Difference between revisions of "How to Use Zenity"
| Line 104: | Line 104: | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | <u>Displaying Text Over Several Lines</u> | ||
| + | <table> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>'''zenity --info --text "Sentence1\n\nSentence2\n\nSentence3"'''</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>Here is output from above command. Notice how each sentence appears on a separate line. The "\n" character represents a new-line:<br /><br />[[Image:newline.png|left|200px]]</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
Have fun :) | Have fun :) | ||
Murray Saul | Murray Saul | ||
Revision as of 01:44, 2 February 2010
Definition of Zenity
Zenity is a Linux / Unix command that uses dialog boxes to make shell script more graphical to end-users.
Here is a link to the Wikipedia definition of the Zenity command: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Zenity
Features of Zenity
There are many different types of dialog boxes that the Zenity command can create. The following is a table that uses options (starting with -- symbol immediately followed by a word to indicate the type dialog box to create:
| --calendar | Display calendar dialog |
|---|---|
| --entry | Display text entry dialog |
| --error | Display error dialog |
| --file-selection | Display file selection dialog |
| --info | Display info dialog |
| --list | Display list dialog |
| --notification | Display notification icon |
| --progress | Display progress indication dialog |
| --question | Display question dialog |
| --text-info | Display text information dialog |
| --warning | Display warning dialog |
| --scale | Display scale dialog |
Adding the --text option provides the dialog box to contain text to provide information for the user (output, or helping guide the user when prompting for a question).
Don't Make it Complicated
Using Zenity is easy - don't make it complicated!
For example, think of Zenity as a replacement for the echo command to display output. You can use --info to display standard input, and --error to display standard error messages.
To obtain input, think of Zenity as a replacement for the read command. You can use --entry to prompt the user for input. When the user enters text and clicks the OK button, or presses the <ENTER> key, zenity will return the value of that entered text. To store it into a variable to be used later in the program, you can use command substitution (enough said, since this is being used for an assignment! You figure it out :) ... ).
To obtain more options with this command, you should use the man pages... (eg. man zenity).
Simple Examples
Displaying Output
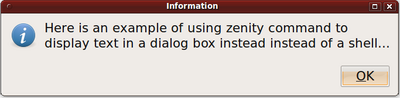
| zenity --info --text "Here is an example of using zenity command to display text in a dialog box instead instead of a shell..." |
| Here is output from above command: |
Prompting User for Input
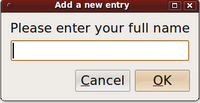
| zenity --entry --text "Please enter your full name" |
| Here is input dialog box for user to enter input: |
Displaying Text Over Several Lines
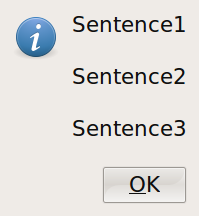
| zenity --info --text "Sentence1\n\nSentence2\n\nSentence3" |
| Here is output from above command. Notice how each sentence appears on a separate line. The "\n" character represents a new-line: |
Have fun :)
Murray Saul