Difference between revisions of "Tutorial2: Unix / Linux File Management"
(→INVESTIGATION 1: MANAGING DIRECTORy FILES) |
(→INVESTIGATION 2: USING THE LINUX SHELL / ONLINE ASSIGNMENTS) |
||
| Line 89: | Line 89: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | =INVESTIGATION 2: USING | + | =INVESTIGATION 2: USING TEXT EDITORS TO CREATE / MODIFY TEXT FILES = |
<br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 08:37, 6 January 2020
Contents
UNIX / LINUX FILE MANAGEMEN
Main Objectives of this Practice Tutorial
- x
- x
- x
- x
- x
- x
- x
- x
Tutorial Reference Material
| Course Notes / Software |
Linux Command/Shortcut Reference |
YouTube Videos | ||
| Course Notes:Tutorials:
|
Directory and File Management Commands | Text File Management Commands
Text Editors
|
Brauer Instructional Videos: | |
Unix / Linux File Management Concepts
x
INVESTIGATION 1: MANAGING DIRECTORIES
x
Part 1: Creating / Removing Directories
x
Perform the Following Steps:
- x
Part 2: Creating / Copying / Moving / Removing Files
x
Perform the Following Steps:
- x
INVESTIGATION 2: USING TEXT EDITORS TO CREATE / MODIFY TEXT FILES
In this section, you will learn how to use the Linux Shell. Topics in the section include:
- Learn the Linux command structure (arguments and options)
- Learn how to get help for Linux commands with manpages (man command).
- Learn Basic Shell Editing
- Learn how to perform online assignments.
- Perform the first two sections of online assignment #1.
Part 1: Using the Linux Shell
The Bash shell in Matrix allows you to interact with your account by issuing commands.
Some Linux commands can be issued by entering the Linux command line without arguments (e.g. pwd, date, ls, cal),
but some Linux commands can be issued with arguments (e.g. cal 2002, cd /bin, ls -la ).
Linux Command Structure
command argument1 argument2 ...
An argument can be a pathname, text, option, etc.
For example:
- The ls command displays a listing of filenames in the current directory
- The ls /bin command displays a listing of filenames in the /bin directory (as opposed to your current directory)
- The ls -l command displays a detailed listing of filenames in the current directory
- The ls -l /bin command displays a details listing of files in the /bin directory
Getting Help with Linux Commands
With the Linux OS containing over 2500 commands and utilities, it is good for a Linux user or sysadmin to learn about how to use commands “on-the-fly”.
The man command can provide information on how to use a command (i.e. usage, arguments, options, examples).
The commands are classified into sections or “volumes”.
Perform the Following Steps:
- Make certain that you are logged into your Matrix account.
- Issue the following command: man man
How many volume numbers are contained in the man pages (like executable commands/programs, games, or system administrator commands)? - Press the letter q to exit the man command.
- Issue the Linux command to get help with the command: ls
NOTE: You can use the following short-cut keys within the man command to
help navigate throughout this utility to get help with the ls command (refer to table below):Keyboard Shortcut Purpose ENTER Move down one line SPACEBAR Move one screen down <ctrl><f> Move one screen up /pattern/ Search for Pattern q quit man utility - Navigate through the man utility for the ls Linux command and note the option letters that correspond to the following:
- Include directory entries whose names begin with a dot
- List in long format
- Recursively list subdirectories encountered
- Sort files by size
- Display a slash (`/') immediately after each pathname that is a directory
- Exit the man utility for the ls command.
- Issue the ls command for each of those option letters you wrote down to see how this command differs for each option.
NOTE: The man utility can be used with the -k option to help list Linux commands that match a text pattern that is contained within the help screen for a Linux command. - Although we will not be learning about pipeline commands (using the | character) until later, try issuing the following pipeline command: man -k copy | grep 8
How this this pipeline command make it easier to obtain information regarding man command? - If you wish to change your password, you can change it by issuing the command: passwd
What option for the passwd command can be used to change user info (such as name)?
Hint: use the manpages for the passwd command.
NOTE: You are NOT required to change your Matrix password for this tutorial. The Matrix server is "synched" with the my.senecacollege.ca server, so it is better to have your Matrix password changed at the same time that you change your myseneca password.
Command Line Editing
Learning shortcut keys in any OS terminal will allow you to be more productive as a sysadmin. You will focus on learning a few common Bash Shell keyboard shortcut keys and learn where you can access online help for additional shortcuts (if required).
Perform the Following Steps:
- Type the following Linux command, but DON’T press the ENTER key: cd /bin
- Press the ctrl-a key combination. What happens?
- Press the alt-F key combination (ESC+F for Mac OSx). What happens?
- Press the ctrl-w shortcut. What happens?
- Type the following command: ls
- Press the ctrl-e key combination and press ENTER
- Press the up arrow key. What happens?
- Press the ctrl-u key combination. What happens?
- Press the up arrow key combination, and see what happens when you press BACKSPACE , <ctrl><BACKSPACE> and <ctrl><h>. Why is it important to know those series of key combinations?
- Press the ctrl-u key combination to clear the line.
- Press the ctrl-l key combination. What happens? What is the advantage of using this key combination then issuing the clear command?
Part 2: Performing Online Assignments
You are required to perform 3 online assignments during this course. This online assignment is used to teach and reinforce Linux commands are techniques as well as using Linux commands to perform tasks and tests students on their knowledge of issuing Linux commands.
In this section, you will learn to select the correct section for your online assignments, how to perform the first two sections of assignment #1, how to verify that you successfully completed both sections, and how to exit your online assignment #1.
Perform the following steps:
- In your Matrix account, issue the following command:
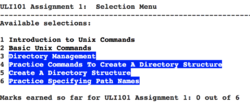
~uli101/assign1 - A screen similar to the one displayed on the right will appear.
WARNING: You need to select the CORRECT section for the course which you belong to.
If you do NOT select your correct section, your assignment may not be recorded for marks! - Select the letter(s) corresponding to the correct ULI101 section and professor and press ENTER
- After you have selected your course section, There will be a screen that provides several important notes before proceeding.
Please take a few moments to read those notes and press ENTER to proceed. - The assignment main menu will then be displayed.
NOTES:- Near the bottom of the window, you will see "You are currently registered to" followed by the section letter and instructor name. Double-check your course timetable to confirm that this the correct section letter. If you have selected the WRONG section, type C in the menu selection area and press ENTER. You will return back to the original window to select your correct course section.
- Near the top of the window displays the sections to complete in the assignment. You are NOT required to complete all sections at the same time. You can check the assignment #1 link on the ULI101 main WIKI page to note the due date for assignment #1. Sections that are NOT completed will be displayed in reverse text with a blue background. On the other hand, when you compete a section, then the section will appear as regular text
(i.e not in reverse text). - If you want to verify that you have completed sections for the assignment, look for the text "Marks earned so far for ULI101 Assignment:" and it will show how many sections have been completed. When it shows all sections completed, then your assignment is finished and you should receive full marks provided that you have selected your correct course section.
- Near the bottom of the window, you will see "You are currently registered to" followed by the section letter and instructor name. Double-check your course timetable to confirm that this the correct section letter. If you have selected the WRONG section, type C in the menu selection area and press ENTER. You will return back to the original window to select your correct course section.
- At the menu assignment #1 window, enter 1 in the menu selection area to begin the first section called "Introduction to Unix Commands".
- When you have completed this section, you will be returned to the main window.
View the contents of this window to confirm that you completed this section. - When you have time this week, enter 2 in the menu selection area to begin the first section called "Basic Unix Commands".
- When you have completed this section, you will be returned to the main window.
View the contents of this window to confirm that you completed this section.
NOTE: Although you are NOT allowed to use reference sheets for course evaluations, it is recommended to create one for your personal use, and write down Linux commands, their arguments and options, so your can successfully perform quizzes, midterm exam, and final exam. - Proceed to the next section to perform additional practice. Linux is about "doing"! The more practice questions you perform, the better mark you will achieve for this course and have a better foundation of issuing Linux commands to be more productive in your future courses.
LINUX PRACTICE QUESTIONS
The purpose of this section is to obtain extra practice to help with quizzes, your midterm, and your final exam.
Here is a link to the MS Word Document of ALL of the questions displayed below but with extra room to answer on the document to simulate a quiz:
https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~murray.saul/uli101/uli101_week1_practice.docx
Your instructor may take-up these questions during class. It is up to the student to attend classes in order to obtain the answers to the following questions. Your instructor will NOT provide these answers in any other form (eg. e-mail, etc).
Review Questions:
- What is a “Linux Cluster”? What is an advantage of using a Linux cluster?
- List three unique server names at Seneca college and briefly explain the purpose of that server.
- List the steps to connect and login to your Matrix Linux server account from a workstation in a computer lab at Seneca College.
- List the steps to connect and login to your Matrix Seneca College account on your laptop or your home computer.
- List 3 unique ways to log-out of your Matrix account (not including closing the SSH window or application).
- What is the difference between a Linux command and an argument?
- What is the purpose of a Linux command option?
- What character(s) is used to separate commands and arguments?
- Create a table listing each Linux command, useful options that were mentioned in the online assignment #1 and command purpose for the following Linux commands: pwd , cd , ls , cal , date , who , w , whoami , who am I , clear