Difference between revisions of "RCP Concepts"
(→JFace: sample) |
(→Eclipse UI: link) |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
=== Eclipse UI === | === Eclipse UI === | ||
| − | Based on the above components | + | Based on the above components [http://www.eclipse.org/articles/Article-UI-Guidelines/Contents.html the Eclipse UI (the Workbench)] is ready to expand the plug-ins from the Eclipse IDE workbench to the functions that are necessary for software development. Your own plug-ins using Eclipse RCP Workbench could be developed based on generic templates. |
Revision as of 14:17, 5 February 2011
Main Page · Course Description · Course Topics · Schedule, Students, Teams · Course Resources · Course Projects
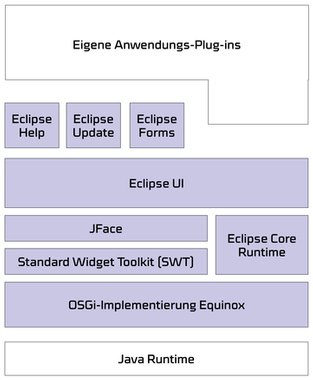
Components of the Eclipse RCP platform
The following components make up the Eclipse RCP platform [1]:
OSGi / Equinox
OSGi is a standard Java framework for developing modular applications. OSGi provides a runtime environment for software modules (so-called bundles or plug-ins ) ready. Eclipse-based applications on the Eclipse's OSGi implementation Eclipse Equinox .
Eclipse Core Runtime
Core runtime provides general, non-UI related functionality for Eclipse applications. It manages the life cycle of Eclipse applications, is therefore responsible for launching and initialization of the application.
Standard Widget Toolkit (SWT)
SWT is the UI toolkit of Eclipse platform. Eclipse RCP applications are not based on the Java GUI framework swing , but rather a private SWT GUI framework, which is native UI widgets of the underlying operating system.
Installing examples via the Update Manager
The Eclipse SDK examples are found on the Eclipse project update site. To locate and install them into a product:
- Open the main update manager by clicking Help > Install New Software....
- This opens the Install Wizard.
- Select The Eclipse Project Updates site.
- Ensure Group items by category is unchecked.
- Type "Eclipse SDK Examples" in the search field.
- Select "Eclipse SDK Examples" and click Next.
- Review the items being installed, and click Next.
- Review and accept the license terms, and click Finish.
- Click Yes when asked to exit and restart the workbench for the changes to take effect.
The examples are now installed in the workbench. Note: you can also click on Apply Now to dynamically install the examples into the current configuration.
Running the Example Launcher
From Eclipse's Window menu, select Show View > Other. In the Show View dialog, expand SWT Examples and select the SWT Example Launcher view. A view containing a list of examples will appear in your current perspective. When you select an example from the list a brief description of the example is displayed. Click on the Run button to launch the example.
JFace
SWT UI Toolkit is limited as a minimal abstraction layer above the UI layer of the operating system. Additional features such as the filling of the UI components using Java model objects are provided in JFace.
An example of how develop a RCP application using JFace table could be found here
Eclipse UI
Based on the above components the Eclipse UI (the Workbench) is ready to expand the plug-ins from the Eclipse IDE workbench to the functions that are necessary for software development. Your own plug-ins using Eclipse RCP Workbench could be developed based on generic templates.