Difference between revisions of "OPS235 Lab 1 - CentOS7"
| Line 243: | Line 243: | ||
#You may have learned about creating and running Bash Shell Scripts in your ULI101 course. Shell scripts help Linux users and system administrators to automatic repetitive tasks to become more efficient and to help them save time. | #You may have learned about creating and running Bash Shell Scripts in your ULI101 course. Shell scripts help Linux users and system administrators to automatic repetitive tasks to become more efficient and to help them save time. | ||
| − | #The <b><code>wget</code></b> command can be used to quickly download files from the Internet. Issue the following command:<br><br><b><code>wget https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/text-report.bash</code></b><br><br> | + | #The <b><code>wget</code></b> command can be used to quickly download files from the Internet. Issue the following command:<br><br><b><code>wget <span style=" pointer-events: none;cursor: default;color:black;">https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/text-report.bash</span></code></b><br><br> |
#Verify that the file '''text-report.bash''' was downloaded to your current directory. | #Verify that the file '''text-report.bash''' was downloaded to your current directory. | ||
#Assign read and execute permissions for this file by issuing the command: <b><code>chmod u+rx text-report.bash</code></b> | #Assign read and execute permissions for this file by issuing the command: <b><code>chmod u+rx text-report.bash</code></b> | ||
| Line 249: | Line 249: | ||
#Check to see if it created a report in your current directory. What is the purpose of the report? | #Check to see if it created a report in your current directory. What is the purpose of the report? | ||
#Use the <b>vi</b> text editor to view the contents of the file <b>text-report.bash</b>. Can you understand how this script works?<br><br> | #Use the <b>vi</b> text editor to view the contents of the file <b>text-report.bash</b>. Can you understand how this script works?<br><br> | ||
| − | #Use the <b><code>wget</code></b> command to download, study, and run the following shell scripts on-line:<ul><li style=" pointer-events: none;cursor: default;color:black;">https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/report.bash</li><li >https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/report3.bash</li></ul><br><br> | + | #Use the <b><code>wget</code></b> command to download, study, and run the following shell scripts on-line:<ul><li style=" pointer-events: none;cursor: default;color:black;">https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/report.bash</li><li style=" pointer-events: none;cursor: default;color:black;" >https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/report3.bash</li></ul><br><br> |
#Try to understand what these Bash Shell scripts do. | #Try to understand what these Bash Shell scripts do. | ||
#You have completed lab1. Proceed to Completing The Lab, and follow the instructions for "lab sign-off". | #You have completed lab1. Proceed to Completing The Lab, and follow the instructions for "lab sign-off". | ||
Revision as of 18:02, 27 March 2015
Contents
LAB PREPARATION
Purpose / Objectives of Lab 1
You need to install a Linux OS to be a host or "platform" to install and use other Linux VMs (Virtual Machines) during this course.
The Linux OS you will be installing in this lab will be a Host Machine (hostname: c7host) that will allow you to run Virtualization Software to create 3 separate virtual machines (to be performed in lab2). It is important to install this host machine correctly since other labs will depend on the stability of this host machine.
Main objectives:
- Correctly install the CentOS 7 FULL INSTALL DVD (not LIVE DVD) on your removable hard disk.
- Record installation characteristics of CentOS 7 FULL INSTALL in a chart (contained in lab2 logbook chart) to compare with other installation methods performed in lab2.
- Verify correct settings prior to proceeding with host installation stages.
- Obtain Linux server information after installation to create a software asset report for later access.
- Disable Linux Kernel security enhancements to allow easier internal networking connections (to be reactivated in a later lab).
- Observe that Bash Shell Scripts can automate routine tasks.
Required Materials / Lab Preparation
My Toolkit (CLI Reference)
| Package Management | System Information | Networking | Miscellaneous
grep
|
INVESTIGATION 1: CREATE HOST MACHINE (c7host)
For the next 3 investigations, you will learn how to install your Centos Full DVD onto your removable hard disk. You will customize your install to setup several separate partitions: root (/), /home, /var/lib/libvirt/images (to store virtual machine images to be created in lab2), and a swap partition.
Make certain to record your observations of this install in the comparison chart for c7host in your lab2 logbook.
Part 1: Start Installation
|
Part 2: Custom Partitioning
|
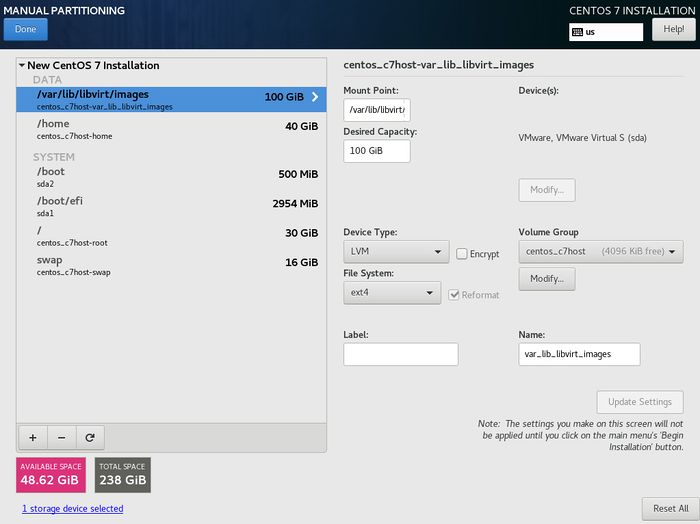 Carefully verify partition mount-names and sizes prior to proceeding with install. Check installation screenshots link for verification. |
Part 3: Completing the Installation
- During the installation process, you will required to create a root password (for administration access) and create a regular user account. Click on Root Password and enter your root password. Think of an appropriate password and record that password somewhere in case you forget! An indicator will appear to show you how secure your password is. Retype your root password and click Done (you may have to click Done twice if your password is strong).
- You need to create a regular user account. This account will be used to graphical log into your host machine. It is never recommended to graphically log into a graphical Linux/Unix system as root. It is better to log into a regualr user account, then run a command to login as root (you will learn how to do this later in this lab.
- Click User Creation and enter your full name, username, and an appropriate password (and confirm password). Click Done to finish.
- Remember to record this host installation information in the comparison chart in lab2.
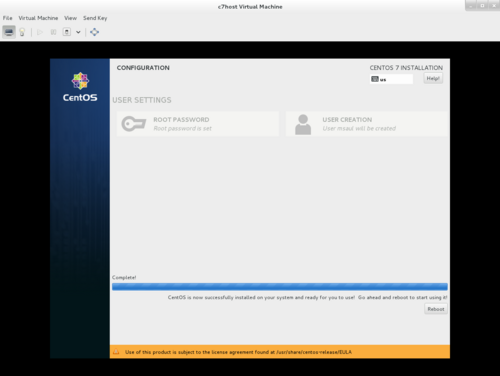
- When installation is complete, you will notice a message at the bottom of the screen stating: CentOS is now successfully installed and ready for you to use!
- Click the Reboot button. Your DVD will briefly open in the DVD drive bay. Make certain to remove this installation DVD so that Centos will boot from your hard drive.
- After the system reboots, login by clicking on your account name and entering the regular user password.
- The last phase of the installation process should now run:
- Click Accept to confirm you will abide by the License and click Done.
- Accept defaults to participate running KDump application that will report errors to developers for improvements to Centos7.
- Select English as the default input source.
- Quickly view Getting Started Resources, then close the help window.
- Proceed to Investigation 2 to obtain basic information from your newly installed Centos Host machine.
Answer Investigation 1 observations (all parts and questions) in your lab log book.
INVESTIGATION 2: OBTAINING HOST MACHINE SYSTEM INFORMATION
Part 1: Obtaining Package Management / Package Information
|
Navigate through your Graphical CentOS system, locate and run a terminal program (in order to issue Linux commands). Issue and record the commands used and the output generated in each of the following steps:
|
Part2: Obtaining System Information
|
Answer the Investigation 2 observations / questions in your lab log book.
Part3: Obtaining Network Information
- Your system may not be automatically connected to Seneca's network. Locate the network icon (on top right-hand panel). Click on that icon, and select: system eth0
- Open a web-browser and log into Seneca's wired network. You will need to perform this set every time you start a new session with your computer to perform future labs.
- Open a shell terminal.
- To check the network configuration settings obtained from the DHCP server, run the following commands, describing the output in your log book:
- ifconfig
- route -n
- nslookup (at the > prompt, enter the word "server" (do not type the quotes) and record the output. Type exit to leave nslookup).
- Find the following information in the output of the above commands:
- MAC address of the ethernet network interface
- Subnet mask
- The IP address assigned to you by the DHCP server
- The default gateway
- The DNS nameserver
Answer the Investigation 3 observations / questions in your lab log book.
INVESTIGATION 3: LOOKING AHEAD
Part 1: Disable SELinux and Perform Software Updates
|
Part 2: Automating Routine Tasks (Shell Scripting)
- You may have learned about creating and running Bash Shell Scripts in your ULI101 course. Shell scripts help Linux users and system administrators to automatic repetitive tasks to become more efficient and to help them save time.
- The
wgetcommand can be used to quickly download files from the Internet. Issue the following command:wget https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/text-report.bash - Verify that the file text-report.bash was downloaded to your current directory.
- Assign read and execute permissions for this file by issuing the command:
chmod u+rx text-report.bash - Run this Bash Shell script by issuing the command:
./text-report.bash - Check to see if it created a report in your current directory. What is the purpose of the report?
- Use the vi text editor to view the contents of the file text-report.bash. Can you understand how this script works?
- Use the
wgetcommand to download, study, and run the following shell scripts on-line:- https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/report.bash
- https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/report3.bash
- Try to understand what these Bash Shell scripts do.
- You have completed lab1. Proceed to Completing The Lab, and follow the instructions for "lab sign-off".
COMPLETING THE LAB / INSTRUCTOR SIGN-OFF
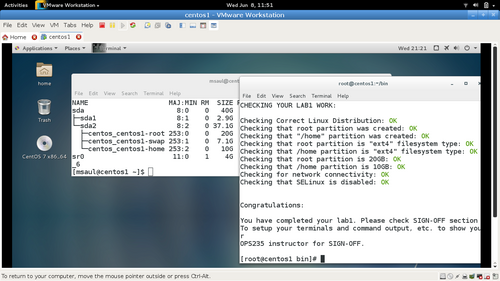
Arrange evidence (command output) for each of these items on your screen, then ask your instructor to review them and sign off on the lab's completion:
- Installed package count
- Output of lsblk command showing correct partition names and sizes
- Correct IP address and MAC address
- Default route (gateway)
- DNS name server IP Address
- lab1 notes and first column of Comparison Chart in lab2.
ADDITIONAL PRACTICE
- How many packages were installed?
- How many files (correct to the nearest hundred) were installed?
- How many users were created automatically on your system (do not count your learn account)?
- What is your learn account's UID and GID?
- What is your learn account's home directory?
- What is the home directory for the user "root"?
- How do you determine the host name of your GNU/Linux workstation?
- What command can display the NIC's MAC address?