Difference between revisions of "OPS335 Lab 1"
(→Completing the Lab) |
(→Configure a Linux Gateway for Linux Hosts inside an Intranet) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Configure a Linux Gateway for Linux Hosts inside an Intranet== | ==Configure a Linux Gateway for Linux Hosts inside an Intranet== | ||
This lab will show you how to set up a simple intranet using one Fedora PC as a gateway. The same Fedora PC will be a host to a Fedora VM (Virtual Machine) which will act as a PC inside an intranet. Here is a diagram of your setup.<br />[[Image:lab01.png]] | This lab will show you how to set up a simple intranet using one Fedora PC as a gateway. The same Fedora PC will be a host to a Fedora VM (Virtual Machine) which will act as a PC inside an intranet. Here is a diagram of your setup.<br />[[Image:lab01.png]] | ||
| − | {{Admon/important|Requirement - Lab 0|Lab 0 should be completed and you should have a copy of Fedora | + | {{Admon/important|Requirement - Lab 0|Lab 0 should be completed and you should have a copy of Fedora 16, x86_64 LIVE ISO Image.}} |
==Instructions== | ==Instructions== | ||
Revision as of 15:44, 15 January 2012
Contents
Configure a Linux Gateway for Linux Hosts inside an Intranet
This lab will show you how to set up a simple intranet using one Fedora PC as a gateway. The same Fedora PC will be a host to a Fedora VM (Virtual Machine) which will act as a PC inside an intranet. Here is a diagram of your setup.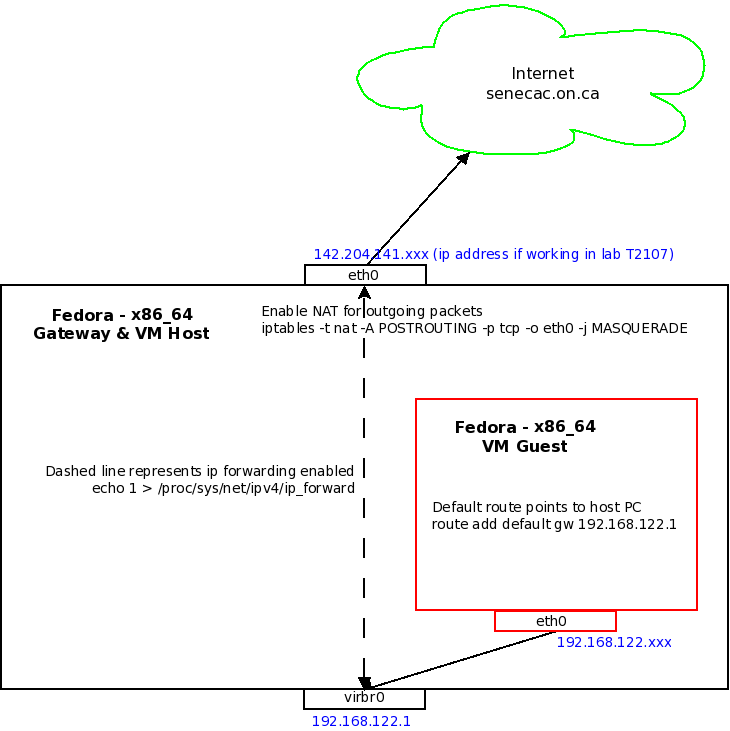
Instructions
Managing services using systemd
Boot up your Fedora 16 x86_64 system, login with your learn id and use Firefox to authenticate yourself on Senenet so you can download and install new software.
- Open a terminal window and su to root.
- Ensure your system date and time are correct.
- Ensure your system is up to date
yum update
- Start your ssh server
service sshd start Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start sshd.service
- Notice that your command was redirected, the command executed was 'systemctl start sshd.service'. Record this in your lab book.
- Enable sshd to start at boot
chkconfig sshd on Note: Forwarding request to 'systemctl enable sshd.service'. ln -s '/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/sshd.service'
- Again notice your command was redirected, the command executed was 'systemctl enable sshd.service'. When the command was executed a symbolic link was created, make note of it in your lab book.
- Install the virtualization software
yum groupinstall virtualization
- Start the libvirt daemon using 'systemctl'
systemctl start libvirtd.service
- Enable libvirtd to start at boot using 'systemctl'
systemctl enable libvirtd.service libvirtd.service is not a native service, redirecting to /sbin/chkconfig. Executing /sbin/chkconfig libvirtd on Warning: unit files do not carry install information. No operation executed.
Installing the first guest machine
You are now ready to build a VM guest. You learned how to do this last semester in OPS235. If you need to be refreshed please refer to OPS235 LAB06.
- Start the virtual machine manager
- virt-manager
- Enter the root password.
- Click on the icon "Create a new virtual machine".
- Name your machine "vm01" then click on the "forward" button.
- Insert your F13 CD and select "Use ISO Image" and select the ISO image you downloaded.For "OS type" select "Linux" and for Version select "Fedora 13" then click on the "Forward" button.
- Let the RAM default to 512MB and the CPUs to 1. Then click on the "Forward" button.
- Leave the disk image size set at 8GB and ensure "Allocate entire disk now" is checked, then click on the "Forward" button.
- At the "Ready to begin installation" window click on the "Finish" button.
- Once your Fedora Live CD boots up, login and double click the "Install to Hard Disk" icon.
- Click the "Next" button to begin your F13 installation.
- Select "US English" for your keyboard and click on the "Next" button.
- Ensure "Basic Storage Devices" is selected and click on the "Next" button.
- Select the "Virtio Block Device" check box and click on the "Next" button.
- Click on the "Re-initialize All" button".
- Change your hostname to "vm01.localdomain" and click on the "Next" button.
- Select "America/Toronto" as your timezone and click on the "Next" button.
- Enter the password for root and click on the "Next" button.
- Select "Use All Space" and click on the "Next" button.
- Click on the "Write Changes to Disk" button.
- When the "Congratulations" window is displayed click on the "Close" button.
- Now, from the System men on the host PC, select "Shutdown" and then click on the "Restart" button.
- At the "Welcome" screen click on the "Forward" button.
- At the "License" window click on the "Forward" button.
- Enter a user name of "Joker" and add the password then click the "Forward" button.
- Enter the correct date and time and click on the "Forward" button.
- In the "Profile" window, click on the "Finish" button and "Do not send profile".
- Now login as user "joker" and open a terminal window.
- Switch to root and update your VM guest machine
- yum update
- This could take a long time and you should reboot after it's done.
- Ensure your VM guest has internet access
- host cbc.ca
Testing your Gateway
- Try pinging each machine from the other.
- Try pinging Matrix from each machine.
- Start the ssh server on both machines
service sshd start
- Enable the ssh server at startup on both machines
chkconfig --levels 2345 sshd on
- Start Firefox on your host machine and authenticate yourself on Senenet.
- Try to ssh from the guest to the host machine. This should work.
- Try to ssh from the host to the guest machine. This should not work.
- Try to ssh to your Matrix account from both the host and guest machines.
- Try to ssh from your Matrix account back to your host and guest machines.
- Add one iptables rule to the guest firewall that will accept new ssh connections to the guest machine.
- Save your new firewall rules
service iptables save
- Reboot your guest machine.
- Try to ssh from the host to the guest machine. This should now work.
- Start Firefox on the guest machine and try surfing the web without authicating yourself on Senenet. i.e. only the host machine is authenticated.
Completing the Lab
Answer the following questions in your logbook.
- What iptables rule was added to allow ssh connections to the guest vm?
- Explain how Network Address Translation is accomplished on the host. Refer and specifically explain the 3 rules in the POSTROUTING chain of the nat table on the host machine.
- How is ping and ssh affected (on both machines) if you disable ip forwarding on the host machine?
- echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
- Did you clean up your work area, power off your PC and push your chair under the table when you completed this lab?