Difference between revisions of "OPS335 Lab 6"
m (Modifying intro to match standardized format.) |
m (Removing reference to deprecated command.) |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
{{Admon/tip|Changing Existing Samba Account Passwords|If you need to change a user's existing Samba account password, you can issue the following command as root: '''smbpasswd username'''.}} | {{Admon/tip|Changing Existing Samba Account Passwords|If you need to change a user's existing Samba account password, you can issue the following command as root: '''smbpasswd username'''.}} | ||
| − | <ol><li value="6">Confirm the user you created has been added using the following command:<br>'''pdbedit -L -v'''</li><li>Test and review your configuration with the command:<br>'''testparm'''</li><li>Use the '''systemctl''' command to start the smb.service and enable the service to run on boot-up</li><li>If you are in one of the sections with SELinux set to enforcing, you will need to tell it to allow samba access to home directories: '''setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs 1'''</li><li> | + | <ol><li value="6">Confirm the user you created has been added using the following command:<br>'''pdbedit -L -v'''</li><li>Test and review your configuration with the command:<br>'''testparm'''</li><li>Use the '''systemctl''' command to start the smb.service and enable the service to run on boot-up</li><li>If you are in one of the sections with SELinux set to enforcing, you will need to tell it to allow samba access to home directories: '''setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs 1'''</li><li>Use the '''ss -nautp''' command to see with port Samba is running on.</li><li>Use the information in the previous step to modify the firewall on VM2 machine to allow samba traffic.</li><li>Test to see that you can connect to your Samba server (locally) by issuing the following command:<br>'''smbclient -U <yourSenecaID> -L 127.0.0.1'''</li><li>When prompted, enter your Samba account password.</li><li>The output from that issued command show appear similar to example displayed below:</li></ol> |
Sharename Type Comment | Sharename Type Comment | ||
Revision as of 04:18, 12 July 2016
Contents
OBJECTIVE & PREPARATION
According to the samba.org website:
"Samba is the standard Windows interoperability suite of programs for Linux and Unix. Samba is Free Software licensed under the GNU General Public License, the Samba project is a member of the Software Freedom Conservancy."
Although a Samba server can provide many features such as printer sharing and backups, this lab's primary focus is to set up a Samba server on a Linux server in order to allow MS Windows users to share common files from the Linux's Samba server.
This lab will first install, setup, and enable a Samba server. Then another virtual machine will be created for a Windows operating system. Finally, within the Windows virtual machine, users will access files from the Linux Samba server (both graphically and command line).
Online Resources
- (Course Notes on Samba Server)
- Samba Server Setup (Simple setup guide for samba server]
INVESTIGATION 1: INSTALLING & CONFIGURING A SAMBA SERVER
In this investigation, we will set up a Samba server on our VM2 machine. We will first install, configure and enable the samba server on our virtual machine, and then we will quickly test to see if the Samba server works.
Perform the following steps:
- Make certain that both your VM1 and VM2 machines are running.
- Switch to your VM2 machine as the root user.
- Issue the following Linux command to install Samba server utlity:
yum install samba samba-client - Copy the file /etc/samba/smb.conf to another filename by issuing the following command:
cp /etc/samba/smb.conf /etc/samba/smb.conf.original - Clear the contents of the configuration file by running cat /dev/null > /etc/samba/smb.conf
- Edit /etc/samba/smb.conf so that the file that contains the following lines:
[global] workgroup = WORKGROUP server string = "put your real name here without the quotes" encrypt passwords = yes smb passwd file = /etc/samba/smbpasswd [home] comment = "put your real name here without the quotes" path = /home/<yourSenecaID> public = yes writable = yes printable = no create mask = 0765
- Append (add) the following parameter to the bottom of the [global] section that will limit access to the share so that only machines in your virtual network and those in the lab room will be able to access it:
hosts allow = 192.168.x. 127.0.0.1
- Append (add) the following parameter to the [home] section so that only your user account can access that share:
valid users = <yourSenecaID>
- Create a Samba account and password for yourSenecaID by issuing the following command:
smbpasswd -a <yourSenecaID>
- Confirm the user you created has been added using the following command:
pdbedit -L -v - Test and review your configuration with the command:
testparm - Use the systemctl command to start the smb.service and enable the service to run on boot-up
- If you are in one of the sections with SELinux set to enforcing, you will need to tell it to allow samba access to home directories: setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs 1
- Use the ss -nautp command to see with port Samba is running on.
- Use the information in the previous step to modify the firewall on VM2 machine to allow samba traffic.
- Test to see that you can connect to your Samba server (locally) by issuing the following command:
smbclient -U <yourSenecaID> -L 127.0.0.1 - When prompted, enter your Samba account password.
- The output from that issued command show appear similar to example displayed below:
Sharename Type Comment
--------- ---- -------
home Disk Your Name
IPC$ IPC IPC Service ("Your Name")
Domain=[WORKGROUP] OS=[Windows 6.1] Server=[Samba 4.2.3]
Server Comment
------ -------
WorkGroup Master
--------- ------
- To access the Samba client shell on your local Samba share, issue the following command:
smbclient '\\127.0.0.1\home' -U <yourSenecaID> - Enter your Samba account password.
- Issue the help command to note common commands (dir, cd, ls, put, get). Note how similar they are to sftp commands.
- Enter exit to terminal your local Samba session.
Although you can use smbclient to access, browse and share files within other Linux and Windows servers, it is more practical to setup a Samba server to allow MS Windows Users to access a common file share on a Linux machine, and will be demonstrated in Investigation 2.
Record steps, commands, and your observations in INVESTIGATION 1 in your OPS335 lab log-book
INVESTIGATION 2: CONNECTING TO A LINUX SMB SERVER FROM A LINUX CLIENT
In this investigation you will explore some of the different ways to access a shared directory from a Linux client machine (VM1).
Perform the following steps on your VM1
Using smbclient
- Install the samba-client and cifs-utils packages.
- Use the "smbclient" command in a terminal window.
smbclient '\\vm2\home' -U <learnid>
- After entering your password you should get a prompt similar to
smb: \>
- Enter the ls command to see a list of the files in your home directory - you may receive the following error if you are in a section with SELinux Enforcing.
smb: \> ls NT_STATUS_ACCESS_DENIED listing \*
- If you received that error, SELinux will need to be adjusted (on the samba server) for this to work.
setsebool -P samba_enable_home_dirs 1
- Once you have access to the directory use the get and put commands (similar to ftp) to move files.
- When you are finished close the connection.
- Note that this tool only gave temporary access with a limited set of commands.
Using 'mount -t cifs'
- The next way is to use the mount command.
- Use the mount command on vm1 to mount your home directory
mkdir /tmp/vm2-home mount -t cifs //vm2/home /tmp/vm2-home -o username=<learnid> ls /tmp/vm2-home
- Create a file in that directory, then switch to vm2 to confirm that it was created.
- Use umount to unmount that directory.
- Note that this tool would leave the directory mounted until the machine rebooted or it was unmounted. It would also allow other users access to the directory, as it effectively became part of the local filesystem. It could even be added to fstab to be mounted on boot.
The following steps require a graphical interface; perform them on your HOST
- Install the samba-client and cifs-utils packages.
- Use the "Places" menu from the desktop and open 'Browse Network'.
- From the menu in the side-bar of the files tool, choose 'Connect to Server'.
- Enter 'smb://vm2/home' as the location, and enter your samba password in the prompt.
- Where vm2 is the name of the server, and home is the name of the directory it is sharing.
- After you have checked that you can access your files, unmount the share by right-clicking its icon in the side-bar and clicking 'Unmount'.
Using a browser
- You can also use a web browser with support for the SMB protocol such as Konqueror.
- Note that firefox does not have such support.
- If Konqueror is not installed then install it with the command:
yum install kdebase
- Start Konqueror, the web/file browser, and in the address bar enter the following
smb://vm2/home
- Enter your username and password when prompted.
- Double click on a file you have some text in.
- Open it with gedit, make some changes, and save it.
- When prompted, choose to upload the file.
- Close Konqueror.
- cat the file on your VM2 to ensure the changes were properly uploaded.
Record steps, commands, and your observations from this INVESTIGATION in your OPS335 lab log-book
INVESTIGATION 3: CONNECTING TO A SAMBA SERVER FROM A WINDOWS CLIENT
This investigation will configure your VM2 machine to act as a Samba File server to allow Windows OS Users access to the Linux Samba server files.
Accessing Files on a Linux Samba Server via Windows Explorer
With some additional "tweaking" to your Linux Samba server configuration file, you should be able to access files on that file from a Windows machine on the same network. You will be creating a Samba share for your home directory of your regular user account.
Perform the following tasks:
- Make certain that both your VM2 and Windows virtual machines are running.
- Power up a Windows system in the lab and login.
- Add the prerouting and forwarding rules to your host's iptables necessary to redirect samba traffic from outside your network to your VM 2.
- Open the Windows Explorer application.
- At the top of the application, enter the following:
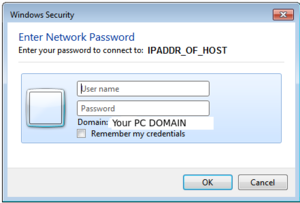
\\IPADDR_OF_HOST_MACHINE\home
- You will be prompted to enter your VM2 username and password (one time only). Refer to diagram on right.
NOTE: It may take approximately 30 seconds to display the file contents. - Where your successful? If not, try to troubleshoot the problem first, then ask your lab assistant or instructor for assistance.
- Close the Windows Explorer application window.
- Click on the START menu, and click on Computer.
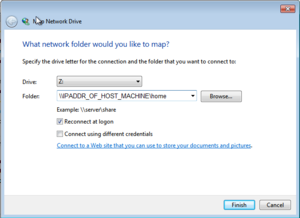
- Click on the Map Network Drive button, and create a mapped network drive (called it drive Z:) which is a Samba share of your VM2 machine for the home directory.
- When finished, click on Network in Windows file manager to confirm that the network share is present.
- Try to create a file on Windows on your Linux Samba machine. Were you able to create a save a file?
- Switch to your VM2 machine and check to see if that file was created in your home directory.
Record steps, commands, and your observations from this INVESTIGATION in your OPS335 lab log-book
COMPLETING THE LAB
In completing this lab you have gained experience using a service that allows remote access to files stored on a Linux server. You have also learned how to use several different tools to access those files, both from a Linux and Windows client..
Depending on your professor you will either be asked to submit the lab in class, or online. Follow the appropriate set of instructions below.
Online Submission
Follow the instructions for lab 6 on moodle.
In Class Submission
Arrange evidence (command output) for each of these items on your screen, then ask your instructor to review them and sign off on the lab's completion:
- ✓ Proof of network share of VM2 machine from Windows VM via Windows Explorer application
- ✓ Firewall settings on your Windows VM to allow Linux Samba network share
- ✓ Display contents of /etc/samba/smb.conf file on VM2 machine
- ✓ Firewall exceptions (both machines) to allow Samba traffic
- ✓ Lab logbook completed
EXPLORATION QUESTIONS
- What does SMB stand for?
- What does CIFS stand for?
- What is the purpose of the testparm command?
- What does the text inside square brackets in the smb.conf file mean? (e.g., "[home]").
- Explain the meaning of the line "create mask = 0765" in the smb.conf file?
- What does the smbpasswd command do?