OPS235 Lab 3 - Fedora17
Contents
Using Virtual Machines
Objectives
- Understand Virtualization
- Use KVM virtualization on Fedora
- Use a variety of installation methods
- Live Image Installation
- Network Installation
- Kickstart Installation
Reference Material
Virtualization
Installation Methods
- Live Image Installation
- Network Installation
- Kickstart Installation
Required Materials
- Removable disk pack with Fedora installed (see Lab 2).
Introduction
A virtual machine is a software simulation of a computer which can be used as though it were actual hardware. It's possible to run multiple virtual machines on one computer, reducing hardware requirements and introducing flexibility. Some common uses of virtualization include:
- Software testing -- Using multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single computer for testing and experimentation.
- Network simulation -- Testing network services, protocols, and security scenarios with a small number of computers.
- Isolation -- Protecting multiple sets of data by storing them on multiple virtual machines.
- Server consolidation -- Reducing the number of physical servers in a network by moving physical machines to virtual machines. This saves hardware, administration, cooling, and electricity costs, and it can increase the utilization of hardware (by ensuring that the hardware is not under-loaded).
- Load-balancing and disaster recovery -- It is possible to migrate virtual machines between different physical machines, to ensure that a workload is balanced across multiple computers, to allow routine hardware maintenance and upgrading, and to compensate for hardware failure or other disasters.
In this lab, you will create three virtual machines. This also gives you an opportunity to experiment with different ways of installing Fedora. Later in this course you will install another operating system distribution in a virtual machines.
You have already used a Fedora live disc and an installation disc. In both cases, the boot media (which you used to load the installation software) and the installation source (where the software that got installed came from) were the same: they CD/DVD provided both. However, the Fedora (and most other Linux distributions) permits you to use any combination of boot media and installation media:
- Boot Media
- CD or DVD
- Hard disk
- USB flash drive
- Network boot
- Installation source
- CD or DVD
- Hard disk
- USB flash drive
- Network HTTP or NFS software repository
When you installed Fedora in Lab 2, you did it interactively -- you manually specified all of the installation options, and then the installation process was started. This is fairly convenient for single-machine installations, but is time-consuming and possibly error-prone when repeated for dozens, hundreds, or thousands of machines.
For large installations, it's possible to specify the installation options in a file so that no user intervention is required. This is called a kickstart installation.
Instructions
Preparation
- Install the Fedora virtualization software:
yum groupinstall "Virtualization"orpkcon install @virtualizationThe virtualization software installed is in three parts:- A system service named libvirtd that manages the VMs.
- Tools to manage virtualization, including the
virt-managergraphical tool and thevirshcommand-line tool. - The actual virtual machines themselves.
- Start the virtualization service:
service libvirtd start - The firewall configuration is altered by the addition of the virtualization software. Restart the firewall so that these changes become active:
service iptables restart - Start the graphical tool by selecting the menu option Applications>System Tools>Virtual Machine Manager or by typing the command
virt-manager
Installing from a Live Disc
These are the details for the first virtual machine:
- Name: fedora1
- Boot media: Fedora Live CD
- Installation source: Fedora Live CD
- Memory: 512MB
- Disk space: 10GB
- CPUs: 1
Perform these steps:
- In the Virtual Machine Manger, click on the icon to Create a Virtual Machine in the upper-left corner:
- A window will appear with the title New VM. There are five steps to be completed; click Forward after each step:
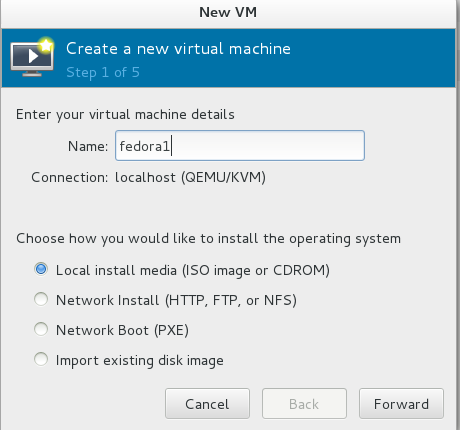
- Step 1 of 5: Enter the virtual machine name and select Local install media.
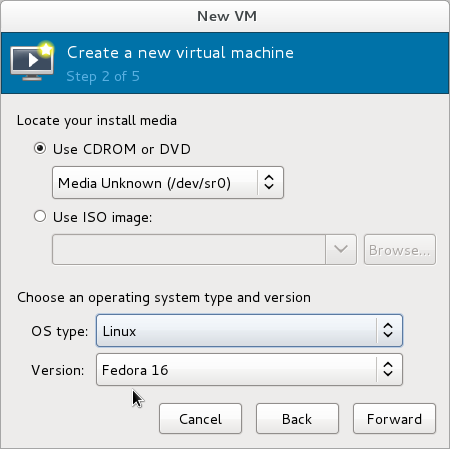
- Step 2 of 5: Insert the CDROM or DVD containing the Fedora Live Disc image. Wait a moment for the disc to be recognized, then select it as the install media. Set the OS type to Linux and the Version to Fedora 12.
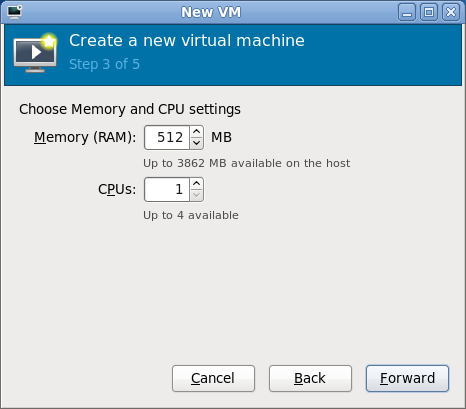
- Step 3 of 5: Set the memory to 512 MB and the number of CPUs to 1.
- This next step creates a disk file that will be used to simulate the virtual machine's disk drive. Select a size of 10 GB and checkmark the box labeled Allocate entire disk now.
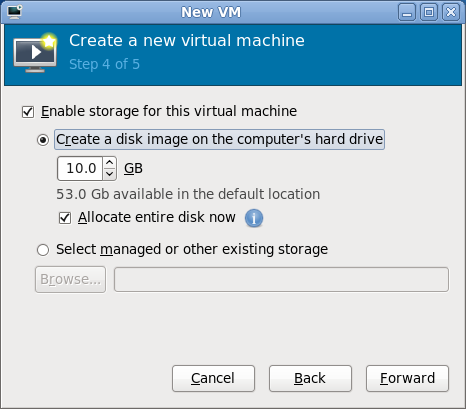
- Step 4 of 5: Review the options that you have selected. Make a note of the storage location. If anything needs to be changed, use the Back button to go back and edit it; otherwise, click Finish.
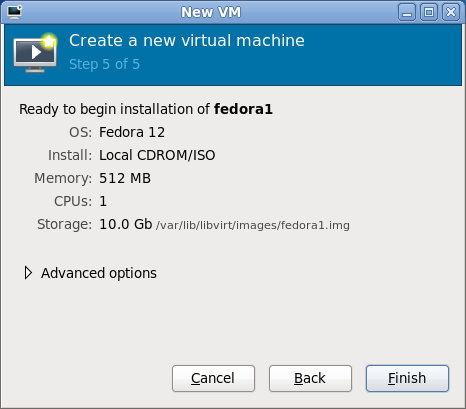
- The virtual machine will now start. You will see a window which displays the virtual video card from the VM. The video It's important to note that the VM can (and often will) run even when this display is not present. The virtual machine is running from the live disc at this point, and no software has been installed on the hard drive of the virtual machine.
- Login to the VM and double-click on the Install to Hard Drive icon. When prompted for the hostname, enter "fedora1", and when prompted for the timezone, select America/Toronto. Use the default values for all other fields. Notice that the installer does not ask you what software should be installed; compare the installation time to the amount of time it took to do your Lab 2 installation.
- When the installation is complete, select the menu option System>Shutdown to stop the Live Disc.
- Start the VM from its disk image by selecting Virtual Machine>Run from the virtual machine menu.