W3 = W3 - lr * dW3;
W2 = W2 - lr * dW2;
W1 = W1 - lr * dW1;
if ((i+1) % 100 == 0){
cout << "-----------------------------------------------Epoch " << i+1 << "--------------------------------------------------"
<<"\n";
cout << "Predictions:" << "\n";
print ( yhat, 10, 10 );
cout << "Ground truth:" << "\n";
print ( b_y, 10, 10 );
vector<float> loss_m = yhat - b_y;
float loss = 0.0;
for (unsigned k = 0; k < BATCH_SIZE*10; ++k){
loss += loss_m[k]*loss_m[k];
}
cout << " Loss " << loss/BATCH_SIZE <<"\n";
cout << "--------------------------------------------End of Epoch :(------------------------------------------------" <<"\n";
};
};
return 0;
}