GPU610/Turing
GPU610/DPS915 | Student List | Group and Project Index | Student Resources | Glossary
Contents
Team Turing
Team Members
- Colin Campbell, Team Leader
- James Shin
- Chaddwick Bailey
Progress
Assignment 1
For assignment 1 we each looked at a different application to profile. Colin profiled a 2d Diffusion equation program. Chaddwick profiled data decomposition and James profiled an image manipulation function.
Colin's Findings
I found a python script located at http://www.timteatro.net/2010/10/29/performance-python-solving-the-2d-diffusion-equation-with-numpy/ that uses a nested For Loop to calculate the diffusion equation. I translated the script into C++ and profiled it using XCode's native profiler.
Example
The program accepts a single number to specify the size of a square matrix and runs the equation 100 times. When run with a 10000x10000 matrix this is the result:
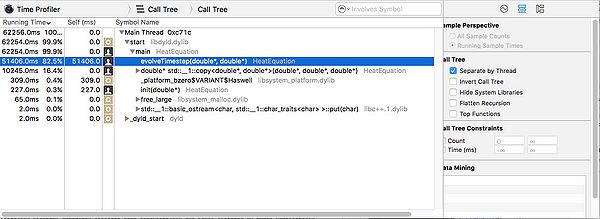
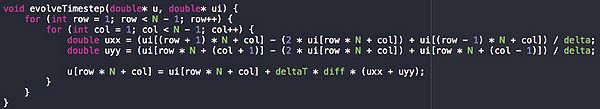
Running a 10000 x 10000 matrix through 100 time steps takes just over 1 minute. 82.5% of the process time is spent in the evolveTimeStep function, which takes approx 600ms per time step. The timeStep function has a nested for loop giving it a O(N^2) runtime. With a 20000 x 20000 matrix each step takes approx. 2200ms on my machine. I cannot accurately benchmark above this size on my machine as the process requires more memory than my computer has.
Potential for parallelism
This is the function that takes most of the time. As you can see it it a single nested for loop that calculates a value from Matrix ui and stores it in Matrix u. Because the first matrix is never changed in each step, the result can therefore be calculated in independent threads safely. this means that this code should be relatively simple to parallelize and should see large speed increases.
James's Research
An image processing code was found here: http://www.dreamincode.net/forums/topic/76816-image-processing-tutorial/ This program takes in an image and processes in various ways. I chose to look at the reflection function (flipping) by editing the code to omit the other sections. Below are the results from profiling where n is the size of the image in bytes.
| n | writeImage(char*, Image&) | readImage(char*, Image&) | Image::reflectImage(bool, Image&) | Image::Image(int, int, int) | Image::operator=(Image const&) | Image::Image(Image const&) | Elapsed Time |
| 10077713 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.07 | 0.11 |
| 25435697 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.09 | 0.26 |
| 117430458 | 0.13 | 0.1 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 1.36 |
What takes the longest running function is the function that copies the old image into the new output image. Below is the code for the function.
Image::Image(const Image& oldImage) {
N = oldImage.N;
M = oldImage.M;
Q = oldImage.Q;
pixelVal = new int* [N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
pixelVal[i] = new int [M];
for(int j = 0; j < M; j++)
pixelVal[i][j] = oldImage.pixelVal[i][j];
}
}
Chadd's Research
Data Decomposition is involves the dividing to a Large chunk a of Data into smaller sections of data. A processes is then preformed on the smaller pieces of data until the entire chunk of data is processed or the programs end because it has reached its goal.
Chadd's Example
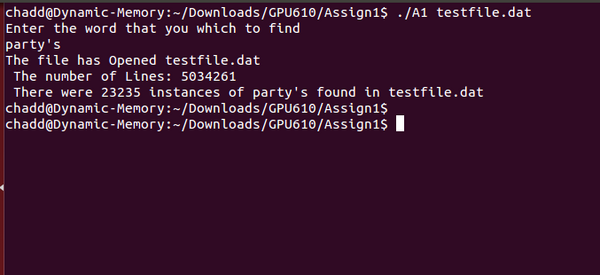
I choose one of the most common application of data decomposition :File Search. I created a program that accepts a file and searches it for a specific word entered by the user. The program also counts the number of lines in the file and the number of matches found in the file.