Difference between revisions of "Android Concepts"
(→Android Architecture) |
(→Android Architecture) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
2. | 2. | ||
| − | |||
{| class="wikitable" border="1" | {| class="wikitable" border="1" | ||
|+ Libraries | |+ Libraries | ||
| Line 29: | Line 28: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| FreeType || an engine for rendering fonts | | FreeType || an engine for rendering fonts | ||
| − | - | + | |- |
| SQLite || core of data storage | | SQLite || core of data storage | ||
| − | - | + | |- |
| WebKit || an open source web browser engine | | WebKit || an open source web browser engine | ||
| − | - | + | |- |
| SSL || security socket layer | | SSL || security socket layer | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 12:26, 8 March 2011
Main Page · Course Description · Course Topics · Schedule, Students, Teams · Course Resources · Course Projects
What is Android
Android is a software product for mobile devices that has three major parts:
- operating system
- middleware
- key applications
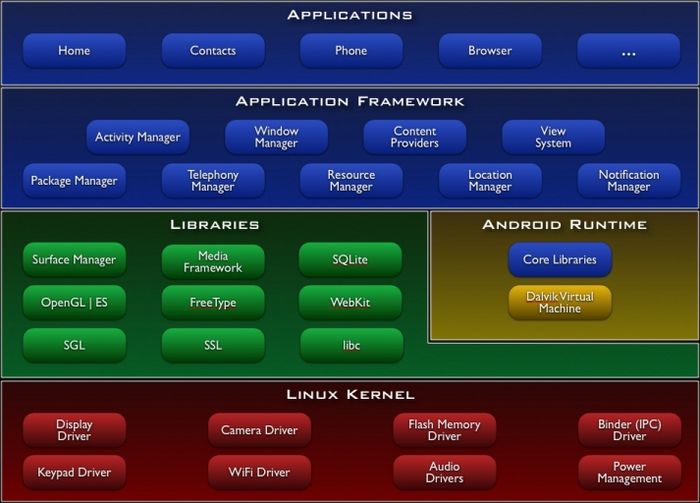
Android Architecture
Here are the major components based on this [source]
Key principles
1. Linux Kernel - proven driver model, memory and process management, etc. (a core service of a reliable operating system)
2.
| Component | Responsability |
|---|---|
| Surface Manager | composing drawing surface onto the screen |
| ES & SGL | core of graphics libraries |
| Media Framework | core media: mpeg, mp3, all video formats, etc. |
| FreeType | an engine for rendering fonts |
| SQLite | core of data storage |
| WebKit | an open source web browser engine |
| SSL | security socket layer |