Difference between revisions of "OPS335 Lab 4c"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Receiving Email = | = Receiving Email = | ||
| − | Last week, we configured and run the '''Postfix''' application (MTA a.k.a. SMTP server) on our '''VM2''' machine. We also installed and configured a graphical Mail User Agent (MUA) called Thunderbird to | + | Last week, we configured and run the '''Postfix''' application (MTA a.k.a. SMTP server) on our '''VM2''' machine. We also installed and configured a graphical Mail User Agent (MUA) called Thunderbird to test the connection to the running MTA by sending an email message to your myseneca address. |
| − | + | ||
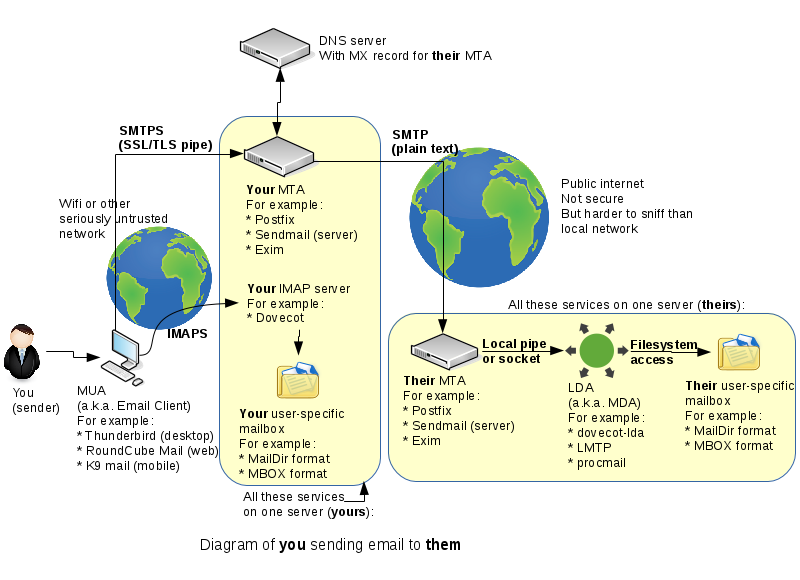
| + | The a diagram below (duplicate to lab 4b) shows your basic setup: | ||
[[Image:Email-servers.png]] | [[Image:Email-servers.png]] | ||
Revision as of 13:26, 11 March 2016
Contents
Receiving Email
Last week, we configured and run the Postfix application (MTA a.k.a. SMTP server) on our VM2 machine. We also installed and configured a graphical Mail User Agent (MUA) called Thunderbird to test the connection to the running MTA by sending an email message to your myseneca address.
The a diagram below (duplicate to lab 4b) shows your basic setup:
This week we'll set up a Postfix instance for receiving email on VM3.
We'll start with the same Postfix service, add an LDA (dovecot-lda) and test to make sure it works.
Finally we'll set up an IMAP server (Dovecot) so you can read your email from an MUA such as Thunderbird or a Webmail (we'll set up webmail in the Apache lab).
MX Record
If you haven't already done it - set up an MX record in your DNS server to make vm3.yoursenecaid.org the server responsible for receiving emails for anyuser@yoursenecaid.org (vm3 will be used for receiving, vm2 for sending only).
MTA for Receiving Email
Assigning Responsibility
The default job of an SMTP server is to forward the message recieved to another email server. That's what we've set up in the previous lab: your postfix receives an email from your client (Thunderbird) and forwards it to the destination SMTP server. The other thing an SMTP server can be configured to do is receive email. It still uses SMTP but instead of forwarding it to another SMTP server it will forward it to the Local Delivery Agent (LDA).
With postfix this is done by setting the mydestination configuration variable to include $mydomain (this is assuming you've set up mydomain, myorigin , and inet_interfaces the same way as in the previous lab).
Edit your /etc/postfix/main.cf file and scroll down to (or search for) mydestination. Set it up to look like this:
mydestination = $mydomain, $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost
Now even though your machine's name is vm2.yoursenecaid.org - your postfix will also receive emails for yoursenecaid.org
LDA
Postfix is capable of performing the function of an LDA but it has limited configurability, and is generally not used for that purpose. Currently the most popular LDA is LMTP but we'll use dovecot-lda because it's also pretty popular and we'll later be setting up Dovecot as an IMAP server. Using the two as a pair will increase the performance of your IMAP server.
Edit your /etc/postfix/main.cf file and scroll down to (or search for) mailbox_command. Add the following line:
mailbox_command = /usr/libexec/dovecot/dovecot-lda -f "$SENDER" -a "$RECIPIENT"
Don't replace any variables, those are set automatically by Postfix when it runs the LDA. If you're interested - you can read about dovecot-lda here and here but it's not required reading.
If you look - you'll see that dovecot-lda doesn't exist yet. Install the dovecot package - that will come with dovecot-lda.
Finally, edit /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf and set where you want your mail delivered:
mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir
Don't forget to restart your postfix service. dovecot-lda is just a program invoked by Postfix, it doesn't have an associated service.
Test
First use netstat and telnet to confirm your service is listening on the correct ports/interfaces. You will probably have to open the appropriate firewall port on vm3 to allow incoming SMTP connections.
If all worked so far - you should be able to send email to any regular user on vm3 using the email address yourusername@yoursenecaid.org using Thunderbird on vm2.
Create a new account on vm3 using only your first name. We'll use this one time for testing receiving email. It's rather important that you don't create this account on vm2 - so that you continue to see the difference between the sending and receiving SMTP servers.
We still haven't set up IMAP (for reading email) but we can test that the message is being delivered. Use the new account in Thunderbird to send an email to firstname@yoursenecaid.org and then check the contents of /home/firstname/Maildir/new/ on vm3. - there should be a file there with the contents of your email.
If there isn't one - check the log file /var/log/maillog to see what went wrong.
If you got it - this is a good time to stop and ponder how it all worked. You've gone through setting up a lot of services. Look at the diagram at the top of the page - which services have you set up?
Reading Email via IMAP
Finally we'll set up the IMAP server so we can read email. The way we've set it up - all the email for anyaccount@yoursenecaid.org should end up on vm3. We will set up Dovecot (with IMAP, IMAPS in a later lab) to get easy access to that email.
The configuration file for the Dovecot service (which is not the same thing as dovecot-lda) is /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf
Modify the protocols option so that Dovecot will work with IMAP connections, no POP3 or LMTP.
Use netstat to confirm the service is listening, and use telnet on the host to confirm you can connect to it.
If you can connect - it's now time to do something wrong, that is connect to our IMAP server using Thunderbird over an unencrypted connection. Edit /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf and set disable_plaintext_auth to no. Then edit /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-ssl.conf and set ssl to yes. This combination of parameters will allow your username and password to be sent over the internet in plain text, for anyone interested to look at. In the following lab we'll set up secure SMTP and IMAP connections, for now this is all we have time for.
To try connect to your IMAP server with Thunderbird - click on your Inbox. If nothing seems to happen - check the Thunderbird Activity Manager for any errors. If the connection is successful - you should see a Trash show up below Inbox.
Finally - send an email from yoursenecaid@yoursenecaid.org to yoursenecaid@yoursenecaid.org using Thunderbird. The message should go out without errors, you should see a Sent folder appear in the list, and you should see your message arrive in the inbox. If all that happend - your setup is correct.
Completing the Lab
Students should be prepared with all required commands (system information) displayed in a terminal (or multiple terminals) prior to calling the instructor for signoff.
Arrange evidence (command output) for each of these items on your screen, then ask your instructor to review them and sign off on the lab's completion:
- ✓Thunderbird with a message sent and received.
- ✓Thunderbird server configuration for your account.
- ✓Logs on vm2 and vm3 showing the message has been sent and received.