Difference between revisions of "GPU621/ApacheSpark"
(→Features) |
|||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
In memory computations <br /> | In memory computations <br /> | ||
Faster than MapReduce for complex application on disks <br /> | Faster than MapReduce for complex application on disks <br /> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:2abc.png ]] | ||
== Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) == | == Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) == | ||
Revision as of 08:58, 26 November 2018
Contents
[hide]Team Members
Introduction
What is Apache Spark ?
An open-source distributed general-purpose cluster-computing framework for Big Data.
History of Apache Spark
2009: a distributed system framework initiated at UC Berkeley AMPLab by MateiZaharia
2010: Open sourced under a BSD license
2013: The project was donated to the Apache Software Foundation and the license was changed to Apache 2.0
2014: Became an Apache Top-Level Project. Used by Databricks to set a world record in large-scale sorting in November
2014-present: Exists as a next generation real-time and batch processing framework
Why Apache Spark
Data is exploded in volume, velocity and variety
The need to have faster analytic results becomes increasingly important
Support near real time analytics to answer business questions
Spark and Hadoop
Hadoop = HDFS(Hadoop Distributed File System) + MapReduce(data processing model)
Spark is advanced data processing/analysis model which is replacing MapReduce
Spark does not have its own file system so it run on the top of HDFS
Spark vs MapReduce
Features
Easy to use
Supporting python. Java and Scala
Libraries for sql, ml, streaming
General-purpose
Batch like MapReduce is included
Iterative algorithm
Interactive queries and streaming which return results immediately
Speed
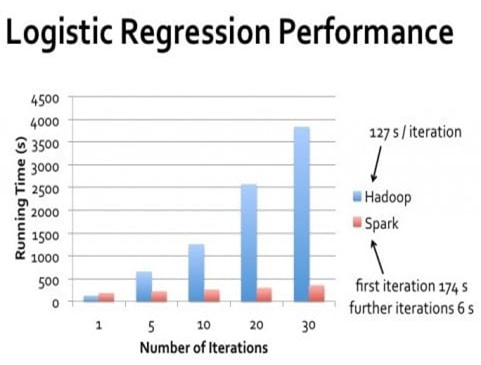
In memory computations
Faster than MapReduce for complex application on disks
Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs)
Spark revolves around RDDs it is a fundamental data structure in spark.
It is an immutable distributed collection of objects which can be operated on in parallel.
Two ways to implement RDDs
1) Parallelizing an existing collection
2) Referencing a data set in an external storage system
Operations
Transformations
Create a new data set from existing one
Actions
Return a value to the driver program after running computation on data set
Examples & Use Case
It is used in healthcare, media, finance, retail, travel.