Difference between revisions of "Android Concepts"
(→Android Architecture) |
|||
| Line 70: | Line 70: | ||
| | | | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Application Building Blocks == | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''1. Activity''' - an UI component that interacts with an user | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''2. Service''' - a task running in background and it does not have any UI | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''3. Content Provider''' - component that allows applications to share data with other applications. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''4. Intent Receiver''' - component that responds to notification or status changes. Allows an application to register some code that will be run when it is triggered by an external event. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The basic idea in Android OS is to reuse and replace components (OSGi model). | ||
Revision as of 13:23, 8 March 2011
Main Page · Course Description · Course Topics · Schedule, Students, Teams · Course Resources · Course Projects
What is Android
Android is a software product for mobile devices that has three major parts:
- operating system
- middleware
- applications framework
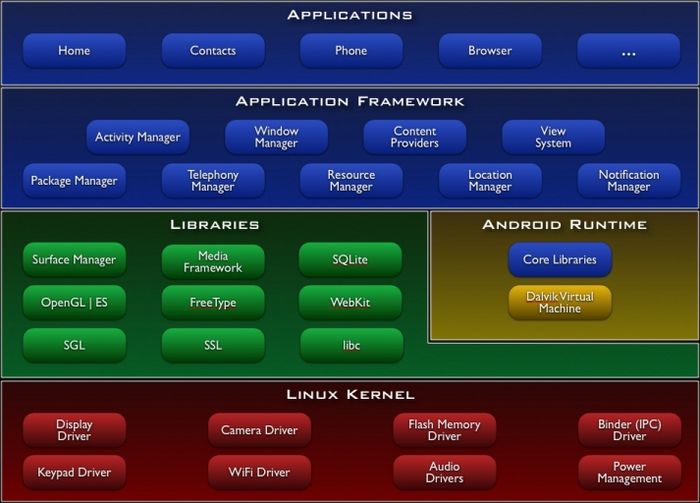
Android Architecture
Here are the major components based on this [source]
Key principles
1. Linux Kernel - proven driver model, memory and process management, etc. (all the core services of a reliable operating system)
The second layer has two parts: Libraries and Android runtime.
2.1 Libraries (written in C/C++)
| Component | Responsability |
|---|---|
| Surface Manager | composing drawing surface onto the screen |
| ES & SGL | core of graphics libraries |
| Media Framework | core media: mpeg, mp3, all video formats, etc. |
| FreeType | an engine for rendering fonts |
| SQLite | core of data storage |
| WebKit | an open source web browser engine |
| SSL | security socket layer |
2.2 Android Runtime
2.2.1 Core Libraries written in JAVA such as: utils, collection, i/o, etc.
2.2.2 Dalvik Virtual Machine runs dex files (bytecodes efficient for small processors)
3. Application Framework written completely in Java Programming Language
| Application | Functionality | |
|---|---|---|
| Activity Manager | life cycle of an application - common back stack | |
| Package Manager | keeps track the applications installed of the device | |
| Window Manager | an abstraction layer on top of surface manager | |
| Telephony Manager | Api for telephony applications | |
| Content Providers | application framework that allow applications to share data | |
| Resource Manager | used to store localized layouts, strings, bitmaps, etc. | |
| View System | building blogs of the UI, handles the event dispacher, drawing, etc. | |
| Notification Manager | anables apps to recognize and display common alerts in the status bar |
Application Building Blocks
1. Activity - an UI component that interacts with an user
2. Service - a task running in background and it does not have any UI
3. Content Provider - component that allows applications to share data with other applications.
4. Intent Receiver - component that responds to notification or status changes. Allows an application to register some code that will be run when it is triggered by an external event.
The basic idea in Android OS is to reuse and replace components (OSGi model).