Difference between revisions of "OPS335 Lab 4"
(→INVESTIGATION 2: SETUP MAIL TRANSFER AGENT (MTA) FOR SENDING MAIL MESSAGES (NO ENCRYPTION)) |
(→Sending a Mail Message within your vm2 Machine) |
||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
#Re-issue the '''mail''' command. What happened? | #Re-issue the '''mail''' command. What happened? | ||
#Exit the mail command. | #Exit the mail command. | ||
| − | |||
'''Record steps, commands, and your observations in INVESTIGATION 1 in your OPS335 lab log-book''' | '''Record steps, commands, and your observations in INVESTIGATION 1 in your OPS335 lab log-book''' | ||
Revision as of 08:49, 2 March 2017
Contents
OVERVIEW & PREPARATION
You may not be aware of it as an user, but email is a very complex system to administer. In fact, the more modern e-mail systems (eg. web-based mail applications, etc) are more technically involved than the other archaic, hard-to-configure, and sometimes inter-operable mail systems.
We are going to spread the remaining email labs over a few weeks, so that by the end of this topic, you will have a sufficient understanding of what services are involved in sending, filtering, and reading email. You will also have the skills to configure a basic mail setup using the default services provided for your Centos7 Linux distribution.
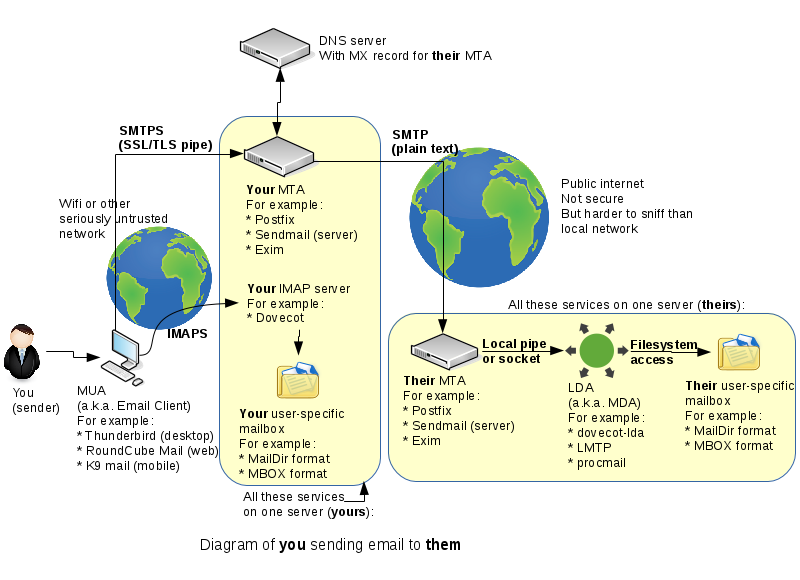
Believe it or not, this is considered to be a simple diagram of how you can send an email to someone else:
This lab will show you how to set up a Mail User Agent (MUA), using the mailx package on your vm2 machine to send and receive e-mails on your local VM. In this case, the Postfix package which represents your MTA is most likely already installed and running on your local VM. In addition to sending and receiving emails on your Local VM, you will also be able to send a text-based e-mail from your vm2 machine to your Seneca mail account. You will also learn how to make multiple MTAs in the same network collaborate in sending emails. In addition, you will learn where the message store (MS) is located that stores mail messages until they are viewed and either deleted or transferred to other folders.
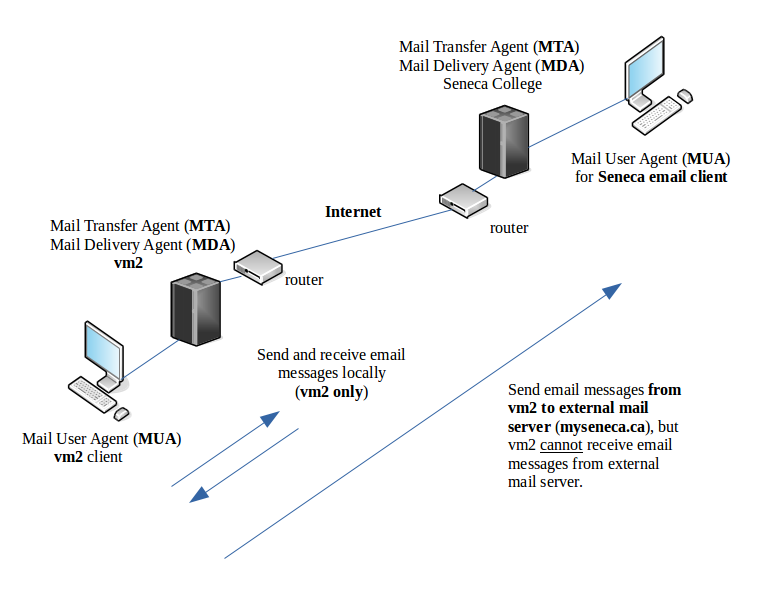
The diagram below shows the layout of the what this lab should be able to accomplish:
Although, you will not be able to receive mail messages from outside sources (such as your Seneca email account), this lab acts as a starting point in order to run a basic email server. You are NOT required you to go into tremendous depth (just the minimum requirements). For example, we will not go over every aspect of the Postfix MTA service, but you should know what it represents and what is its main purpose, as opposed to the following: complex diagram 1 , complex diagram 2.
Online References:
- Email Servers: Basic Terms (online slide notes)
- Mail Send Command (examples how to send e-mail using mail command)
- View and Manage Received e-mail Mesages (Common commands to view and manage received email messages)
- Reading Full Email Headers (Explanation of message header information)
- Here's an overview (common mail server terms)
INVESTIGATION 1: INSTALL, SET-UP, AND USE THE MAIL USER AGENT (MUA)
We will be using a simple text-based Mail User Agent (MUA) called mailx in this lab to send and receive mail messages within your vm2 machine and to send mail messages to your Seneca e-mail account.
NOTE: Due to the simplicity of this mail server setup and the lack of other DNS servers pointing to your network, and the setup of Seneca College's mail server, you cannot send Seneca e-mail messages to your vm2 machine.
Installing the Mail User Agent (MUA)
Perform the following Steps:
- Make certain you are in your vm2 machine.
- Issue the following command to install the mailx application (MUA):
yum install mailx
- NOTE: You can refer to the link below to acquaint yourself on how to send e-mail messages using mailx application:
Mail Send Command Examples
Sending a Mail Message from your vm2 Machine to your Seneca Email Account
We will now test to see if your MTA for your vm2 machine is correctly running by sending email messages from your vm2 machine to your Seneca e-mail account.
Perform the following steps:
- Make certain you are still in your vm2 machine.
- Test email from your machine by sending an email to your Seneca email account using the following command:
mail -s "Lab4a - test1" <Your Seneca email address>
NOTE: after you type in the body of the mail message, move to an empty line, type period "." and press the ENTER key to send the message. - Check your Seneca email account to see if you got the email (note that it may take a few minutes to arrive, so you may also wish to try an alternate email account if you have one like gmail, etc). When you do receive that email, make a note of the return address.
- If you did not receive the mail, check the mail logs on your vm2 machine to determine any errors messages that would indicate a mail server setup problem.
- Once you have succeeded in sending the first email, send a second email to the same destination using the following command:
mail -r "hacker.com (Canadian Revenue Agency)" -s "Lab4a - test2" <Your Seneca email address> - Check your email to see if you got the email. If you did, make a note of the return address. How would you think that including the -r option could be used by penetration hackers to gain access to a computer system? What sort of steps do you think should be taken to help prevent this type of attack from happening?
Sending a Mail Message within your vm2 Machine
We will now test both your MUA (mailx) and MTA (postfix) by sending and receiving e-mail messages on the local vm2 machine only.
Perform the following Steps:
- Send an email message locally (i.e. only within) your vm2 machine by issuing the command:
mail -s "Lab4a - Local - Test1" <yourSenecaID> - After you type in the body of the mail message, move to an empty line, type period "." and press the ENTER key to send the message.
- Issue the following command to read the mail message you send to yourself:
mail
NOTE: You can refer to the link below to view a reference chart on how to read and delete received e-mail messages at the mail command prompt:
Commands to View and Manage Received e-mail Mesages - Issue the following command: cat /var/spool/mail/<yourSenecaID>
What do you see? What does this show you in terms of where mail is stored on your e-mail server? - If you received an e-mail message, the message and subject line should appear as a listing in your mail command.
If you did not receive a mail message, check your mail server settings, check to see if you mail server is running and also check /var/log/maillog and /var/log/messages. - Once you have received the message, type the mail message number that is displayed in your e-mail message list in the prompt and press ENTER. You should be able to confirm the message body that you sent.
- Exit the mail program by typing the letter q and press ENTER.
- Re-issue the mail command. What happened?
- Exit the mail command.
Record steps, commands, and your observations in INVESTIGATION 1 in your OPS335 lab log-book
INVESTIGATION 2: SETUP MTA TO SEND MAIL MESSAGES (NO ENCRYPTION)
We will be using the Postfix application as the MTA, and we will be setting it up on your vm2 and vm3 machines. They will act as the "sending" email servers for your internal network. You will be able to send email out of your network, and receive email from within your network, but you will not receive email from outside of your network due to the following reasons:
- Individuals outside of your domain will never find the MX records because there are no .org servers pointing to your DNS server (i.e. you haven't paid for it).
- Even if the individuals could read your MX records, your local network is using IP addresses on a private subnet, which is not routeable on the Internet, so it cannot be reached from outside of your system.
Verify the Postfix Service Status
Perform the following steps:
- The postfix application should be installed by default. If it isn't, install it.
- Postfix is capable of sending email with the default configuration, so start and enable this service, and verify that the postfix service is running.
- Look for the running postfix service in the list of listening ports by issuing the following command:
ss -atnp
- Which service is postfix running? Locate the port used by SMTP, and look for connections with the state LISTEN (i.e. currently listening).
- Write your observations in your lab logbook.
Testing the connection to the Postfix Service
We will be demonstrating the use of the nc application to test that the postfix service is running and listening.
Perform the following steps:
- Connect from your vm2 to itself using nc by issuing the following command:
nc localhost 25
- You should see a response:
220 vm2.yourdomain.org ESMTP Postfix
- You could theoretically use SMTP commands to send an email here, but this would be a very unusual use of your mail server. You have an MUA for a reason.
- Enter the command QUIT to close the connection to the server, then <ctrl>-c to terminate the nc command.
- NOTE: If it worked, this indicates that the postfix service is running, listening, and responding to connections.
- Let's see if it works from other machines. Use nc to connect to vm2 from vm3 and see if it works. If your firewall is set up properly, the nc command should not permit a connection.
- Create an iptables rule to allow incoming connections to your SMTP server.
- Once you open the port in the firewall, retry the nc command. You should get a different error this time. This time the problem is that your service isn't listening on the outside interface, it's currently configured to listen only on the loopback (lo) interface.
- Add the iptables rule to your saved script so that it will be loaded automatically from now on.
Listening on all interfaces
Our first editing change to the Postfix configuration will be to make the service "listen" for incoming connections on the external interface (i.e eth0 from the VMs point of view).
Perform the following steps:
- Launch in editing session for the postfix configuration file called: /etc/postfix/main.cf
- Change the value of the following parameter to what is displayed below:
inet_interfaces = all
- We should also set the string that will end up in the From: header in messages sent by this server. Change mydomain to your domain name and myorigin to $myhostname.
- Ensure your hostname is properly set (including the domain name), otherwise you will need to set the myhostname parameter.
- Restart the postfix service and confirm (using ss) that the service is now listening on all interfaces (not just loopback)
- Test by connecting to it (using nc) from your vm3 machine.
INVESTIGATION 3: SENDING EMAIL BETWEEN MTAs (NO ENCRYPTION)
With these steps complete, vm2 should now be capable of sending and receiving email, but we can't be certain until we test it. This also would not help the users on the other machines in the network, which are still not capable of receiving email.
Repeat the configuration from investigation 2 on vm3 (swap vm2 and vm3 in the instructions so that you are configuring vm3, and using vm2 to test the connections).
Once that is complete, send an email from root on vm2 to root on vm3, and then reply from vm3 to vm2.
If both messages arrive, both MTAs are working. If not, use the troubleshooting tools and techniques you have already learned to diagnose and fix the problem.
COMPLETING THE LAB
Upon completion of this lab you should have postfix mail servers running on two machines, and starting automatically when they do. These servers must have sent email both ways between each other (from vm2 to vm3, and from vm3 to vm2), and to your seneca email (or other external mail server).
Depending on your professor you will either be asked to submit the lab in class, or online. Follow the appropriate set of instructions below
Online Submission (Peter Callaghan's Classes only)
Follow the instructions for lab 4a on moodle.
In Class Submission
- ✓Arrange proof that you can send e-mail from your vm2 machine to your Seneca College e-mail account, and than you can send and receive e-mail messages between on your vm2 and vm3 machines.
- ✓Download the labcheck4a.bash checking bash shell script by issuing the command:
wget http://matrix.senecac.on.ca/~peter.callaghan/files/OPS335/labcheck4a.bash
set execute permission and run the shell script on your c7host machine.- For Peter's classes, follow his Online Submission instructions in Moodle.
- For Murray's classes, run command (piping to the more command) and show output to instructor.
- ✓Completed Lab4a log-book notes.
EXPLORATION QUESTIONS
- Briefly list the steps to install the MUA on your server for text-based messaging.
- Briefly list the steps to trouble-shoot your server if you could not send e-mail messages from your vm2 machine to an external e-mail server.
- Write the command to send an e-mail message from your vm2 to your Seneca College e-mail account.
- What are the commands to issue in the mail prompt to:
- Read the first e-mail message displayed
- Save the 4th e-mail message to the file pathname: ~/maildir/3.msg.txt
- Delete the 3rd e-mail message displayed
- Exit the mail command prompt and return to the shell
- What were the results of sending emails locally on your vm2 machine? Show log segments to verify your answers.
- What is the purpose of an MTA?
- What is the purpose of an MUA?
- Draw a simple diagram showing how an MUA and an MTA are used to send e-mail messages between different servers.
- List the steps to test a running postfix service using the nc application.