Difference between revisions of "GPU621/VTuners"
(→Algorithm Optimization) |
(→Algorithm Optimization) |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
==== Hotspot Analysis ==== | ==== Hotspot Analysis ==== | ||
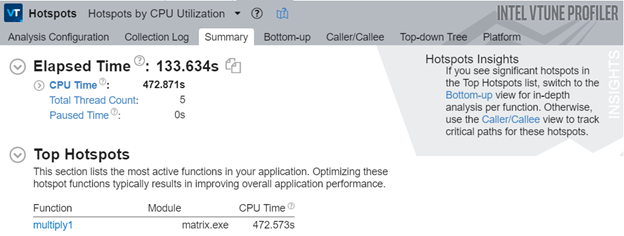
| − | [[File:Hotspot Analysis.png|600px|frame|Here we can see the summary of the output of the Vtune Profiler which shows some general information about the run time and thread usage]] | + | [[File:Hotspot Analysis.png|600px|frame|Vtune Summary: Here we can see the summary of the output of the Vtune Profiler which shows some general information about the run time and thread usage]] |
== Microarchitecture and Memory Bottlenecks == | == Microarchitecture and Memory Bottlenecks == | ||
Revision as of 14:53, 27 November 2022
Contents
Intel Vtune Profiler
Group Members
Vtune Profiler Features
The Vtune Profiler has a variety of features that provide information to assist in the optimization of application performance, system performance. The profiler also assists in system configuration for HPC, Cloud, IoT, media, storage, etc.
The profiler provides compatibility for a variety of systems and platforms that include the following:
CPU, GPU, and FGPA
Any combination of the following languages: SYCL, C, C++, C+, Fortran, OpenCL, Python, Google Go, Java, .NET, Assembly
Optimized performance that avoids power or thermal throttling
Collection of coarse-grained data over extended periods with details results including mapping to source code
Algorithm Optimization
Analyzing Hot Code Paths
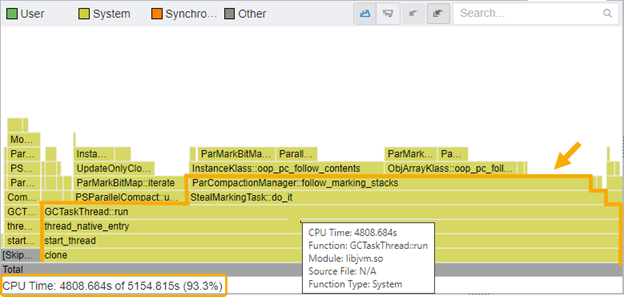
Flame Graphs
The Intel Vtune Profiler provides flame graphs to display a representation of stacks and stack frames in an application. All functions in an application are plotted on a graph and the associated stack depth is represented as height on the y-axis and the width of the bar represents the amount of CPU usage time. The “hottest” functions in an application are then the widest parts on the flame graph.