Difference between revisions of "Prototype"
(→Sample code) |
(→Sample code) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
'''Java Sample:''' | '''Java Sample:''' | ||
Prototype pattern in java is implemented using the Clonable interface which provides the clone() method. Cloneable is an empty interface. It simply acts as a tag to indicate that the implementing classes need their instances to support clonning. | Prototype pattern in java is implemented using the Clonable interface which provides the clone() method. Cloneable is an empty interface. It simply acts as a tag to indicate that the implementing classes need their instances to support clonning. | ||
| − | |||
Subclasses must implement the Clonable interface and then override the clone() method and call the super classes clone method in the implementation of overridden clone method using super.clone() statement.If you don't implement Cloneable, the super.clone() implementation will throw a CloneNotSupportedException. | Subclasses must implement the Clonable interface and then override the clone() method and call the super classes clone method in the implementation of overridden clone method using super.clone() statement.If you don't implement Cloneable, the super.clone() implementation will throw a CloneNotSupportedException. | ||
The following is the implementation of Cookie class in apache tomcat server. This class makes use of prototype pattern and Clonable interface to create clones of cookie object. | The following is the implementation of Cookie class in apache tomcat server. This class makes use of prototype pattern and Clonable interface to create clones of cookie object. | ||
| + | |||
apache-tomcat-6.0.10 - Cookie.java | apache-tomcat-6.0.10 - Cookie.java | ||
| − | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
/* | /* | ||
| Line 512: | Line 511: | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 00:04, 18 March 2007
Contents
[hide]Prototype Design Pattern
Definition:
Specify the kinds of objects to create using a prototypical instance, and create new objects by copying this prototype. -- "Design Patterns" Gamma et al., Addison-Wesley, ISBN:0-201-63361-2"
Friendly Definition:
Prototype pattern is a creational pattern. Meaning it deals with the most efficient ways to create object in a given situation. when you do not want to directly call an objects' constructor , you can use this pattern to clone an existing object of that class thus reducing the number of classes. The basic principle behind this pattern is to determine the type of objects to be created by using a prototypical reference.
Advantages
Side Effects
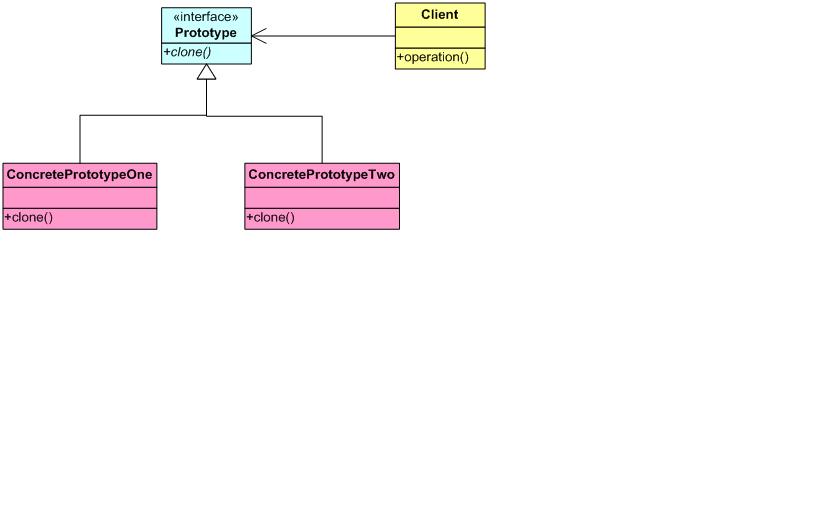
Pattern diagram
Sample code
Java Sample: Prototype pattern in java is implemented using the Clonable interface which provides the clone() method. Cloneable is an empty interface. It simply acts as a tag to indicate that the implementing classes need their instances to support clonning. Subclasses must implement the Clonable interface and then override the clone() method and call the super classes clone method in the implementation of overridden clone method using super.clone() statement.If you don't implement Cloneable, the super.clone() implementation will throw a CloneNotSupportedException.
The following is the implementation of Cookie class in apache tomcat server. This class makes use of prototype pattern and Clonable interface to create clones of cookie object.
apache-tomcat-6.0.10 - Cookie.java
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package javax.servlet.http;
import java.text.MessageFormat;
import java.util.ResourceBundle;
/**
*
* Creates a cookie, a small amount of information sent by a servlet to
* a Web browser, saved by the browser, and later sent back to the server.
* A cookie's value can uniquely
* identify a client, so cookies are commonly used for session management.
*
* <p>A cookie has a name, a single value, and optional attributes
* such as a comment, path and domain qualifiers, a maximum age, and a
* version number. Some Web browsers have bugs in how they handle the
* optional attributes, so use them sparingly to improve the interoperability
* of your servlets.
*
* <p>The servlet sends cookies to the browser by using the
* {@link HttpServletResponse#addCookie} method, which adds
* fields to HTTP response headers to send cookies to the
* browser, one at a time. The browser is expected to
* support 20 cookies for each Web server, 300 cookies total, and
* may limit cookie size to 4 KB each.
*
* <p>The browser returns cookies to the servlet by adding
* fields to HTTP request headers. Cookies can be retrieved
* from a request by using the {@link HttpServletRequest#getCookies} method.
* Several cookies might have the same name but different path attributes.
*
* <p>Cookies affect the caching of the Web pages that use them.
* HTTP 1.0 does not cache pages that use cookies created with
* this class. This class does not support the cache control
* defined with HTTP 1.1.
*
* <p>This class supports both the Version 0 (by Netscape) and Version 1
* (by RFC 2109) cookie specifications. By default, cookies are
* created using Version 0 to ensure the best interoperability.
*
*
* @author Various
* @version $Version$
*
*/
// XXX would implement java.io.Serializable too, but can't do that
// so long as sun.servlet.* must run on older JDK 1.02 JVMs which
// don't include that support.
public class Cookie implements Cloneable {
private static final String LSTRING_FILE =
"javax.servlet.http.LocalStrings";
private static ResourceBundle lStrings =
ResourceBundle.getBundle(LSTRING_FILE);
//
// The value of the cookie itself.
//
private String name; // NAME= ... "$Name" style is reserved
private String value; // value of NAME
//
// Attributes encoded in the header's cookie fields.
//
private String comment; // ;Comment=VALUE ... describes cookie's use
// ;Discard ... implied by maxAge < 0
private String domain; // ;Domain=VALUE ... domain that sees cookie
private int maxAge = -1; // ;Max-Age=VALUE ... cookies auto-expire
private String path; // ;Path=VALUE ... URLs that see the cookie
private boolean secure; // ;Secure ... e.g. use SSL
private int version = 0; // ;Version=1 ... means RFC 2109++ style
/**
* Constructs a cookie with a specified name and value.
*
* <p>The name must conform to RFC 2109. That means it can contain
* only ASCII alphanumeric characters and cannot contain commas,
* semicolons, or white space or begin with a $ character. The cookie's
* name cannot be changed after creation.
*
* <p>The value can be anything the server chooses to send. Its
* value is probably of interest only to the server. The cookie's
* value can be changed after creation with the
* <code>setValue</code> method.
*
* <p>By default, cookies are created according to the Netscape
* cookie specification. The version can be changed with the
* <code>setVersion</code> method.
*
*
* @param name a <code>String</code> specifying the name of the cookie
*
* @param value a <code>String</code> specifying the value of the cookie
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the cookie name contains illegal characters
* (for example, a comma, space, or semicolon)
* or it is one of the tokens reserved for use
* by the cookie protocol
* @see #setValue
* @see #setVersion
*
*/
public Cookie(String name, String value) {
if (!isToken(name)
|| name.equalsIgnoreCase("Comment") // rfc2019
|| name.equalsIgnoreCase("Discard") // 2019++
|| name.equalsIgnoreCase("Domain")
|| name.equalsIgnoreCase("Expires") // (old cookies)
|| name.equalsIgnoreCase("Max-Age") // rfc2019
|| name.equalsIgnoreCase("Path")
|| name.equalsIgnoreCase("Secure")
|| name.equalsIgnoreCase("Version")
|| name.startsWith("$")
) {
String errMsg = lStrings.getString("err.cookie_name_is_token");
Object[] errArgs = new Object[1];
errArgs[0] = name;
errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs);
throw new IllegalArgumentException(errMsg);
}
this.name = name;
this.value = value;
}
/**
*
* Specifies a comment that describes a cookie's purpose.
* The comment is useful if the browser presents the cookie
* to the user. Comments
* are not supported by Netscape Version 0 cookies.
*
* @param purpose a <code>String</code> specifying the comment
* to display to the user
*
* @see #getComment
*
*/
public void setComment(String purpose) {
comment = purpose;
}
/**
* Returns the comment describing the purpose of this cookie, or
* <code>null</code> if the cookie has no comment.
*
* @return a <code>String</code> containing the comment,
* or <code>null</code> if none
*
* @see #setComment
*
*/
public String getComment() {
return comment;
}
/**
*
* Specifies the domain within which this cookie should be presented.
*
* <p>The form of the domain name is specified by RFC 2109. A domain
* name begins with a dot (<code>.foo.com</code>) and means that
* the cookie is visible to servers in a specified Domain Name System
* (DNS) zone (for example, <code>www.foo.com</code>, but not
* <code>a.b.foo.com</code>). By default, cookies are only returned
* to the server that sent them.
*
*
* @param pattern a <code>String</code> containing the domain name
* within which this cookie is visible;
* form is according to RFC 2109
*
* @see #getDomain
*
*/
public void setDomain(String pattern) {
domain = pattern.toLowerCase(); // IE allegedly needs this
}
/**
* Returns the domain name set for this cookie. The form of
* the domain name is set by RFC 2109.
*
* @return a <code>String</code> containing the domain name
*
* @see #setDomain
*
*/
public String getDomain() {
return domain;
}
/**
* Sets the maximum age of the cookie in seconds.
*
* <p>A positive value indicates that the cookie will expire
* after that many seconds have passed. Note that the value is
* the <i>maximum</i> age when the cookie will expire, not the cookie's
* current age.
*
* <p>A negative value means
* that the cookie is not stored persistently and will be deleted
* when the Web browser exits. A zero value causes the cookie
* to be deleted.
*
* @param expiry an integer specifying the maximum age of the
* cookie in seconds; if negative, means
* the cookie is not stored; if zero, deletes
* the cookie
*
*
* @see #getMaxAge
*
*/
public void setMaxAge(int expiry) {
maxAge = expiry;
}
/**
* Returns the maximum age of the cookie, specified in seconds,
* By default, <code>-1</code> indicating the cookie will persist
* until browser shutdown.
*
*
* @return an integer specifying the maximum age of the
* cookie in seconds; if negative, means
* the cookie persists until browser shutdown
*
*
* @see #setMaxAge
*
*/
public int getMaxAge() {
return maxAge;
}
/**
* Specifies a path for the cookie
* to which the client should return the cookie.
*
* <p>The cookie is visible to all the pages in the directory
* you specify, and all the pages in that directory's subdirectories.
* A cookie's path must include the servlet that set the cookie,
* for example, <i>/catalog</i>, which makes the cookie
* visible to all directories on the server under <i>/catalog</i>.
*
* <p>Consult RFC 2109 (available on the Internet) for more
* information on setting path names for cookies.
*
*
* @param uri a <code>String</code> specifying a path
*
*
* @see #getPath
*
*/
public void setPath(String uri) {
path = uri;
}
/**
* Returns the path on the server
* to which the browser returns this cookie. The
* cookie is visible to all subpaths on the server.
*
*
* @return a <code>String</code> specifying a path that contains
* a servlet name, for example, <i>/catalog</i>
*
* @see #setPath
*
*/
public String getPath() {
return path;
}
/**
* Indicates to the browser whether the cookie should only be sent
* using a secure protocol, such as HTTPS or SSL.
*
* <p>The default value is <code>false</code>.
*
* @param flag if <code>true</code>, sends the cookie from the browser
* to the server only when using a secure protocol;
* if <code>false</code>, sent on any protocol
*
* @see #getSecure
*
*/
public void setSecure(boolean flag) {
secure = flag;
}
/**
* Returns <code>true</code> if the browser is sending cookies
* only over a secure protocol, or <code>false</code> if the
* browser can send cookies using any protocol.
*
* @return <code>true</code> if the browser uses a secure protocol;
* otherwise, <code>true</code>
*
* @see #setSecure
*
*/
public boolean getSecure() {
return secure;
}
/**
* Returns the name of the cookie. The name cannot be changed after
* creation.
*
* @return a <code>String</code> specifying the cookie's name
*
*/
public String getName() {
return name;
}
/**
*
* Assigns a new value to a cookie after the cookie is created.
* If you use a binary value, you may want to use BASE64 encoding.
*
* <p>With Version 0 cookies, values should not contain white
* space, brackets, parentheses, equals signs, commas,
* double quotes, slashes, question marks, at signs, colons,
* and semicolons. Empty values may not behave the same way
* on all browsers.
*
* @param newValue a <code>String</code> specifying the new value
*
*
* @see #getValue
* @see Cookie
*
*/
public void setValue(String newValue) {
value = newValue;
}
/**
* Returns the value of the cookie.
*
* @return a <code>String</code> containing the cookie's
* present value
*
* @see #setValue
* @see Cookie
*
*/
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
/**
* Returns the version of the protocol this cookie complies
* with. Version 1 complies with RFC 2109,
* and version 0 complies with the original
* cookie specification drafted by Netscape. Cookies provided
* by a browser use and identify the browser's cookie version.
*
*
* @return 0 if the cookie complies with the
* original Netscape specification; 1
* if the cookie complies with RFC 2109
*
* @see #setVersion
*
*/
public int getVersion() {
return version;
}
/**
* Sets the version of the cookie protocol this cookie complies
* with. Version 0 complies with the original Netscape cookie
* specification. Version 1 complies with RFC 2109.
*
* <p>Since RFC 2109 is still somewhat new, consider
* version 1 as experimental; do not use it yet on production sites.
*
*
* @param v 0 if the cookie should comply with
* the original Netscape specification;
* 1 if the cookie should comply with RFC 2109
*
* @see #getVersion
*
*/
public void setVersion(int v) {
version = v;
}
// Note -- disabled for now to allow full Netscape compatibility
// from RFC 2068, token special case characters
//
// private static final String tspecials = "()<>@,;:\\\"/[]?={} \t";
private static final String tspecials = ",; ";
/*
* Tests a string and returns true if the string counts as a
* reserved token in the Java language.
*
* @param value the <code>String</code> to be tested
*
* @return <code>true</code> if the <code>String</code> is
* a reserved token; <code>false</code>
* if it is not
*/
private boolean isToken(String value) {
int len = value.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
char c = value.charAt(i);
if (c < 0x20 || c >= 0x7f || tspecials.indexOf(c) != -1)
return false;
}
return true;
}
/**
*
* Overrides the standard <code>java.lang.Object.clone</code>
* method to return a copy of this cookie.
*
*
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
return super.clone();
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
Related Patterns
- a
- b
- c