Difference between revisions of "OPS235 Lab 2"
(→Part 2: Installing from a Network (Minimal install - CLI)) |
|||
| (147 intermediate revisions by 7 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
= LAB PREPARATION = | = LAB PREPARATION = | ||
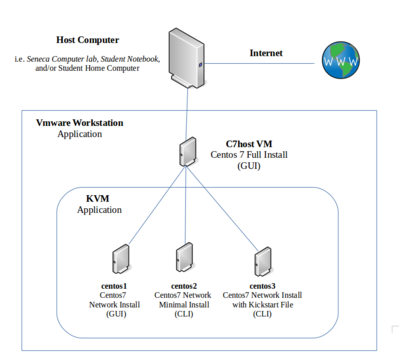
[[Image:vmware-1a.png|thumb|right|400px|At the end of lab2, your VMware Workstation application will contain '''4 virtual machines''' ('''c7host''' in your '''VMware Workstation''' application, and '''centos1, centos2, centos3 VMs''' in your '''KVM''' application). You will now have the option to run one virtual machine at a time, or run all machines simultaneously to learn about networking (covered in later labs) ]] | [[Image:vmware-1a.png|thumb|right|400px|At the end of lab2, your VMware Workstation application will contain '''4 virtual machines''' ('''c7host''' in your '''VMware Workstation''' application, and '''centos1, centos2, centos3 VMs''' in your '''KVM''' application). You will now have the option to run one virtual machine at a time, or run all machines simultaneously to learn about networking (covered in later labs) ]] | ||
| − | === Purpose / Objectives of | + | === Purpose / Objectives of Lab 2=== |
| − | In this lab, you will create 3 remaining virtual machines using another virtualization program called KVM that will run in your c7host VM. These VMs will be used throughout the remainder of this course to learn how to administer them (installing software, managing services, networking, etc). | + | In this lab, you will create 3 remaining virtual machines using another virtualization program called '''KVM''' that will run in your c7host VM. These VMs will be used throughout the remainder of this course to learn how to administer them (installing software, managing services, networking, etc). |
While you are performing this lab, it is recommended to generally note the major differences in the different installation methods, and which method you prefer to use if you were a Linux system administrator in charge of installing many Linux distributions for an organization. | While you are performing this lab, it is recommended to generally note the major differences in the different installation methods, and which method you prefer to use if you were a Linux system administrator in charge of installing many Linux distributions for an organization. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<u>Main Objectives</u> | <u>Main Objectives</u> | ||
* Installing additional Virtualization Software on your '''c7host''' machine ('''KVM''') | * Installing additional Virtualization Software on your '''c7host''' machine ('''KVM''') | ||
* '''Create 3 separate VMs (virtual machines) using different installation methods:''' | * '''Create 3 separate VMs (virtual machines) using different installation methods:''' | ||
| − | :* Network | + | :* '''centos1''': Network CentOS Installation ('''Graphical''') |
| − | :* Network | + | :* '''centos2''': Network CentOS Installation (minimal install - '''CLI only''') |
| − | :* Network | + | :* '''centos3''': Network CentOS Installation with Kickstart configuration file ('''CLI only''') |
* Manipulate virtual machines by CLI ('''virsh''') | * Manipulate virtual machines by CLI ('''virsh''') | ||
* Properly '''backup VM images''' and backup '''VM configuration files''' | * Properly '''backup VM images''' and backup '''VM configuration files''' | ||
| Line 50: | Line 45: | ||
|valign="top" style="padding-left:20px;"| | |valign="top" style="padding-left:20px;"| | ||
Miscellaneous<br> | Miscellaneous<br> | ||
| − | [http:// | + | [http://linuxcommand.org/lc3_man_pages/gzip1.html gzip , gunzip]<br> |
| − | [http:// | + | [http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man8/ip.8.html ip]<br> |
| + | [http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/grep.1.html grep]<br> | ||
[http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/wc.1.html wc]<br> | [http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/wc.1.html wc]<br> | ||
[http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/pwd.1.html pwd]<br> | [http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/pwd.1.html pwd]<br> | ||
| Line 60: | Line 56: | ||
[http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/chmod.1.html chmod]<br> | [http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/chmod.1.html chmod]<br> | ||
[http://ss64.com/vi.html vi] | [http://ss64.com/vi.html vi] | ||
| − | |valign="top" style="padding-left:20px;"|Matrix Online Tutorials:<br><ul><li>Shell Scripting - Part 2 (Logic & Math Expressions):<br>'''/home/ | + | |valign="top" style="padding-left:20px;"|Matrix Online Tutorials:<br><ul><li>Shell Scripting - Part 2 (Logic & Math Expressions):<br>'''/home/ops235/scripting-2'''</li><li>Shell Scripting - Part 3 (Loops)<br>'''/home/ops235/scripting-3'''</li></ul> |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 66: | Line 62: | ||
=INVESTIGATION 1: SETUP FOR NESTED VIRTUAL MACHINES= | =INVESTIGATION 1: SETUP FOR NESTED VIRTUAL MACHINES= | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Part 1: Install KVM Virtualization Application=== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
We will now install the KVM package in order to create our remaining "nested" VMs. We will also be starting several services (including iptables) and disabling the firewalld service. We will learn more about managing firewalls using iptables in lab6. | We will now install the KVM package in order to create our remaining "nested" VMs. We will also be starting several services (including iptables) and disabling the firewalld service. We will learn more about managing firewalls using iptables in lab6. | ||
| Line 95: | Line 69: | ||
:'''Perform the following steps:''' | :'''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
| − | # | + | # Log into your c7host machine, and switch to root user. |
| − | + | # perform a software update on your '''c7host''' VM by issuing the following command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">yum update</span></code></b> | |
| − | # | + | |
| − | + | {{Admon/important |Yum Update Hangs|If you experience yum update "hanging" around item 689 of over 1200 packages, issue the following commands <b>(in a new terminal!)</b>:<br><source>pkill systemctl | |
| − | + | yum clean all | |
| + | yum update | ||
| + | </source>'''NOTE:''' Do NOT press '''<ctrl>c''' since it may cause your machine to cause a kernel panic when you restart your machine.}} | ||
| − | + | <ol><li value="3">As root, install the virtualization software by issuing the command:<br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python \<br>libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils</span></code></b> <br><br></li> | |
| − | < | + | <li>'''Restart your c7host virtual machine'''. If you fail to do this, you may experience virtualization network problems. |
| − | + | {| width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | |
| − | + | |- valign="top" | |
| − | < | + | | |
| + | {{Admon/note|About KVM|There are actually several key programs installed for virtualization using KVM:<ul><li>'''kvm/qemu''' - the hypervisor and other hardware emulation systems.</li><li>A system service named '''libvirtd''' that manages the VMs.</li><li>A graphical tool for managing virtual machines ('''virt-manager''') and the '''virsh''' command-line tool.</li></ul>}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </li><li>Start the virtualization service: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">systemctl start libvirtd</span></code></b><br><br>'''NOTE:''' The most recent variants of CentOS and Fedora are using a service called '''firewalld''' that is intended to replace '''iptables''', however the ''iptables'' service is still in relatively common usage. In this course we will concentrate on ''iptables''.<br><br></li> | ||
| + | <li>To disable and remove firewalld, issue the following commands:<br> | ||
<b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">systemctl disable firewalld</span></code></b><br> | <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">systemctl disable firewalld</span></code></b><br> | ||
<b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">systemctl stop firewalld</span></code></b><br> | <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">systemctl stop firewalld</span></code></b><br> | ||
| + | <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">yum remove firewalld</span></code></b><br> | ||
<br></li> | <br></li> | ||
<li>To install and enable the IPTables services, issue the following commands:<br> | <li>To install and enable the IPTables services, issue the following commands:<br> | ||
| Line 117: | Line 98: | ||
{{Admon/important|Run virt-manager as a regular user, not as root|Otherwise all your virtual machines will be owned by root and you won't be able to use them as a regular user.}} | {{Admon/important|Run virt-manager as a regular user, not as root|Otherwise all your virtual machines will be owned by root and you won't be able to use them as a regular user.}} | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
| − | <li value=" | + | <li value="8">Start the graphical tool by selecting the menu options '''Applications'''>'''System Tools'''>'''Virtual Machine Manager''' or by typing the command<b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;"> virt-manager</span></code></b></li> |
| − | <li>You will be learning to perform several different | + | <li>You will be learning in the next investigation to perform several different types of CentOS Linux installs.</li> |
| − | <li> | + | </ol> |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Part 2: Configure VMware Workstation for Nested VMs === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Although we are using VMware Workstation to run our c7host VM, we will now install and configure another virtualization package called KVM in order to install the remaining VMs for this course. | ||
| + | Since we are "nesting" VMs (i.e. running a VM inside another VM) we need to configure our c7host's Linux boot-up parameters in order to allow these VMs to run efficiently. | ||
| + | |||
| + | :'''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | # In a terminal as the root user, edit the file called: '''/boot/efi/EFI/centos/grub.cfg'''<ul><li>'''If this file doesn't exist, double-check your UEFI settings in VMWare Workstation for c7host. If BIOS is selected, <u>you MUST redo Lab 1</u>.'''</li></ul> | ||
| + | # Search for the <b>first occurrence</b> of the Linux Kernel boot command. Do not make the following changes on more than one entry! | ||
| + | # Insert the boot option: '''kvm-intel.nested=1''' at the end of the Linux kernel boot options. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | {{Admon/important|About the reference settings shown below| | ||
| + | * Only '''ONE''' of these settings might be applicable. | ||
| + | * Enter '''JUST''' the text highlighted in '''BLUE''' as your kernel version, root, and LVM settings might vary slightly.}} | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <blockquote><code style="font-family:courier;font-size:1.2em;margin-left:20px;"> | ||
| + | <br>linuxefi /vmlinuz-3.10.0-1062.1.2.el7.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/centos_c7host-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=centos_c7host/root rd.lvm.lv=centos_c7host/swap rhgb quiet LANG=en_CA.UTF-8 <span style="color:blue;font-weight:bold">kvm-intel.nested=1</span> | ||
| + | <br> initrdefi /initramfs-3.10.0-1062.1.2.el7.x86_64.img | ||
| + | </code></blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="color:red;font-weight:bold">OR</span> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <blockquote><code style="font-family:courier;font-size:1.2em;margin-left:20px;"> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | linuxefi /boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-1062.el7.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/centos_c7host-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=centos_c7host/root rd.lvm.lv=centos_c7host/swap rhgb quiet LANG=en_CA.UTF-8 <span style="color:blue;font-weight:bold">kvm-intel.nested=1</span><br>initrdefi /boot/initramfs-3.10.0-1062.el7.x86_64.img | ||
| + | </code></blockquote> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ol><li value="4">Save your editing changes, close the virtual machine application, and <u>'''reboot'''</u> your c7host VM.</li> | ||
| + | <li>If you configured your c7host VM for nested VMs, then you should get the output <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">Y</span></code></b> when you issue the following command:<br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/nested</span></code></b></li><ul><li>For '''AMD''' processors, check the /sys/module/'''kvm_amd'''/parameters/nested file.</li></ul> | ||
| + | <ul><li>And if kvm_intel directory doesn't exist, double-check your '''Processors => Virtualization Engine (Intel VT-x/EPT...)''' settings in VMWare Workstation.</li></ul> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| + | |||
'''Answer the INVESTIGATION 1 observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | '''Answer the INVESTIGATION 1 observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | ||
| + | =INVESTIGATION 2: INSTALL NESTED VIRTUAL MACHINES (KVM)= | ||
| − | = | + | {|width="50%" cellspacing="0" |
| + | |||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | |{{Admon/important|Keep the root password the same for Host and VMs|In order to simplify running the lab checking scripts in future labs, using the same root password for ALL machines (c7host and virtual machines). Also use the same username and passwords for all of your machines (c7host and virtual machines).}}<br><br> | ||
| + | |} | ||
=== Part 1: Installing VM from a Network (Graphical)=== | === Part 1: Installing VM from a Network (Graphical)=== | ||
| Line 133: | Line 154: | ||
:: '''VM Name (and hostname):''' centos1 | :: '''VM Name (and hostname):''' centos1 | ||
:: '''Boot media:''' Network installation | :: '''Boot media:''' Network installation | ||
| − | :: ''' | + | :: '''CentOS Full Network Install URL:''' |
| − | :::*Seneca Lab: | + | :::*Seneca Lab: https://mirror.senecacollege.ca/centos/7/os/x86_64/ |
| − | :::*Home: http://mirror. | + | :::*Home: http://mirror.netflash.net/centos/7/os/x86_64/ |
:: '''VM Image Pathname:''' /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos1.qcow2 | :: '''VM Image Pathname:''' /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos1.qcow2 | ||
:: '''Memory:''' 2048MB | :: '''Memory:''' 2048MB | ||
:: '''Disk space:''' 15GB | :: '''Disk space:''' 15GB | ||
| − | :: '''CPUs:''' | + | :: '''CPUs:''' 2 |
| + | |||
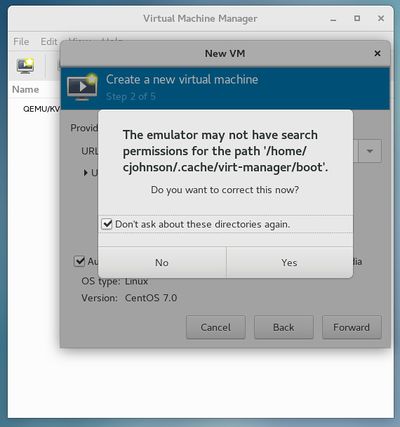
| + | [[Image:Kvm-warning.jpg|thumb|right|400px|You may see this warning when creating your first VM inside CentOS. Select''' ''Don't ask me about these directories again'' '''and click''' ''Yes'''''.]] | ||
:'''Perform the following steps:''' | :'''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
# Launch the ''KVM virtual machine manager'' by clicking '''Applications''' -> '''System Tools''' -> '''Virtual Machine Manager'''. | # Launch the ''KVM virtual machine manager'' by clicking '''Applications''' -> '''System Tools''' -> '''Virtual Machine Manager'''. | ||
| − | # When prompted, enter your root password. | + | # When prompted, enter your '''root''' password. |
| − | # Click | + | # Click the '''create a new VM icon''' located near the top left-corner of the application window. |
| − | # Select the Network Install option and click '''Forward'''. | + | # Select the '''Network Install''' option and click '''Forward'''. |
# Enter (copy and paste) the URL located at the top of this section (depending whether you are at Seneca College or not) and click '''Forward'''. | # Enter (copy and paste) the URL located at the top of this section (depending whether you are at Seneca College or not) and click '''Forward'''. | ||
# Set RAM size to 2048 MB and click '''Forward'''. | # Set RAM size to 2048 MB and click '''Forward'''. | ||
# Set Hard Disk size to 15GB and click '''Forward'''. | # Set Hard Disk size to 15GB and click '''Forward'''. | ||
| − | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Enter the name: '''centos1''', select the option: '''Customize configuration before install''', and click '''Finish'''.</span> | + | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Enter the name: '''centos1''', <u>AND</u> then select the option: '''Customize configuration before install''', and click '''Finish'''.</span> |
| − | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Another dialog will appear. Click ''' | + | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Another dialog will appear. Click '''CPUs''' (or "processors") and on right-side under Configuration select '''Copy Host CPU Configuration''', click '''Apply''', and then click '''Begin Installation''' at the top left-hand side.</span> |
| − | #<span style="background-color:yellow;">During the install, select '''Gnome Desktop''' software selection), | + | #<span style="background-color:yellow;">During the install, select '''Gnome Desktop''' software selection). For partitioning, select '''I will configure partition settings''', click done, then select '''Click here to create them automatically'''. Set the / partition for '''ext4''' file-system type, and click '''Done'''.</span> |
| − | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Complete the installation. Login to your regular user account, and perform a '''yum update''' for the | + | #<span style="background-color:yellow;">Set the correct '''Date and Time Zone''', and then click on '''Network and Hostname'''. The network should be turned on. For hostname, enter: '''centos1''' and then click '''Done'''.</span> |
| − | + | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Complete the installation. Login to your regular user account, switch to the root user with <b>su -</b>, and perform a '''yum update''' for the centos1 VM (reboot if required). Make certain to adjust your screen-saver settings if desired.</span> | |
| − | # Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations in your lab2 logbook. | + | <br> |
| − | + | {{Admon/important|Use same root password / regular username / regular user passwords for c7host and ALL VMs|To simplify the lab checking process make certain that you use the identical root password, regular username, and regular username password for VMs that you create in this labs as you did for c7host machine in lab1.<br><br>}} | |
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | <ol><li value="13"><span style="background-color:yellow;">Repeat the steps as you did in the previous investigation ([https://wiki.cdot.senecacollege.ca/wiki/OPS235_Lab_2#Part_1:_Install_KVM_Virtualization_Application Investigation1 Part 1]) to '''stop and disable firewalld, install iptables-services, start and enable iptables''' for this newly-created VM.</span></li> | ||
| + | <li><span style="background-color:yellow;">Repeat the steps as you did with c7host post-install to '''disable SELinux''' and perform a '''yum update'''.</span></li> | ||
| + | <li>Issue the following command to obtain the IPADDR for your centos1 VM to record in your lab2 logbook: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">ifconfig</span></code></b></li> | ||
| + | <li>Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations in your lab2 logbook.</li> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| − | === Part 2: Installing from a Network === | + | === Part 2: Installing from a Network (Minimal install - CLI) === |
:'''VM Details:''' | :'''VM Details:''' | ||
| Line 165: | Line 193: | ||
:: '''VM Name (and hostname):''' centos2 | :: '''VM Name (and hostname):''' centos2 | ||
:: '''Boot media:''' Network installation | :: '''Boot media:''' Network installation | ||
| − | :: ''' | + | :: '''CentOS Full Network Install URL:''' |
| − | :::*Seneca Lab: | + | :::*Seneca Lab: https://mirror.senecacollege.ca/centos/7/os/x86_64/ |
| − | :::*Home: http://mirror. | + | :::*Home: http://mirror.netflash.net/centos/7/os/x86_64/ |
:: '''VM Image Pathname:''' /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos2.qcow2 | :: '''VM Image Pathname:''' /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos2.qcow2 | ||
:: '''Memory:''' 2048MB | :: '''Memory:''' 2048MB | ||
| Line 175: | Line 203: | ||
:'''Perform the following steps:''' | :'''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
| − | # Create the VM (called '''centos2''') as you did with the ''centos1'' machine, | + | # Create the VM (called '''centos2''') as you did with the ''centos1'' machine. |
| − | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Complete the installation. Login to your regular user account | + | # Make certain to enter the name: '''centos2''', <u>AND</u> then select the option: '''Customize configuration before install''', and select '''Copy Host CPU Configuration''', click '''Apply''', and then click '''Begin Installation'''. |
| − | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Repeat the steps as you did to ''' | + | #When selecting the install options for centos2, do the same operation that you did in centos1 (but with '''Minimal Install''' software selection instead), but after '''automatically creating the partitions''', reduce the size of the root logical volume to '''8 GiB''' and add a logical volume with a size of '''2 GiB''' (mount point: '''/home''', name: '''home''', and make certain root and /home logical volumes have '''ext4''' file system).<br><br> |
| + | |||
| + | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Complete the installation. Login to your regular user account.</span> | ||
| + | #<span style="background-color:yellow;">Repeat the steps as you did in the previous investigation ([https://wiki.cdot.senecacollege.ca/wiki/OPS235_Lab_2#Part_1:_Install_KVM_Virtualization_Application Investigation1 Part 1]) to '''stop and disable firewalld, install iptables-services, start and enable iptables''' for this newly-created VM.</span> | ||
| + | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Repeat the steps as you did with c7host post-install to '''disable SELinux''' (using the command 'vi' instead of 'vim') and perform a '''yum update'''.</span> | ||
| + | # The ifconfig command is not available in centos2. Issue the following command to obtain and record your centos2 IPADDR in your lab2 logbook: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">ip address</span></code></b> | ||
# Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations in your lab2 logbook. | # Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations in your lab2 logbook. | ||
| − | |||
=== Part 3: Installing from a Network using a Kickstart File === | === Part 3: Installing from a Network using a Kickstart File === | ||
| Line 187: | Line 219: | ||
:: '''VM Name (and hostname):''' centos3 | :: '''VM Name (and hostname):''' centos3 | ||
:: '''Boot media:''' Network installation | :: '''Boot media:''' Network installation | ||
| − | :: ''' | + | :: '''CentOS 7 Full Install Network URL:''' |
| − | :::*Seneca Lab: | + | :::*Seneca Lab: https://mirror.senecacollege.ca/centos/7/os/x86_64/ |
| − | :::*Home: http://mirror. | + | :::*Home: http://mirror.netflash.net/centos/7/os/x86_64/ |
| − | :: '''Kickstart File URL:''' | + | :: '''Kickstart File URL (Kernel options): ''' |
| + | :::* Seneca Lab:''' <span style="color:green;font-weight:bold">ks=</span>https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/centos7-kickstart.cfg | ||
| + | :::* Home:''' <span style="color:green;font-weight:bold">ks=</span>https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/centos7-kickstart-ext.cfg | ||
:: '''VM Image Pathname:''' /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos3.qcow2 | :: '''VM Image Pathname:''' /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos3.qcow2 | ||
| − | :: '''Memory:''' 2048MB | + | :: '''Memory:''' 2048MB ('''IMPORTANT''' Do not use less than 2048MB during installation.) |
:: '''Disk space:''' 15GB | :: '''Disk space:''' 15GB | ||
| − | :: '''CPUs:''' | + | :: '''CPUs:''' 2 |
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | {{Admon/important|Include ''ks='' in the URL options field!|When using a kickstart file, make sure you include the''' ''ks='' '''portion of the link. If done correctly, you should not be able to select partitions or any other settings.}} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
:'''Perform the following steps:''' | :'''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
| − | # Create the VM | + | # Create the VM (called '''centos3''') |
| + | # During the install, copy the network URL, then click the '''URL options''' to expand the '''kernel options''' input textbox. Type the following in the kernel options textbox: <ul><li>Seneca Lab:''' <span style="color:green;font-weight:bold">ks=</span>https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/centos7-kickstart.cfg</li><li>'''Home:''' <span style="color:green;font-weight:bold">ks=</span>https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/centos7-kickstart-ext.cfg</li></ul> | ||
| + | # Then click the '''forward''' button to proceed. Make certain to select the correct Memory Size and Disk Space size shown in the VM Details above | ||
| + | # Make certain to enter the name: '''centos3''', <u>AND</u> then select the option: '''Customize configuration before install''', and select '''Copy Host CPU Configuration''', click '''Apply''', and then click '''Begin Installation'''. | ||
# Observe the installation. How is it different from booting from a downloaded image? | # Observe the installation. How is it different from booting from a downloaded image? | ||
| − | # Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations.<br><br>If | + | # Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations.<br><br>If during the installation, you see the message at the bottom '''Pane is Dead''', click the '''Virtual Machine''' menu at the top, select '''Shut Down''' -> '''Force Off''', '''right-click''' on '''centos3''' in the ''virtual manager'' window and select '''Delete'''. Redo the VM setup for a new instance of the ''centos3'' VM.<br><br> |
# What happens when the installation is finished? | # What happens when the installation is finished? | ||
| − | # | + | # '''In a web browser''', click the kickstart (KS) link above. This link is a text file. Read through it to find the following information (pay attention to lines starting with #) and record it in your Lab Logbook:<ul><li>'''Regular-user account name'''</li><li>'''Regular-user account password'''</li><li>'''Root Password'''</li></ul> |
# Boot the virtual machine and log in (use the user ID and password information from the previous step to gain access to this VM). | # Boot the virtual machine and log in (use the user ID and password information from the previous step to gain access to this VM). | ||
# Compare the experience to the first time you booted the other virtual machines. | # Compare the experience to the first time you booted the other virtual machines. | ||
| − | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Repeat the steps as you did to ''' | + | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Repeat the steps as you did in the previous investigation ([https://wiki.cdot.senecacollege.ca/wiki/OPS235_Lab_2#Part_1:_Install_KVM_Virtualization_Application Investigation1 Part 1]) to '''stop and disable firewalld, install iptables-services, start and enable iptables''' for this newly-created VM.</span> |
| + | # <span style="background-color:yellow;">Repeat the steps as you did with c7host post-install to '''disable SELinux''' and perform a '''yum update'''.</span> | ||
| + | # The ifconfig command may not be available in centos3. Issue the following command to obtain and record your centos2 IPADDR in your lab2 logbook: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">ip address</span></code></b> | ||
# Remember that centos3 is text-based interface only (no graphics). To recover from a blank screen, press a key (like the SPACE key) to return to the screen display. | # Remember that centos3 is text-based interface only (no graphics). To recover from a blank screen, press a key (like the SPACE key) to return to the screen display. | ||
# Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations in your lab2 logbook. | # Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations in your lab2 logbook. | ||
| Line 212: | Line 253: | ||
'''Answer the INVESTIGATION 2 observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | '''Answer the INVESTIGATION 2 observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | ||
| − | + | =INVESTIGATION 3: MANAGING VIRTUAL MACHINES (KVM)= | |
| − | =INVESTIGATION | ||
| Line 224: | Line 264: | ||
:'''Perform the following steps:''' | :'''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
| − | # Shut down your '''centos1''', '''centos2''', and '''centos3''' VMs. | + | # Shut down your '''centos1''', '''centos2''', and '''centos3''' VMs. For ''centos2'' and ''centos3'', which are CLI-only, you can issue the following command as root to shutdown: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">shutdown -h</span></code></b>. Please be patient, the VMs will shut down! |
| − | # In your '''c7host''' VM, | + | # In your '''c7host''' VM, open a new Terminal window, and '''switch to the root account ''inside'' the terminal'''. |
| − | # Make a compressed backup of | + | # Change to the images directory by issuing the command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">cd /var/lib/libvirt/images/</span></code></b><ul><li>Note the size of the files in this directory. What do these files contain?</li></ul> |
| − | + | # Make a compressed backup of your '''centos1.qcow2''', '''centos2.qcow2''', and '''centos3.qcow2''' files to your regular user's home directory by issuing each command (one at a time):<br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">gzip < centos1.qcow2 > ~YourRegularUsername/centos1.qcow2.backup.gz</span></code></b><br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">gzip < centos2.qcow2 > ~YourRegularUsername/centos2.qcow2.backup.gz</span></code></b><br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">gzip < centos3.qcow2 > ~YourRegularUsername/centos3.qcow2.backup.gz</span></code></b><ul>'''NOTE:''' Make certain to use the redirection signs "<" and ">" properly in the command!</ul> | |
| − | + | {{Admon/important |Please be patient|It may look like the command prompt is stuck but it could take a while for gzip to compress an entire operating system. '''NOTE:''' Do NOT press '''<ctrl>c''' to cancel this process. If you do, your archive will become incomplete and your recovery will be corrupt.}} | |
| − | + | <ol><li value="5"> Compare the size of the compressed and original files (hint: use '''ls -lh'''). If file is very large (like 15GB), you didn't compress it and you need to remove that file and perform the previous step until you get it right!</li> | |
| − | + | <li> Start the '''''centos3''''' VM.</li> | |
| − | + | <li> '''Make certain that you are in your VM and <u>not</u> in your main system!''' </li> | |
| − | + | <li> Wreck <u>only</u> your centos3 system! Try this command inside the centos3 virtual machine:<b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">rm -rf /*</span></code></b> (ignore error messages).</li> | |
| − | + | <li> Shut down the centos3 VM. If you tried to start the centos3 VM, it would not boot since all system files have been removed!</li> | |
| − | + | <li> Make certain you are in your '''/var/lib/libvirt/images directory'''. Restore the original image from the backup from your home directory to your '''images''' directory by typing this command:<br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">gunzip < ~YourUserId/centos3.qcow2.backup.gz > centos3.qcow2'''</span></code></b></li> | |
| − | + | <li> Restart the VM. Is it working normally?</li> | |
| − | + | <li> You should make a copy of the XML configuration file in case you "wipe" and re-install the host machine, and want to add a restored VM backups to the virtual machine manager list. We will demonstrate using the centos3 XML configuration file, and prove that a "clone" can be added to your list.Please perform the following step:</li> | |
| − | + | <li> Execute the following command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">virsh dumpxml centos3 > centos3.xml</span></code></b></li> | |
| − | # We will now learn how to download a compressed image file and | + | <li> Examine the file <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">centos3.xml</span></code></b>. What does it contain? What format is it in?<br></li></ol> |
| − | # Issue the following commands:<ul><li><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">wget | + | |
| − | + | === Part 2: Restoring Virtual Machines === | |
| − | {{Admon/important|Shutting Down the Host while Virtual Machines are Running|If you shut down your host system while virtual machines are running, they will be suspended, and will resume the next time you boot your host system.}} | + | |
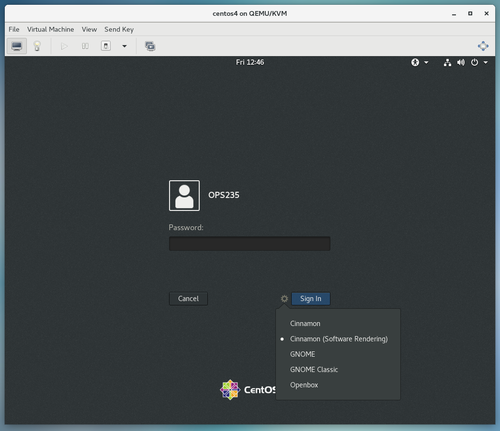
| − | <ol> | + | [[Image:Cinnamon-2.png|thumb|right|500px|Click on the cog icon to select different installed desktop environments.]] |
| − | + | ||
| + | # We will now learn how to download a compressed image file and XML configuration file and add it as a VM to the Virtual Machine Manager menu. | ||
| + | # Issue the following commands:<ul><li><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">wget https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/centos4.qcow2.backup.gz</span></code></b></li><li><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">wget https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/centos4.xml</span></code></b></li></ul> | ||
| + | # Copy these files to the '''/var/lib/libvirt/images''' directory and decompress the qcow2 image file. | ||
| + | # Make certain your present working directory is: '''/var/lib/libvirt/images''' | ||
| + | # Issue the command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">virsh define centos4.xml</span></code></b> | ||
| + | # What happened in the virtual manager window? To remove a VM entry in the Virtual Manager window, simply issue the command: '''virsh undefine vm_name''' (without the '''.xml''' file extension) | ||
| + | # Start up your new centos4 VM. | ||
| + | # Click on the user <i>OPS235</i>, and click the cog icon. | ||
| + | # Notice <i>Cinnamon (Software Rendering)</i> is selected. The Cinnamon desktop environment has been installed on this VM. From this menu, you can select other installed desktop environments. This is how you switch between them. Write it down. | ||
| + | # Login with the password <b><i>ops235</i></b>. Feel free to explore the new environment. | ||
| + | # Prior to your practical test, you will be required to perform a similar operation to download, unzip and run a VM image for your practical test.<br> | ||
| + | {{Admon/important|Shutting Down the Host while Virtual Machines are Running|If you shut down your host system while virtual machines are running, they will be suspended, and will resume the next time you boot your host system.}}<ol><li value="12">For the remainder of these labs, it is assumed that you will backup <u>'''both'''</u> the images and XML configuration files for <u>'''all'''</u> Virtual machines, when asked to backup your virtual machines. It is also highly recommended to backup these files to an external storage device (eg. USB key) in case the host machine gets "wiped" and you need to rebuild your HOST machine and then restore your Virtual Machines...</li> | ||
<li>Answer this question in your log book:</li> | <li>Answer this question in your log book:</li> | ||
</ol> | </ol> | ||
::* In order to fully back up a virtual machine, what information should be saved in addition to the virtual machine image? | ::* In order to fully back up a virtual machine, what information should be saved in addition to the virtual machine image? | ||
| − | === Part | + | === Part 3: Using Shell Scripts for VM Backup & Management=== |
{|width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | {|width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| Line 268: | Line 320: | ||
{{Admon/important|Virtual Machine Does not Shutdown from Command|If the Virtual machine fails to shutdown from the <code>virsh shutdown</code> command, then you can go to the '''Virtual Machine manager''' and '''halt''' or '''shutdown''' within the VM itself, then you can click the '''PowerOff''' button in the VM window. You'll want to avoid a forced shutdown since those are equivalent to yanking the power cord out of the wall on a physical machine!|}} | {{Admon/important|Virtual Machine Does not Shutdown from Command|If the Virtual machine fails to shutdown from the <code>virsh shutdown</code> command, then you can go to the '''Virtual Machine manager''' and '''halt''' or '''shutdown''' within the VM itself, then you can click the '''PowerOff''' button in the VM window. You'll want to avoid a forced shutdown since those are equivalent to yanking the power cord out of the wall on a physical machine!|}} | ||
<ol><li value="9">Open a Bash shell terminal and login as root.</li> | <ol><li value="9">Open a Bash shell terminal and login as root.</li> | ||
| − | <li>Use a text editor (such as <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">vi</span></code></b> or <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">nano</span></code></b>) to create a Bash Shell script called: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">backupVM.bash</span></code></b> in /root | + | <li>Use a text editor (such as <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">vi</span></code></b> or <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">nano</span></code></b>) to create a Bash Shell script called: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">backupVM.bash</span></code></b> in /root/bin directory.</li> |
| − | <li>Enter the following text content into your text-editing session: | + | <li>Enter the following text content into your text-editing session:</li></ol> |
| − | <code style="color:#3366CC;font-family:courier;font-size:.9em | + | <code style="color:#3366CC;font-family:courier;font-size:.9em;"> |
<br> | <br> | ||
#!/bin/bash | #!/bin/bash | ||
| Line 289: | Line 341: | ||
fi | fi | ||
</code> | </code> | ||
| − | <br>< | + | <br> |
| + | <ol> | ||
<li value="12">Save your editing session, but remain in the text editor.</li><li>This shell script is designed particularly for your centos1, centos2, and centos3 VMS.</li><li>The code displayed below will prompt the user if they wish for all VMs to be backed-up; otherwise, allow the user the option of specifying which VMs to be backed-up. Add the following code</li></ol> | <li value="12">Save your editing session, but remain in the text editor.</li><li>This shell script is designed particularly for your centos1, centos2, and centos3 VMS.</li><li>The code displayed below will prompt the user if they wish for all VMs to be backed-up; otherwise, allow the user the option of specifying which VMs to be backed-up. Add the following code</li></ol> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| Line 313: | Line 366: | ||
echo "Backing up VM #$numanswer"<br> | echo "Backing up VM #$numanswer"<br> | ||
gzip < /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos$numanswer.qcow2 > /root/centos$numanswer.qcow2.backup.gz<br><br> | gzip < /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos$numanswer.qcow2 > /root/centos$numanswer.qcow2.backup.gz<br><br> | ||
| − | echo "VM #$numanswer BACKUP DONE" | + | echo "VM #$numanswer BACKUP DONE"<br> |
else<br> | else<br> | ||
echo "Invalid Selection... Aborting program"<br> | echo "Invalid Selection... Aborting program"<br> | ||
| Line 323: | Line 376: | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
| − | <li value="15">Save, set permissions, and then run that shell script to backup centos1. Confirm that this script did backup this image to root's home directory</li><li>Use the <b><code>wget</code></b> command to download, study, and run the following shell scripts on-line:<blockquote><b><code><span style=" pointer-events:none;cursor:default;color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">https:// | + | <li value="15">Save, set permissions, and then run that shell script to backup centos1. Confirm that this script did backup this image to root's home directory</li><li>Use the <b><code>wget</code></b> command to download, study, and run the following shell scripts on-line:<blockquote><b><code><span style=" pointer-events:none;cursor:default;color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/vm-start-text.bash<br>https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/vm-stop-text.bash</span></code></b><br><b><code><span style=" pointer-events:none;cursor:default;color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/vm-start.bash<br>https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/vm-stop.bash</span></code></b></blockquote></li><li>Try to understand what these Bash Shell scripts do.</li><li>You have completed lab2. Proceed to Completing The Lab, and follow the instructions for "lab sign-off".</li></ol> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''Answer INVESTIGATION 3 observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | ||
= LAB 2 SIGN-OFF (SHOW INSTRUCTOR) = | = LAB 2 SIGN-OFF (SHOW INSTRUCTOR) = | ||
| − | {{Admon/important|Backup ALL of your VMs!|If you have successfully completed this lab, make a new backup of all of your virtual machines onto your | + | ===Exclusively for Summer 2020 term, submissions are accepted only online!=== |
| − | + | Follow the submission instructions for lab 2 on Blackboard. | |
| + | {{Admon/important|Backup ALL of your VMs!|If you have successfully completed this lab, make a new backup of all of your virtual machines onto your USB Key.}} | ||
:'''Perform the Following Steps:''' | :'''Perform the Following Steps:''' | ||
| − | # | + | # Use the '''virsh start''' command to launch all the VMs ('''centos1''', '''centos2''', and '''centos3'''). |
| + | # Inside each virtual machine, run <b><code>ip a</code></b> on the command line. Open a Terminal window in centos1 to do so. You'll need the IP address of each machine for the next steps. | ||
# Switch to your '''c7host''' VM, open a terminal, login as root, and change directory to '''/root/bin'''. | # Switch to your '''c7host''' VM, open a terminal, login as root, and change directory to '''/root/bin'''. | ||
| − | # Issue the Linux command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">wget | + | # Issue the Linux command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">wget https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/lab2-check.bash</span></code></b> |
# Give the '''lab2-check.bash''' file execute permissions (for the file owner). | # Give the '''lab2-check.bash''' file execute permissions (for the file owner). | ||
# Run the shell script and if any warnings, make fixes and re-run shell script until you receive "congratulations" message. | # Run the shell script and if any warnings, make fixes and re-run shell script until you receive "congratulations" message. | ||
| Line 342: | Line 396: | ||
::✓ '''<u>All</u> VMs''':<blockquote><ul><li>All 4 VMs '''created''' and '''running'''</li><li> Proof of '''yum updates''' on ALL VMs (i.e. results from '''yum update''' command)</li></ul></blockquote> | ::✓ '''<u>All</u> VMs''':<blockquote><ul><li>All 4 VMs '''created''' and '''running'''</li><li> Proof of '''yum updates''' on ALL VMs (i.e. results from '''yum update''' command)</li></ul></blockquote> | ||
| − | ::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>''' | + | ::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>'''c7host VM''':<blockquote><ul><li>Run the '''lab2-check.bash''' script in front of your instructor (must have all <b><code><span style="color:#66cc00;border:thin solid black;font-size:1.2em;"> OK </span></code></b> messages)</li></ul></blockquote> |
::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span> Lab2 logbook notes completed. | ::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span> Lab2 logbook notes completed. | ||
| Line 363: | Line 417: | ||
# What is the difference between a determinant loop and an in-determinant loop? | # What is the difference between a determinant loop and an in-determinant loop? | ||
# Show a few examples how loops can be used to error-check when prompting the user for data. | # Show a few examples how loops can be used to error-check when prompting the user for data. | ||
| − | # What is the purpose of the '''&&''' and '''||''' symbols when used with logic? | + | # What is the purpose of the '''&&''' and '''||''' symbols when used with logic?' |
| + | # What does the command '''rpm -qi centos-release''' do and why is it important? | ||
| + | # What is the difference between '''rpm -q centos-release''' and '''uname -a'''? | ||
| + | |||
[[Category:OPS235]] | [[Category:OPS235]] | ||
[[Category:OPS235 Labs]] | [[Category:OPS235 Labs]] | ||
| + | [[Category:CentOS 7]] | ||
| + | [[Category:SSD2]] | ||
| + | [[Category:Digital Classroom]] | ||
Latest revision as of 03:49, 18 September 2020
Contents
LAB PREPARATION
Purpose / Objectives of Lab 2
In this lab, you will create 3 remaining virtual machines using another virtualization program called KVM that will run in your c7host VM. These VMs will be used throughout the remainder of this course to learn how to administer them (installing software, managing services, networking, etc).
While you are performing this lab, it is recommended to generally note the major differences in the different installation methods, and which method you prefer to use if you were a Linux system administrator in charge of installing many Linux distributions for an organization.
Main Objectives
- Installing additional Virtualization Software on your c7host machine (KVM)
- Create 3 separate VMs (virtual machines) using different installation methods:
- centos1: Network CentOS Installation (Graphical)
- centos2: Network CentOS Installation (minimal install - CLI only)
- centos3: Network CentOS Installation with Kickstart configuration file (CLI only)
- Manipulate virtual machines by CLI (virsh)
- Properly backup VM images and backup VM configuration files
- Create and run Bash Shell scripts to automatically create a post-install report for an installed VM.
| Minimum Required Materials |
Linux Command Reference | ||||
|
Virtualization |
Miscellaneous |
Matrix Online Tutorials:
| |||
INVESTIGATION 1: SETUP FOR NESTED VIRTUAL MACHINES
Part 1: Install KVM Virtualization Application
We will now install the KVM package in order to create our remaining "nested" VMs. We will also be starting several services (including iptables) and disabling the firewalld service. We will learn more about managing firewalls using iptables in lab6.
- Perform the following steps:
- Log into your c7host machine, and switch to root user.
- perform a software update on your c7host VM by issuing the following command:
yum update
- As root, install the virtualization software by issuing the command:
yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python \
libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils - Restart your c7host virtual machine. If you fail to do this, you may experience virtualization network problems.
- Start the virtualization service:
systemctl start libvirtd
NOTE: The most recent variants of CentOS and Fedora are using a service called firewalld that is intended to replace iptables, however the iptables service is still in relatively common usage. In this course we will concentrate on iptables. - To disable and remove firewalld, issue the following commands:
systemctl disable firewalld
systemctl stop firewalld
yum remove firewalld
- To install and enable the IPTables services, issue the following commands:
yum install iptables-services
systemctl enable iptables
systemctl start iptables
- Start the graphical tool by selecting the menu options Applications>System Tools>Virtual Machine Manager or by typing the command
virt-manager - You will be learning in the next investigation to perform several different types of CentOS Linux installs.
Part 2: Configure VMware Workstation for Nested VMs
Although we are using VMware Workstation to run our c7host VM, we will now install and configure another virtualization package called KVM in order to install the remaining VMs for this course. Since we are "nesting" VMs (i.e. running a VM inside another VM) we need to configure our c7host's Linux boot-up parameters in order to allow these VMs to run efficiently.
- Perform the following steps:
- In a terminal as the root user, edit the file called: /boot/efi/EFI/centos/grub.cfg
- If this file doesn't exist, double-check your UEFI settings in VMWare Workstation for c7host. If BIOS is selected, you MUST redo Lab 1.
- Search for the first occurrence of the Linux Kernel boot command. Do not make the following changes on more than one entry!
- Insert the boot option: kvm-intel.nested=1 at the end of the Linux kernel boot options.
linuxefi /vmlinuz-3.10.0-1062.1.2.el7.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/centos_c7host-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=centos_c7host/root rd.lvm.lv=centos_c7host/swap rhgb quiet LANG=en_CA.UTF-8 kvm-intel.nested=1
initrdefi /initramfs-3.10.0-1062.1.2.el7.x86_64.img
OR
linuxefi /boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-1062.el7.x86_64 root=/dev/mapper/centos_c7host-root ro crashkernel=auto rd.lvm.lv=centos_c7host/root rd.lvm.lv=centos_c7host/swap rhgb quiet LANG=en_CA.UTF-8 kvm-intel.nested=1
initrdefi /boot/initramfs-3.10.0-1062.el7.x86_64.img
- Save your editing changes, close the virtual machine application, and reboot your c7host VM.
- If you configured your c7host VM for nested VMs, then you should get the output
Ywhen you issue the following command:cat /sys/module/kvm_intel/parameters/nested - For AMD processors, check the /sys/module/kvm_amd/parameters/nested file.
- And if kvm_intel directory doesn't exist, double-check your Processors => Virtualization Engine (Intel VT-x/EPT...) settings in VMWare Workstation.
Answer the INVESTIGATION 1 observations / questions in your lab log book.
INVESTIGATION 2: INSTALL NESTED VIRTUAL MACHINES (KVM)
Part 1: Installing VM from a Network (Graphical)
- VM Details:
- VM Name (and hostname): centos1
- Boot media: Network installation
- CentOS Full Network Install URL:
- VM Image Pathname: /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos1.qcow2
- Memory: 2048MB
- Disk space: 15GB
- CPUs: 2
- Perform the following steps:
- Launch the KVM virtual machine manager by clicking Applications -> System Tools -> Virtual Machine Manager.
- When prompted, enter your root password.
- Click the create a new VM icon located near the top left-corner of the application window.
- Select the Network Install option and click Forward.
- Enter (copy and paste) the URL located at the top of this section (depending whether you are at Seneca College or not) and click Forward.
- Set RAM size to 2048 MB and click Forward.
- Set Hard Disk size to 15GB and click Forward.
- Enter the name: centos1, AND then select the option: Customize configuration before install, and click Finish.
- Another dialog will appear. Click CPUs (or "processors") and on right-side under Configuration select Copy Host CPU Configuration, click Apply, and then click Begin Installation at the top left-hand side.
- During the install, select Gnome Desktop software selection). For partitioning, select I will configure partition settings, click done, then select Click here to create them automatically. Set the / partition for ext4 file-system type, and click Done.
- Set the correct Date and Time Zone, and then click on Network and Hostname. The network should be turned on. For hostname, enter: centos1 and then click Done.
- Complete the installation. Login to your regular user account, switch to the root user with su -, and perform a yum update for the centos1 VM (reboot if required). Make certain to adjust your screen-saver settings if desired.
- Repeat the steps as you did in the previous investigation (Investigation1 Part 1) to stop and disable firewalld, install iptables-services, start and enable iptables for this newly-created VM.
- Repeat the steps as you did with c7host post-install to disable SELinux and perform a yum update.
- Issue the following command to obtain the IPADDR for your centos1 VM to record in your lab2 logbook:
ifconfig - Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations in your lab2 logbook.
Part 2: Installing from a Network (Minimal install - CLI)
- VM Details:
- VM Name (and hostname): centos2
- Boot media: Network installation
- CentOS Full Network Install URL:
- VM Image Pathname: /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos2.qcow2
- Memory: 2048MB
- Disk space: 20GB
- CPUs: 1
- Perform the following steps:
- Create the VM (called centos2) as you did with the centos1 machine.
- Make certain to enter the name: centos2, AND then select the option: Customize configuration before install, and select Copy Host CPU Configuration, click Apply, and then click Begin Installation.
- When selecting the install options for centos2, do the same operation that you did in centos1 (but with Minimal Install software selection instead), but after automatically creating the partitions, reduce the size of the root logical volume to 8 GiB and add a logical volume with a size of 2 GiB (mount point: /home, name: home, and make certain root and /home logical volumes have ext4 file system).
- Complete the installation. Login to your regular user account.
- Repeat the steps as you did in the previous investigation (Investigation1 Part 1) to stop and disable firewalld, install iptables-services, start and enable iptables for this newly-created VM.
- Repeat the steps as you did with c7host post-install to disable SELinux (using the command 'vi' instead of 'vim') and perform a yum update.
- The ifconfig command is not available in centos2. Issue the following command to obtain and record your centos2 IPADDR in your lab2 logbook:
ip address - Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations in your lab2 logbook.
Part 3: Installing from a Network using a Kickstart File
- VM Details:
- VM Name (and hostname): centos3
- Boot media: Network installation
- CentOS 7 Full Install Network URL:
- Kickstart File URL (Kernel options):
- VM Image Pathname: /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos3.qcow2
- Memory: 2048MB (IMPORTANT Do not use less than 2048MB during installation.)
- Disk space: 15GB
- CPUs: 2
- Perform the following steps:
- Create the VM (called centos3)
- During the install, copy the network URL, then click the URL options to expand the kernel options input textbox. Type the following in the kernel options textbox:
- Then click the forward button to proceed. Make certain to select the correct Memory Size and Disk Space size shown in the VM Details above
- Make certain to enter the name: centos3, AND then select the option: Customize configuration before install, and select Copy Host CPU Configuration, click Apply, and then click Begin Installation.
- Observe the installation. How is it different from booting from a downloaded image?
- Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations.
If during the installation, you see the message at the bottom Pane is Dead, click the Virtual Machine menu at the top, select Shut Down -> Force Off, right-click on centos3 in the virtual manager window and select Delete. Redo the VM setup for a new instance of the centos3 VM. - What happens when the installation is finished?
- In a web browser, click the kickstart (KS) link above. This link is a text file. Read through it to find the following information (pay attention to lines starting with #) and record it in your Lab Logbook:
- Regular-user account name
- Regular-user account password
- Root Password
- Boot the virtual machine and log in (use the user ID and password information from the previous step to gain access to this VM).
- Compare the experience to the first time you booted the other virtual machines.
- Repeat the steps as you did in the previous investigation (Investigation1 Part 1) to stop and disable firewalld, install iptables-services, start and enable iptables for this newly-created VM.
- Repeat the steps as you did with c7host post-install to disable SELinux and perform a yum update.
- The ifconfig command may not be available in centos3. Issue the following command to obtain and record your centos2 IPADDR in your lab2 logbook:
ip address - Remember that centos3 is text-based interface only (no graphics). To recover from a blank screen, press a key (like the SPACE key) to return to the screen display.
- Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations in your lab2 logbook.
Answer the INVESTIGATION 2 observations / questions in your lab log book.
INVESTIGATION 3: MANAGING VIRTUAL MACHINES (KVM)
Part 1: Backing Up Virtual Machines
- Perform the following steps:
- Shut down your centos1, centos2, and centos3 VMs. For centos2 and centos3, which are CLI-only, you can issue the following command as root to shutdown:
shutdown -h. Please be patient, the VMs will shut down! - In your c7host VM, open a new Terminal window, and switch to the root account inside the terminal.
- Change to the images directory by issuing the command:
cd /var/lib/libvirt/images/- Note the size of the files in this directory. What do these files contain?
- Make a compressed backup of your centos1.qcow2, centos2.qcow2, and centos3.qcow2 files to your regular user's home directory by issuing each command (one at a time):
gzip < centos1.qcow2 > ~YourRegularUsername/centos1.qcow2.backup.gzgzip < centos2.qcow2 > ~YourRegularUsername/centos2.qcow2.backup.gzgzip < centos3.qcow2 > ~YourRegularUsername/centos3.qcow2.backup.gz- NOTE: Make certain to use the redirection signs "<" and ">" properly in the command!
- Compare the size of the compressed and original files (hint: use ls -lh). If file is very large (like 15GB), you didn't compress it and you need to remove that file and perform the previous step until you get it right!
- Start the centos3 VM.
- Make certain that you are in your VM and not in your main system!
- Wreck only your centos3 system! Try this command inside the centos3 virtual machine:
rm -rf /*(ignore error messages). - Shut down the centos3 VM. If you tried to start the centos3 VM, it would not boot since all system files have been removed!
- Make certain you are in your /var/lib/libvirt/images directory. Restore the original image from the backup from your home directory to your images directory by typing this command:
gunzip < ~YourUserId/centos3.qcow2.backup.gz > centos3.qcow2 - Restart the VM. Is it working normally?
- You should make a copy of the XML configuration file in case you "wipe" and re-install the host machine, and want to add a restored VM backups to the virtual machine manager list. We will demonstrate using the centos3 XML configuration file, and prove that a "clone" can be added to your list.Please perform the following step:
- Execute the following command:
virsh dumpxml centos3 > centos3.xml - Examine the file
centos3.xml. What does it contain? What format is it in?
Part 2: Restoring Virtual Machines
- We will now learn how to download a compressed image file and XML configuration file and add it as a VM to the Virtual Machine Manager menu.
- Issue the following commands:
- Copy these files to the /var/lib/libvirt/images directory and decompress the qcow2 image file.
- Make certain your present working directory is: /var/lib/libvirt/images
- Issue the command:
virsh define centos4.xml - What happened in the virtual manager window? To remove a VM entry in the Virtual Manager window, simply issue the command: virsh undefine vm_name (without the .xml file extension)
- Start up your new centos4 VM.
- Click on the user OPS235, and click the cog icon.
- Notice Cinnamon (Software Rendering) is selected. The Cinnamon desktop environment has been installed on this VM. From this menu, you can select other installed desktop environments. This is how you switch between them. Write it down.
- Login with the password ops235. Feel free to explore the new environment.
- Prior to your practical test, you will be required to perform a similar operation to download, unzip and run a VM image for your practical test.
- For the remainder of these labs, it is assumed that you will backup both the images and XML configuration files for all Virtual machines, when asked to backup your virtual machines. It is also highly recommended to backup these files to an external storage device (eg. USB key) in case the host machine gets "wiped" and you need to rebuild your HOST machine and then restore your Virtual Machines...
- Answer this question in your log book:
- In order to fully back up a virtual machine, what information should be saved in addition to the virtual machine image?
Part 3: Using Shell Scripts for VM Backup & Management
You will continue our use of Bash Shell scripting by first creating a Bash Shell script that will allow the Linux sysadmin to select their created VMs for backup to root's home directory. Afterwards you will download, view and run a couple Bash Shell scripts that use the virsh command to start and stop your virtual machines.
- Perform the following steps:
- Start the centos1 virtual machine, and stop the centos2 and centos3 virtual machines.
- Switch to the c7host machine, and open a shell terminal.
- Enter these admin commands into your c7host machine and note the result:
-
virsh list -
virsh list --all -
virsh list --inactive
-
- Now, shut-down your centos1 VM normally, and close the centos1 VM window.
- Switch to your terminal and issue the command:
virsh start centos1 - Using the appropriate command check to see if your centos1 VM is now running.
- There are other commands that can be used (such as suspend, or shutdown). The "shutdown" command may not always work since it relies on the guest handling a particular ACPI event. Why do you think it is useful to have commands to manipulate VMs?
- Since this is a text-based version of Linux, you do not need to turn off the screen-saver.
- Open a Bash shell terminal and login as root.
- Use a text editor (such as
viornano) to create a Bash Shell script called:backupVM.bashin /root/bin directory. - Enter the following text content into your text-editing session:
#!/bin/bash
# backupVM.bash
# Purpose: Creates system info report
#
# USAGE: ./report.bash
#
# Author: *** INSERT YOUR NAME ***
# Date: *** CURRENT DATE ***
if [ $PWD != "/root" ] # only runs if in root's directory
then
echo "You must be located in /root" >&2
exit 1
fi
- Save your editing session, but remain in the text editor.
- This shell script is designed particularly for your centos1, centos2, and centos3 VMS.
- The code displayed below will prompt the user if they wish for all VMs to be backed-up; otherwise, allow the user the option of specifying which VMs to be backed-up. Add the following code
read -p "Backup all VMs? (y|n):" answer # prompt if all VMs to be backed-up
if [ "$answer" = "y" ] # Backup all VMs if answer is yes
then
for num in 1 2 3 # Determinant loop for 3 arguments: 1, 2, and 3
do
echo "Backing up VM #$num"
gzip < /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos$num.qcow2 > /root/centos$num.qcow2.backup.gz
echo "VM #$num BACKUP DONE"
done
elif [ "$answer" = "n" ]
then
read -p "Which VM should be backed up? (1/2/3): " numanswer
until echo $numanswer | grep "^[123]$" >> /dev/null # Look for match of single digit: 1,2, or 3
do
read -p "Invalid Selection. Select 1, 2, or 3: " numanswer
done
echo "Backing up VM #$numanswer"
gzip < /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos$numanswer.qcow2 > /root/centos$numanswer.qcow2.backup.gz
echo "VM #$numanswer BACKUP DONE"
else
echo "Invalid Selection... Aborting program"
exit 2
fi
- Save, set permissions, and then run that shell script to backup centos1. Confirm that this script did backup this image to root's home directory
- Use the
wgetcommand to download, study, and run the following shell scripts on-line:https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/vm-start-text.bash
https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/vm-stop-text.bashhttps://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/vm-start.bash
https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/vm-stop.bash - Try to understand what these Bash Shell scripts do.
- You have completed lab2. Proceed to Completing The Lab, and follow the instructions for "lab sign-off".
Answer INVESTIGATION 3 observations / questions in your lab log book.
LAB 2 SIGN-OFF (SHOW INSTRUCTOR)
Exclusively for Summer 2020 term, submissions are accepted only online!
Follow the submission instructions for lab 2 on Blackboard.
- Perform the Following Steps:
- Use the virsh start command to launch all the VMs (centos1, centos2, and centos3).
- Inside each virtual machine, run
ip aon the command line. Open a Terminal window in centos1 to do so. You'll need the IP address of each machine for the next steps. - Switch to your c7host VM, open a terminal, login as root, and change directory to /root/bin.
- Issue the Linux command:
wget https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~ops235/labs/lab2-check.bash - Give the lab2-check.bash file execute permissions (for the file owner).
- Run the shell script and if any warnings, make fixes and re-run shell script until you receive "congratulations" message.
- Arrange proof of the following on the screen:
- ✓ All VMs:
- All 4 VMs created and running
- Proof of yum updates on ALL VMs (i.e. results from yum update command)
- ✓c7host VM:
- Run the lab2-check.bash script in front of your instructor (must have all
OKmessages)
- Run the lab2-check.bash script in front of your instructor (must have all
- ✓ Lab2 logbook notes completed.
- ✓ All VMs:
Practice For Quizzes, Tests, Midterm & Final Exam
- What is the name of the CentOS installation program?
- What is the name of the file created by the CentOS installation program?
- Which type of installation works best for confirming compatibility with hardware before installation? Why?
- Which type of installation works best for installing large numbers of computers? Why?
- How can you reduce the number of software updates required immediately after installation?
- How do you start and stop virtual machines?
- How do you SSH into your virtual machines?
- List the steps to install a VM from:
- Downloaded iso file
- Network install (without kickstart file)
- Network install (with kickstart file)
- What is the purpose of the virsh command?
- How to start and stop VMs using the virsh command?
- List the steps to correctly backup your VMs to a USB disk
- List the steps to correctly restore your VMs from a USB disk to your c7host VM.
- How can you prompt the user for data and store into a variable?
- How do you perform mathematical operations in the Bash shell and within a Bash shell script?
- What is the difference between a determinant loop and an in-determinant loop?
- Show a few examples how loops can be used to error-check when prompting the user for data.
- What is the purpose of the && and || symbols when used with logic?'
- What does the command rpm -qi centos-release do and why is it important?
- What is the difference between rpm -q centos-release and uname -a?