Difference between revisions of "OPS235 Lab 2 - CentOS7"
| (291 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Category:OPS235]] | [[Category:OPS235]] | ||
| + | {{Admon/caution|THIS IS AN OLD VERSION OF THE LAB|'''This is an archived version. Do not use this in your OPS235 course.'''}} | ||
| + | = LAB PREPARATION = | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Purpose / Objectives of Lab2== | == Purpose / Objectives of Lab2== | ||
[[Image:hostmachine.png|thumb|right|300px|The c7host Linux server will run virtualization software to install and run 3 virtual machines (installed in lab2). ]] | [[Image:hostmachine.png|thumb|right|300px|The c7host Linux server will run virtualization software to install and run 3 virtual machines (installed in lab2). ]] | ||
| − | '''In this lab, you will create three virtual machines'''. This also gives you an opportunity to experiment with different ways of installing CentOS. | + | |
| − | + | '''In this lab, you will create three virtual machines'''. This also gives you an opportunity to experiment with different ways of installing CentOS. | |
| − | + | <br><br> | |
| − | + | <u>Main Objectives</u> | |
| − | : | + | |
| − | : | + | * '''Installing Virtualization Software''' on your '''c7host''' machine |
| − | : | + | * '''Create 3 separate VMs (virtual machines) using different installation methods:''' |
| − | + | :* Centos Live DVDInstallation | |
| − | + | :* Network Installation without configuration file | |
| − | + | :* Network Installation with configuration file (Kickstart) | |
| − | + | * Understand the '''advantages and disadvantages of each type of installation''', and be able to '''select the best installation method''' for a particular situation. | |
| + | * '''Manipulate virtual machines by CLI''' (virsh) | ||
| + | * '''Properly backup VMs and VM configuration''' in virtual manager application onto home directory and to external source (USB Key) | ||
| + | * Observe how '''Bash Shell Scripting''' can be used to automate routine tasks involving VM management | ||
== What is a Virtual Machine?== | == What is a Virtual Machine?== | ||
| − | A '''virtual machine''' is a software simulation of a computer which can be used as though it were actual hardware. It's possible to run multiple virtual machines on one computer, reducing hardware requirements and | + | A '''virtual machine''' is a software simulation of a computer which can be used as though it were actual hardware. It's possible to run multiple virtual machines on one computer, reducing hardware requirements and promoting flexibility when working with multiple operating systems. Some common uses of virtualization include: |
:* '''Software testing''' -- Using multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single computer for testing and experimentation. | :* '''Software testing''' -- Using multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single computer for testing and experimentation. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 33: | ||
| − | == Required Materials | + | ==Minimum Required Materials== |
{|cellpadding="15" width="40%" | {|cellpadding="15" width="40%" | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|width="10%" | [[Image:harddrive.png|thumb|left|85px|<b>Removable Hard Disk Pack</b> (SATA)]] | |width="10%" | [[Image:harddrive.png|thumb|left|85px|<b>Removable Hard Disk Pack</b> (SATA)]] | ||
| Line 50: | Line 51: | ||
{|width="100%" cellpadding="15" | {|width="100%" cellpadding="15" | ||
|- valign="top" | |- valign="top" | ||
| − | |width=" | + | |width="20%" |<u>Virtualization:</u> |
[http://linux.die.net/man/1/virt-manager virt-manager]<br> | [http://linux.die.net/man/1/virt-manager virt-manager]<br> | ||
[http://linux.die.net/man/1/virsh virsh] | [http://linux.die.net/man/1/virsh virsh] | ||
| − | |width=" | + | |width="20%" |<u>Commands</u> |
| − | + | [http://unixhelp.ed.ac.uk/CGI/man-cgi?gzip gzip, gunzip]<br> | |
| − | [ ]<br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[http://unixhelp.ed.ac.uk/CGI/man-cgi?grep grep]<br> | [http://unixhelp.ed.ac.uk/CGI/man-cgi?grep grep]<br> | ||
[http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/wc.1.html wc]<br> | [http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/wc.1.html wc]<br> | ||
| Line 70: | Line 65: | ||
[http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/chmod.1.html chmod]<br> | [http://man7.org/linux/man-pages/man1/chmod.1.html chmod]<br> | ||
[http://ss64.com/vi.html vi] | [http://ss64.com/vi.html vi] | ||
| + | |width="20%" |<u>Installation Guides</u> | ||
| + | [http://wiki.centos.org/HowTos/KVM Installing & Using KVM on CentOS ]<br> | ||
| + | [http://www.dedoimedo.com/computers/kvm-intro.html Using KVM (tutorial)]<br> | ||
| + | [https://www.centos.org/docs/5/html/5.2/Virtualization/sect-Virtualization-Commands_for_Red_Hat_Virtualization-virsh_the_command_line_interface_tool_for_virtualization.html virsh command reference ]<br> | ||
| + | [http://www.centos.org/docs/5/html/Installation_Guide-en-US/ch-kickstart2.html CentOS Kickstart Reference ]<br> | ||
| − | + | |width="40%" |{{Admon/tip|Online Linux Command Review|The following tutorial will allow you to learn essential shell scripting skills. Login to your '''Matrix''' account, and issue the pathname to run the online tutorial in Matrix:<br><ul><li>Shell Scripting - Part 2 (Logic & Math Expressions):<br>'''/home/murray.saul/scripting-2'''</li><li>Shell Scripting - Part 3 (Loops)<br>'''/home/murray.saul/scripting-3'''</li></ul>| | |
| − | |||
| − | |width=" | ||
}} | }} | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | =INVESTIGATION 1: USING VIRTUALIZATION SOFTWARE TO CREATE VIRTUAL MACHINES= |
| − | + | ==Virtualization Application Setup / Comparison Chart== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
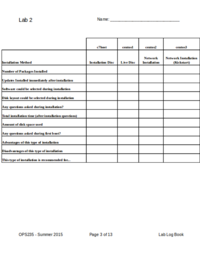
| − | + | [[Image:lab2-logbook.png|thumb|right|200px|'''comparison chart''' in lab2 logbook.]] | |
| − | |||
| − | [ | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | | | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Record VM Installation in Lab2 (Installation Comparison Chart):''' | |
| − | |||
| − | You will be learning to perform several different type of CENTOS Linux installs. | + | You will be learning to perform several different type of CENTOS Linux installs. Lab2 already has an empty table for comparing various Linux installs. You were required in lab1 to record your observation for your '''c7host''' installation. |
| − | + | As you proceed throughout this lab, you will be required to fill in the comparison chart for three of the VMs (virtual machines) that you will be installing. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | '''Complete the following steps to install and run the virtual manager application:''' | ||
| − | = | + | # Open a web-browser, and open the OPS235 Lab #2 WIKI. |
| + | # Open a shell terminal.<br><br>'''WARNING:''' You must perform a '''yum update''' on your '''c7host''' machine before proceeding with the next steps.<br><br> | ||
| + | # You will need to download an image file for the Centos7 LIVE DVD by issuing the following command (best works while at Seneca):<br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">wget http://belmont.senecac.on.ca/centos/7/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7-x86_64-LiveGNOME-1511.iso</span></code></b><br><br> | ||
| + | # Install the virtualization software by issuing the command:<br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python \<br>python-virtinst libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils</span></code></b> <br><br> | ||
| + | {{Admon/important|Restart your Host Machine|You must restart your '''c7host''' machine after installing the virtualization program above. If you fail to do this, you may experience virtualization network problems!}} | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | ::This will install many applications (including): | |
| − | + | :::* '''kvm/qemu''' - the hypervisor and other hardware emulation systems. | |
| − | :* kvm/qemu - the hypervisor and other hardware emulation systems. | + | :::* A system service named '''libvirtd''' that manages the VMs. |
| − | :* A system service named libvirtd that manages the VMs. | + | :::* A graphical tool for managing virtual machines ('''virt-manager''') and the '''virsh''' command-line tool.<br><br> |
| − | :* A graphical tool for managing virtual machines and the virsh command-line tool. | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
| − | <li value=" | + | <li value="5">Start the virtualization service: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">service libvirtd start</span></code></b></li> |
| − | <li>The firewall configuration is altered by the addition of the virtualization software. | + | <li>The firewall configuration is altered by the addition of the virtualization software. Centos7 uses firewalld for firewall, but we will be switching back to using iptables. Issue the following series of command to install iptables and restart the firewall:<br><br> <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">systemctl stop firewalld</span></code></b><br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">systemctl mask firewalld</span></code></b><br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">yum install iptables-services</span></code></b><br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">systemctl enable iptables</span></code></b><br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">systemctl start iptables</span></code></b><br><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">service iptables save</span></code></b><br><br></li> |
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| + | {| width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | |colspan="2"|{{Admon/important|Run virt-manager as a regular user, not as root|Otherwise all your virtual machines will be owned by root and you won't be able to use them as a regular user.}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
| − | <li value=" | + | <li value="7">Start the graphical tool by selecting the menu options '''Applications'''>'''System Tools'''>'''Virtual Machine Manager''' or by typing the command<b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;"> virt-manager</span></code></b></li> |
</ol> | </ol> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | == Part 1: Installing from a Downloaded Image (Centos7 LIVE CD) == | |
| + | {| width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | |{{Admon/tip|Perform Downloads and Network installs at Seneca|'''It is recommended to perform this lab in one of Seneca College's labs'''. This lab uses servers which are on the Seneca network and which are not available from other locations (such as your home). If you attempt this lab from another location, adjust the belmont.senecac.on.ca URLs to point to another mirror server -- note that you may need to change the directory name as well as the server name. The installation of the '''centos3''' virtual machine <u>must</u> be done at Seneca.}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Admon/important|Removing and Recreating VMs|If for some reason the user wants to remove a Virtual Machine, they can right-click the VM, and select delete in the Virtual Machine Manager. It is recommended to '''"delete the image file" in the remove VM dialog box when removing and then recreating a VM'''. Note: If you fail to properly remove the VM image file, it may affect the hard disk size for the new VM (i.e. use the old smaller size. Make certain to remove that VM image file prior to recreating the VM.|'''}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{Admon/important|Restart your Host Machine Again|You must restart your '''c7host''' machine again, prior to creating your virtual machines. If you fail to do this, you may experience virtualization network problems!}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | :'''VM Details:''' | |
| + | :: '''VM Name (and hostname):''' centos1 | ||
| + | :: '''Boot media:''' LIVE CD Image | ||
| + | :: '''Installation source:''' Downloaded Centos7 LIVE CD image (http://belmont.senecac.on.ca/centos/7/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7-x86_64-LiveGNOME-1511.iso) | ||
| + | :: '''VM Image Pathname:''' /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos1.img | ||
| + | :: '''Memory:''' 2GB | ||
| + | :: '''Disk space:''' 10GB | ||
| + | :: '''File System (root partition):''' ext4 | ||
| + | :: '''CPUs:''' 1 | ||
| + | |||
| + | # Make certain you used the wget command to download the LiveGNOME iso file from the Belmont server (from previous instructions). | ||
# In the Virtual Machine Manger, click on the icon to ''Create a Virtual Machine'' in the upper-left corner: | # In the Virtual Machine Manger, click on the icon to ''Create a Virtual Machine'' in the upper-left corner: | ||
# A window will appear with the title ''New VM''. There are five steps to be completed; click Forward after each step: | # A window will appear with the title ''New VM''. There are five steps to be completed; click Forward after each step: | ||
| − | # '''Step 1 of 5:''' | + | # '''Step 1 of 5:'''Select '''Local install media''' and click '''Forward'''. |
| − | # '''Step 2 of 5:''' | + | # '''Step 2 of 5:''' Select '''Use ISO Image''', click the '''Browse''' button, and then the '''Browse Local''' button. Navigate to the location of the downloaded Centos7 LIVE CD image, select the image file and click '''Open'''. When finished, click Forward to proceed. |
| − | # '''Step 3 of 5:''' Set the memory to ''' | + | # '''Step 3 of 5:''' Set the memory to '''2048 MB''' and the number of CPUs to '''1''' |
| − | + | [[Image:vm-path.png|thumb|right|300px|It is extremely important to '''correctly specify the VM image file path-name'''. Double-check the spelling of the path-name before proceeding!]] | |
| − | + | <ol><li value="7">'''Step 4 of 5:''' This next step creates a disk file that will be used to simulate the virtual machine's disk drive. Select a size of '''10 GB'''. Click on<br> '''Select managed or other existing storage''' and type the VM image file pathame:<br> '''/var/lib/libvirt/images/centos1.img''' (make certain that the pathname is correct) and then click '''Forward''' to proceed.</li><li>'''Step 5 of 5:''' Enter the virtual machine name: '''centos1'''. Review the VM information, and click '''Finish'''.<br><br></li><li>'''The virtual machine will now start''' - start timing your installation and making notes for '''centos1''' virtual machine in the installation comparison chart in lab2 logbook. The virtual machine is running from the live disc at this point, and no software has been installed on the ''hard drive'' of the virtual machine. The point of a live disk is to allow you to test the distribution to see whether you like it without installing to the hard-drive first.</li><li>Double-click '''Install to Hard Drive'''. The installation program, similar to the one used when installing CentOS in Lab 1, will appear. You basically perform the same installation operations for this VM including for '''Date & Time''', '''Network & Hostname''', and '''Installation Destination'''. Make certain to use the '''hostname''': '''<u>centos1</u>''' as opposed to ''c7host'') for this installation. (with a few slight differences).</li><li>For '''Installation Destination''', select the destination option: '''I will configure partitioning''' and then click '''Done'''. Make certain that the '''Partition Scheme''' is set to '''LVM''' and then click on the link: '''Click to Create Automatically'''. '''Done'''. Check to make certain that the root partition has file system type: '''ext4'''.</li><li>Accept the changes and then click '''Begin Installation'''.<ol type="a"><li>You will be required to make selections very similar to what you did in lab1.</li><li>While the system is installing, take a few minutes to record your observations (including slight differences with centos1 install as opposed to c7host install).</li><li>When the installation process is complete, note the time required to install this system and record in the installation comparison chart of your lab2 logbook.<br><br></li></ol></li><li>Power-off your Centos7 LIVE system.</li><li>You should notice that the Centos7 boot menu appears. Either press '''ENTER''' to start or wait for it to start automatically.</li><li>Finish the final steps in the setup process (like you did in lab1).</li><li>#You may want to turn off the screen-saver (like you did in Lab1): [http://zenit.senecac.on.ca/wiki/index.php/OPS235_Lab_1_-_CentOS7#Customizing_Your_Account How to Turn-off Screen Saver (lab1)]</li></ol> | |
| − | + | {| width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | |
| − | + | |- valign="top" | |
| − | + | |colspan="2"|{{Admon/important|Network / Service Considerations|Please perform the tasks below in order allow these CentOS systems to be able to communicate with each other. '''Failure to properly perform these operations can cause problems in future labs'''.| | |
| − | < | + | }} |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | </ol> | ||
| − | |||
<ol> | <ol> | ||
| − | <li value=" | + | <li value="13">Enable SSH access to your virtual machine with these commands (semi-colon allows commands to be run in sequence):<br /> <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">service sshd start; chkconfig sshd on</span></code></b></li> |
| − | </ol> | + | <li>Find out the IP address of your virtual machine and the name of your Ethernet network adaptor: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">ifconfig</span></code></b> </li> |
| + | <li>Enter the following command on your virtual machine to create a firewall exception to allow ssh traffic into the machine:<br /> <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -s0/0 -d0/0 --dport 22 -j ACCEPT</span></code></b></li><li>If you are logged in as root, logout to your regular user account.</li><li>Confirm that you can ssh to your virtual machine from the host (your main CentOS installation): <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">ssh regularuserid@IPaddress</span></code></b> (where '''regularuserid''' is your regular user login id, and '''IPaddress''' is the '''IP_ADDRESS''' of your '''centos1''' VM!).</li><li>Make certain to '''disable SELinux for centos1''' (refer to lab1)</li><li>Adjust your screen-saver settings and run a '''yum update''' on your centos1 VM before proceeding to ''Part 2''</li></ol> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
'''Answer the Investigation 1 observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | '''Answer the Investigation 1 observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | ||
| − | == | + | == Part 2: Installing from a Network == |
| − | + | {| width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | |
| − | {{Admon/ | + | |- valign="top" |
| − | + | |colspan="2"|{{Admon/important|Authenticate to the network|The rest of this lab uses network access.''' Be sure to authenticate to the network using your browser before proceeding'''.}} | |
| − | + | |} | |
| − | + | :'''VM Details:''' | |
| − | + | :: '''VM Name (and hostname):''' centos2 | |
| + | :: '''Boot media:''' Network installation | ||
| + | :: '''Installation source URL:''' http://belmont.senecac.on.ca/centos/7/os/x86_64/ | ||
| + | :: '''VM Image Pathname:''' /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos2.img | ||
| + | :: '''Memory:''' 2048MB | ||
| + | :: '''Disk space:''' 20GB | ||
| + | :: '''CPUs:''' 1 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | # Create the VM (called '''centos2''') as you did with the ''c7host'' machine, except for the following differences:<br><br><ol type="a"><li>Select '''Network Installation''' using the installation source URL displayed above.</li><li>When customizing your partitions, do the same operation that you did in centos1, but after automatically creating the partitions, reduce the size of the root LVM partition to '''8000 MB''' and add an LVM partition with a size of '''2000 MB''' (mount point: '''/home''', name: '''home''', and make certain root and /home partitions have '''ext4''' file system).</li><li>Don't forget to install the GNOME desktop here as you will need a GUI for Centos2<br><br></li></ol> | |
| − | # Create the VM (called '''centos2''') as you did with the '' | + | # Complete the installation. Login to your regular user account, and perform a yum update for the centos2 VM (reboot if required). Make certain to adjust your screen-saver settings if desired. |
| − | + | # Repeat the steps as you did to '''start the SSH service''', '''set iptables to accept connections via ssh''', '''test connections between centos2 and c7host''', and '''disable SELinux''' (refer to lab1). | |
| − | + | # Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations. Record your findings in the Installation Comparison chart in lab2 logbook. | |
| − | |||
| − | # | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | # | ||
'''Answer the Investigation 2 observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | '''Answer the Investigation 2 observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | ||
| − | == | + | == Part 3: Installing from a Network using a Kickstart File == |
| − | + | :'''VM Details:''' | |
| − | + | :: '''VM Name (and hostname):''' centos3 | |
| + | :: '''Boot media:''' Network installation | ||
| + | :: '''Installation source URL:''' http://belmont.senecac.on.ca/centos/7/os/x86_64/ | ||
| + | :: '''Kickstart File URL:''' http://matrix.senecac.on.ca/~andrew.smith/ops235/centos7-kickstart-v01.cfg | ||
| + | :: '''VM Image Pathname:''' /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos3.img | ||
| + | :: '''Memory:''' 2048MB | ||
| + | :: '''Disk space:''' 15GB | ||
| + | :: '''CPUs:''' 1 | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
# Create the VM as you did with the ''centos2'' virtual machine, specifying a network install as before, but specify the kickstart location under the "options section" for network install. What do you think is the purpose of this kickstart file? | # Create the VM as you did with the ''centos2'' virtual machine, specifying a network install as before, but specify the kickstart location under the "options section" for network install. What do you think is the purpose of this kickstart file? | ||
| − | # Observe the installation. How is it different from booting from | + | # Observe the installation. How is it different from booting from a downloaded image? |
| − | # Complete the installation. Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations. | + | # Complete the installation. Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations.<br><br>If the during the installation, you see the message at the bottom '''Pane is Dead''', click the '''Virtual Machine''' menu at the top, select '''Shut Down''' -> '''Force Off''', '''right-click''' on '''centos3''' in the ''virtual manager'' window and select '''Delete'''. Redo the VM setup for a new instance of the ''centos3'' VM. |
# What happens when the installation is finished? | # What happens when the installation is finished? | ||
| − | # Take a look at the kickstart file (eg. view url in a webj-browser) to determine the root password as well as the name and password for the first user account | + | # Take a look at the kickstart file (eg. view url in a webj-browser) to determine the root password as well as the name and password for the first user account! |
# Boot the virtual machine and log in (use the user ID and password information from the previous step). Compare the experience to the first time you booted the other virtual machines. Record this information in the '''table contained in Investigation 4'''. | # Boot the virtual machine and log in (use the user ID and password information from the previous step). Compare the experience to the first time you booted the other virtual machines. Record this information in the '''table contained in Investigation 4'''. | ||
| + | # Repeat the steps as you did to '''start the SSH service''', '''set iptables to accept connections via ssh''', '''test connections between centos3 and c7host''', and '''disable SELinux''' (refer to lab1). | ||
| + | # Remember that centos3 is text-based interface only (no graphics). To recover from a blank screen, press a key (like the SPACE key) to return to the screen display. | ||
| + | # Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations. Record your findings in the Installation Comparison chart in lab2 logbook. | ||
| − | ''' | + | =INVESTIGATION 2: MANAGING VIRTUAL MACHINES= |
| + | == Part 1: Managing Virtual Machines from the Command Line == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | |colspan="2"|{{Admon/note|Manage virtual machines from the host|The commands used to manage virtual machines must be executed on the host (your disk pack) and not inside a virtual machine.}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | # Start the '''centos1''' virtual machine, and stop the '''centos2''' and '''centos3''' virtual machines. | ||
| + | # Switch to the '''c7host''' machine, and open a shell terminal. | ||
| + | # Enter these admin commands into your '''c7host''' machine and note the result: | ||
| + | :: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">virsh list</span></code></b> | ||
| + | :: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">virsh list --all</span></code></b> | ||
| + | :: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">virsh list --inactive</span></code></b> | ||
| + | {| width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | |colspan="2"|{{Admon/note|Virtual Machine Does not Shutdown from Command|If the Virtual machine fails to shutdown from the <code>virsh shutdown</code> command, then you can go to the '''Virtual Machine manager''' and '''halt''' or '''shutdown''' within the VM itself, then you can click the '''PowerOff''' button in the VM window. You'll want to avoid a forced shutdown since those are equivalent to yanking the power cord out of the wall on a physical machine!|}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <ol><li value="4">Now, shut-down your centos1 VM normally, and close the centos1 VM window.</li><li>Switch to your terminal and issue the command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">virsh start centos1</span></code></b></li><li>Using the appropriate command check to see if your centos1 VM is now running.</li><li>There are other commands that can be used (such as '''suspend''', or '''shutdown'''). The "shutdown" command may not always work since it relies on the guest handling a particular ACPI event. Why do you think it is useful to have commands to manipulate VMs?</li><li>Since this is a text-based version of Linux, you do not need to turn off the screen-saver.</li></ol> | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | '''Answer all observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | |
| + | == Part 2: Backing Up Virtual Machines == | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | {| width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | |colspan="2"|{{Admon/important|Backing up VMs|There are two general processes in order to back up your images:<ol><li>'''Compressing your images''' (also recommended to backup up to external storage USB Key) using the '''gzip''' command.</li><li>'''Backup the VM xml configuration file''' (preferably to USB key) using '''virsh''' shell command to add VM to virtual machine manager list (in the event that the HOST machine is "wiped" and re-installed, but VM images and xml configuration files have been backed up external storage).</li></ol><br />Taking the time to backup the image of the Operating System's file system allows the user to return to a '''"restoration point"''' using the '''gunzip''' command in case something bad occurs to the OS during a lab.<br />Failure to take the time to make and confirm backups can result in loss of lab work for the student!|}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | # Shut down all of the virtual machines. | ||
| + | # Change to the directory <b><code>/var/lib/libvirt/images/</code></b>. Note the size of the files in this directory. What do these files contain? | ||
| + | # Make a compressed backup of the '''centos3.img''' file to your home directory with this command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">gzip < centos3.img > ~YourUserId/centos3.img.backup.gz</span></code></b><br />(Note: Make certain to use the redirection signs "<" and ">" properly in the command!) | ||
| + | # Compare the size of the compressed and original files (hint: use '''ls -lh'''). If file is very large (like 15GB), you didn't compress it and you need to remove that file and perform the previous step until you get it right! | ||
| + | # Start the '''''centos3''''' VM. | ||
| + | # '''Make certain that you are in your VM and <u>not</u> in your main system!''' | ||
| + | # Wreck <u>only</u> your centos3 system! Try this command inside the centos3 virtual machine:<b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">rm -rf /*</span></code></b> (ignore error messages). | ||
| + | # Shut down the centos3 VM. If you tried to start the centos3 VM, it would not boot since all system files have been removed! | ||
| + | # Restore the original image from the backup in your home directory by typing this command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">gunzip < ~YourUserId/centos3.img.backup.gz > centos3.img'''</span></code></b> | ||
| + | # Restart the VM. Is it working normally? | ||
| + | # Create compressed backups of your other virtual machines (ie. '''centos1''' and '''centos2'''). | ||
| + | # You should make a copy of the xml configuration file in case you "wipe" and re-install the host machine, and want to add a restored VM backups to the virtual machine manager list. We will demonstrate using the centos3 xml configuration file, and prove that a "clone" can be added to your list.Please perform the following step: | ||
| + | # Execute the following command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">virsh dumpxml centos3 > centos3.xml</span></code></b> | ||
| + | # Examine the file <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">centos3.xml</span></code></b>. What does it contain? What format is it in?<br><br> | ||
| + | # We will now learn how to download a compressed image file and xml configuration file and add it as a VM to the virtual manager menu. | ||
| + | # Issue the following commands:<ul><li><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">wget http://cs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/ops235/practical1.img.gz</span></code></b></li><li><b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">wget https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/ops235/practical1.xml</span></code></b><br><br></li></ul> | ||
| + | <ol><li value="17">Copy these files to the '''/var/lib/libvirt/images''' directory and decompress the image</li><li>Make certain your present working directory is: '''/var/lib/libvirt/images'''</li><li>Issue the command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">virsh define practical1.xml</span></code></b></li><li>What happened in the virtual manager window? To remove a VM entry in the Virtual Manager window, simply issue the command: '''virsh undefine vm_name''' (without the '''.xml''' file extension)</li><li> Launch the VM to see if it boots-up</li><li>Can you log into this VM? Perhaps your instructor will give you a clue in week #7... >;p<br><br></li></ol> | ||
| + | {| width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | |colspan="2"|{{Admon/tip|Shutting Down the Host while Virtual Machines are Running|If you shut down your host system while virtual machines are running, they will be suspended, and will resume the next time you boot your host system.}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | <ol> | ||
| + | <li value="22">For the remainder of these labs, it is assumed that you will backup <u>'''both'''</u> the images and xml configuration files for <u>'''all'''</u> Virtual machines, when asked to backup your virtual machines. It is also highly recommended to backup these files to an external storage device (eg. USB key) in case the host machine gets "wiped" and you need to rebuild your HOST machine and then restore your Virtual Machines...</li> | ||
| + | <li>Answer this question in your log book:</li> | ||
| + | </ol> | ||
| + | ::* In order to fully back up a virtual machine, what information should be saved in addition to the virtual machine image? | ||
| + | <ol><li value="24">A previous OPS235 student graciously created a shell script that you can download and run to check to see how you performed this lab (to see if you are on the right track).<br>Simply issue the command: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">wget http://matrix.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/ops235/lab2check2.bash</span></code></b> and run on your '''c7host machine'''.<br><br>'''If the shell script indicates any major errors, please inform your OPS235 instructor or lab assistant to advise what to do'''.<br><br></li></ol> | ||
| − | + | '''Answer the Investigation observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | |
| + | = INVESTIGATION 3: LOOKING AHEAD = | ||
| − | == | + | ==Part 1: Automating Routine Tasks (Shell Scripting)== |
| + | {|width="40%" align="right" cellpadding="10" | ||
| + | |- valign="top" | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | {{Admon/tip|Bash Shell Scripting Tips:|<br><ul><li>'''Data Input:'''<br><br>A shell script can obtain data from a number of methods: '''reading input files''', using '''arguments when issuing command''' (positional parameters), or '''prompting for data to store in a variable'''. The later method can be accomplished by using the '''read''' command, for example: '''read -p "Enter your name: " userName'''.<br><br></li><li>'''Mathematical Expressions:'''<br><br>In shell scripting, data is stored in variable as text, not other data types (ints, floats, chars, etc) like in compiled programs like C or Java. In order to have a shell script perform '''mathematical operations''', number or variable need to be surrounded by two sets of parenthesis '''((..))''' in order to convert a number stored as text to a binary number.<br><br><u>'''Examples'''</u><br><br>''var1=5;var2=10''<br>''echo "$var1 + $var2 = $((var1+var2))"''<br><br>'''Note:''' shell does not perform floating point calculations (like '''5/10'''). Instead, other commands like '''awk''' or '''bc''' would be required for floating point calculations (decimals)<br><br></li><li>'''Loops (iteration):'''<br><br>Loops and logic are a very important elements of shell scripting (not to mention programming as well). Determinant loops (such as '''for''' loops) usually repeat for a preset number of times (eg. counts, positional parameters stored). In-determinant loops (such as '''while''' or '''until''' loops) may repeat based on unknown conditions (like waiting for user to enter correct data). Test conditions can be used with in-determinant loops, or even commands! If a command runs successfully (eg ls, cd, grep matching a pattern), zero (true) value is returned, otherwise a non-zero (false) value is returned. Command options or redirection to /'''dev/null''' can be used to just test if command runs, but not display stdout or stderr. Conditional statements "and" (&&) / "or" (||) can also be used when testing multiple conditions.<br><br>'''<u>Examples (try in a shell script)</u>'''<br><br>''set ops235 is fun''<br>''for x''<br>''do''<br> ''echo "argument is $x"''<br>''done''<br><br>''for x in $(ls)''<br>''do''<br> ''echo "Filename: $x"''<br>''done''<br><br>''read -p "enter a whole number: " num''<br>''until echo $num | grep -q "^[0-9][0-9]*$"''<br>''do''<br> ''read -p "Incorrect. Please enter WHOLE NUMBER: " num''<br>''done''<br><br>''read -p "pick a number between 1 and 10: " num''<br>''while [ $num -lt 1 ] || [ $num -gt 10 ]<br>''do''<br> ''read -p "Incorrect. Please pick number between 1 and 10: " num''<br>''done''<br><br></li></ul>}} | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | You will continue our use of Bash Shell scripting by first creating a Bash Shell script that will allow the Linux sysadmin to select their created VMs for backup to root's home directory. Afterwards you will download, view and run a couple Bash Shell scripts that use the virsh command to start and stop your virtual machines. | |
| − | + | If you require <u>'''additional practice'''</u> in creating shell scripts using logic, loops and mathematical operations, run the commands in your '''Matrix''' account: <ul><li>'''/home/murray.saul/scripting-2'''</li><li>'''/home/murray.saul/scripting-3'''</li></ul> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | Perform the following steps in your c7host machine: | |
| − | ' | + | # Open a Bash shell terminal and login as root. |
| + | # Use a text editor (such as <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">vi</span></code></b> or <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">nano</span></code></b>) to create a Bash Shell script called: <b><code><span style="color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">backupVM.bash</span></code></b> in /root's home directory. | ||
| + | # Enter the following text content into your text-editing session: | ||
| + | <code style="color:#3366CC;font-family:courier;font-size:.9em;margin-left:20px;"> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | #!/bin/bash | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | # backupVM.bash<br> | |
| + | # Purpose: Creates system info report<br> | ||
| + | #<br> | ||
| + | # USAGE: ./report.bash<br> | ||
| + | #<br> | ||
| + | # Author: *** INSERT YOUR NAME ***<br> | ||
| + | # Date: *** CURRENT DATE *** | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | if [ $PWD != "/root" ] # only runs if in root's directory<br> | |
| + | then<br> echo "You must be located in /root" >&2<br> | ||
| + | exit 1<br> | ||
| + | fi | ||
| + | </code> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <ol><li value="4">Save your editing session, but remain in the text editor.</li><li>This shell script is designed particularly for your centos1, centos2, and centos3 VMS.</li><li>The code displayed below will prompt the user if they wish for all VMs to be backed-up; otherwise, allow the user the option of specifying which VMs to be backed-up. Add the following code</li></ol> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <code style="color:#3366CC;font-family:courier;font-size:.9em;"> | ||
| − | + | read -p "Backup all VMs? (y|n):" answer # prompt if all VMs to be backed-up | |
| − | + | if [ "$answer" = "y" ] # Backup all VMs if answer is yes<br> | |
| + | then<br> | ||
| + | for num in 1 2 3 # Determinant loop for 3 arguments: 1, 2, and 3<br> | ||
| + | do<br> | ||
| + | echo "Backing up VM #$num"<br> | ||
| + | gzip < /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos$num.img > /root/centos$num.img.backup.gz<br> | ||
| + | <br> echo "VM #$num BACKUP DONE"<br> | ||
| + | done<br><br> | ||
| + | elif [ "$answer" = "n" ]<br> | ||
| + | then<br> | ||
| + | read -p "Which VM should be backed up? (1/2/3): " numanswer<br> | ||
| + | until echo $numanswer | grep "^[123]$" >> /dev/null # Look for match of single digit: 1,2, or 3<br> | ||
| + | do<br> | ||
| + | read -p "Invalid Selection. Select 1, 2, or 3: " numanswer<br> | ||
| + | done<br> | ||
| + | echo "Backing up VM #$numanswer"<br> | ||
| + | gzip < /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos$numanswer.img > /root/centos$numanswer.img.backup.gz<br><br> | ||
| + | echo "VM #$numanswer BACKUP DONE":<br> | ||
| + | else<br> | ||
| + | echo "Invalid Selection... Aborting program"<br> | ||
| + | exit 2<br> | ||
| + | fi | ||
| − | + | </code> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | '''Answer | + | <ol> |
| + | <li value="7">Save, set permissions, and then run that shell script to backup centos1. Confirm that this script did backup this image to root's home directory</li><li>Use the <b><code>wget</code></b> command to download, study, and run the following shell scripts on-line:<blockquote><b><code><span style=" pointer-events:none;cursor:default;color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/vm-start-text.bash<br>https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/vm-stop-text.bash</span></code></b><br><b><code><span style=" pointer-events:none;cursor:default;color:#3366CC;font-size:1.2em;">https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/vm-start.bash<br>https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/vm-stop.bash</span></code></b></blockquote></li><li>Try to understand what these Bash Shell scripts do.</li><li>You have completed lab2. Proceed to Completing The Lab, and follow the instructions for "lab sign-off".</li></ol> | ||
| + | '''Answer all observations / questions in your lab log book.''' | ||
| − | = | + | = LAB 2 SIGN-OFF (SHOW INSTRUCTOR) = |
| + | {{Admon/important|Time for a new backup!|If you have successfully completed this lab, make a new backup of your virtual machines as well as your host machine.}} | ||
| − | '''Arrange | + | '''Arrange proof of the following on the screen:''' |
| − | # | + | <ol><li><span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span> '''<u>All</u> VMs''':<blockquote><ul><li>Working virtual machines '''created''' and '''running'''</li><li>'''Disk layout''' and '''size''' correct on all virtual machines</li><li> Proof of '''yum updates'''</li><li>'''All virtual machines backed-up''' (eg. usb stick and/or home directory)</li></ul></blockquote></li><li><span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>'''c7host''' machine:<blockquote><ul><li>'''Correct VM image filenames''' contained in '''/var/lib/libvirt/images directory'''</li><li>Creation of your bash shell script called '''backupVM.bash'''</li><li>A list of your '''iptables''' rules (command: '''iptables -L''')</li></ul></blockquote></li><li><span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span> Lab2 logbook notes and '''Installation Comparison chart''' completed</li></ol> |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | # | ||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | == Practice For Quizzes, Tests, Midterm & Final Exam == |
# What is the name of the CentOS installation program? | # What is the name of the CentOS installation program? | ||
| − | # | + | # What is the name of the file created by the CentOS installation program? |
# Which type of installation works best for confirming compatibility with hardware before installation? Why? | # Which type of installation works best for confirming compatibility with hardware before installation? Why? | ||
# Which type of installation works best for installing large numbers of computers? Why? | # Which type of installation works best for installing large numbers of computers? Why? | ||
| − | |||
# How can you reduce the number of software updates required immediately after installation? | # How can you reduce the number of software updates required immediately after installation? | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
# How do you start and stop virtual machines? | # How do you start and stop virtual machines? | ||
# How do you SSH into your virtual machines? | # How do you SSH into your virtual machines? | ||
| − | # What is | + | # What is procedure to backup your VM images (and XML config files) to your USB key? |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
# The kickstart installation (centos3) was a network installation. Can a kickstart file be used with a DVD installation? | # The kickstart installation (centos3) was a network installation. Can a kickstart file be used with a DVD installation? | ||
# The kickstart installation (centos3) was fairly fast. Why? Under what circumstances would it take a long time, even on a fast network? | # The kickstart installation (centos3) was fairly fast. Why? Under what circumstances would it take a long time, even on a fast network? | ||
| − | + | ||
[[Category:OPS235]] | [[Category:OPS235]] | ||
[[Category:OPS235 Labs]] | [[Category:OPS235 Labs]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:28, 24 September 2018
Contents
LAB PREPARATION
Purpose / Objectives of Lab2
In this lab, you will create three virtual machines. This also gives you an opportunity to experiment with different ways of installing CentOS.
Main Objectives
- Installing Virtualization Software on your c7host machine
- Create 3 separate VMs (virtual machines) using different installation methods:
- Centos Live DVDInstallation
- Network Installation without configuration file
- Network Installation with configuration file (Kickstart)
- Understand the advantages and disadvantages of each type of installation, and be able to select the best installation method for a particular situation.
- Manipulate virtual machines by CLI (virsh)
- Properly backup VMs and VM configuration in virtual manager application onto home directory and to external source (USB Key)
- Observe how Bash Shell Scripting can be used to automate routine tasks involving VM management
What is a Virtual Machine?
A virtual machine is a software simulation of a computer which can be used as though it were actual hardware. It's possible to run multiple virtual machines on one computer, reducing hardware requirements and promoting flexibility when working with multiple operating systems. Some common uses of virtualization include:
- Software testing -- Using multiple operating systems simultaneously on a single computer for testing and experimentation.
- Network simulation -- Testing network services, protocols, and security scenarios with a small number of computers.
- Isolation -- Protecting multiple sets of data by storing them on multiple virtual machines. If one of the virtual machines is compromised, the data on other virtual machines is still protected.
- Server consolidation -- Reducing the number of physical servers in a network by moving physical machines to virtual machines. This saves hardware, administration, cooling, and electricity costs, and it can increase the utilization of hardware (by ensuring that the hardware is not under-loaded).
- Load-balancing and disaster recovery -- It is possible to migrate virtual machines between different physical machines, to ensure that a workload is balanced across multiple computers, to allow routine hardware maintenance and upgrading, and to compensate for hardware failure or other disasters.
Minimum Required Materials
My Toolkit (CLI Reference)
| Virtualization: | Commands | Installation Guides
Installing & Using KVM on CentOS |
INVESTIGATION 1: USING VIRTUALIZATION SOFTWARE TO CREATE VIRTUAL MACHINES
Virtualization Application Setup / Comparison Chart
Record VM Installation in Lab2 (Installation Comparison Chart):
You will be learning to perform several different type of CENTOS Linux installs. Lab2 already has an empty table for comparing various Linux installs. You were required in lab1 to record your observation for your c7host installation.
As you proceed throughout this lab, you will be required to fill in the comparison chart for three of the VMs (virtual machines) that you will be installing.
Complete the following steps to install and run the virtual manager application:
- Open a web-browser, and open the OPS235 Lab #2 WIKI.
- Open a shell terminal.
WARNING: You must perform a yum update on your c7host machine before proceeding with the next steps. - You will need to download an image file for the Centos7 LIVE DVD by issuing the following command (best works while at Seneca):
wget http://belmont.senecac.on.ca/centos/7/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7-x86_64-LiveGNOME-1511.iso - Install the virtualization software by issuing the command:
yum install qemu-kvm qemu-img virt-manager libvirt libvirt-python \
python-virtinst libvirt-client virt-install virt-viewer bridge-utils
- This will install many applications (including):
- kvm/qemu - the hypervisor and other hardware emulation systems.
- A system service named libvirtd that manages the VMs.
- A graphical tool for managing virtual machines (virt-manager) and the virsh command-line tool.
- This will install many applications (including):
- Start the virtualization service:
service libvirtd start - The firewall configuration is altered by the addition of the virtualization software. Centos7 uses firewalld for firewall, but we will be switching back to using iptables. Issue the following series of command to install iptables and restart the firewall:
systemctl stop firewalldsystemctl mask firewalldyum install iptables-servicessystemctl enable iptablessystemctl start iptablesservice iptables save
- Start the graphical tool by selecting the menu options Applications>System Tools>Virtual Machine Manager or by typing the command
virt-manager
Part 1: Installing from a Downloaded Image (Centos7 LIVE CD)
- VM Details:
- VM Name (and hostname): centos1
- Boot media: LIVE CD Image
- Installation source: Downloaded Centos7 LIVE CD image (http://belmont.senecac.on.ca/centos/7/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7-x86_64-LiveGNOME-1511.iso)
- VM Image Pathname: /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos1.img
- Memory: 2GB
- Disk space: 10GB
- File System (root partition): ext4
- CPUs: 1
- Make certain you used the wget command to download the LiveGNOME iso file from the Belmont server (from previous instructions).
- In the Virtual Machine Manger, click on the icon to Create a Virtual Machine in the upper-left corner:
- A window will appear with the title New VM. There are five steps to be completed; click Forward after each step:
- Step 1 of 5:Select Local install media and click Forward.
- Step 2 of 5: Select Use ISO Image, click the Browse button, and then the Browse Local button. Navigate to the location of the downloaded Centos7 LIVE CD image, select the image file and click Open. When finished, click Forward to proceed.
- Step 3 of 5: Set the memory to 2048 MB and the number of CPUs to 1
- Step 4 of 5: This next step creates a disk file that will be used to simulate the virtual machine's disk drive. Select a size of 10 GB. Click on
Select managed or other existing storage and type the VM image file pathame:
/var/lib/libvirt/images/centos1.img (make certain that the pathname is correct) and then click Forward to proceed. - Step 5 of 5: Enter the virtual machine name: centos1. Review the VM information, and click Finish.
- The virtual machine will now start - start timing your installation and making notes for centos1 virtual machine in the installation comparison chart in lab2 logbook. The virtual machine is running from the live disc at this point, and no software has been installed on the hard drive of the virtual machine. The point of a live disk is to allow you to test the distribution to see whether you like it without installing to the hard-drive first.
- Double-click Install to Hard Drive. The installation program, similar to the one used when installing CentOS in Lab 1, will appear. You basically perform the same installation operations for this VM including for Date & Time, Network & Hostname, and Installation Destination. Make certain to use the hostname: centos1 as opposed to c7host) for this installation. (with a few slight differences).
- For Installation Destination, select the destination option: I will configure partitioning and then click Done. Make certain that the Partition Scheme is set to LVM and then click on the link: Click to Create Automatically. Done. Check to make certain that the root partition has file system type: ext4.
- Accept the changes and then click Begin Installation.
- You will be required to make selections very similar to what you did in lab1.
- While the system is installing, take a few minutes to record your observations (including slight differences with centos1 install as opposed to c7host install).
- When the installation process is complete, note the time required to install this system and record in the installation comparison chart of your lab2 logbook.
- Power-off your Centos7 LIVE system.
- You should notice that the Centos7 boot menu appears. Either press ENTER to start or wait for it to start automatically.
- Finish the final steps in the setup process (like you did in lab1).
- #You may want to turn off the screen-saver (like you did in Lab1): How to Turn-off Screen Saver (lab1)
- Enable SSH access to your virtual machine with these commands (semi-colon allows commands to be run in sequence):
service sshd start; chkconfig sshd on - Find out the IP address of your virtual machine and the name of your Ethernet network adaptor:
ifconfig - Enter the following command on your virtual machine to create a firewall exception to allow ssh traffic into the machine:
iptables -I INPUT -p tcp -s0/0 -d0/0 --dport 22 -j ACCEPT - If you are logged in as root, logout to your regular user account.
- Confirm that you can ssh to your virtual machine from the host (your main CentOS installation):
ssh regularuserid@IPaddress(where regularuserid is your regular user login id, and IPaddress is the IP_ADDRESS of your centos1 VM!). - Make certain to disable SELinux for centos1 (refer to lab1)
- Adjust your screen-saver settings and run a yum update on your centos1 VM before proceeding to Part 2
Answer the Investigation 1 observations / questions in your lab log book.
Part 2: Installing from a Network
- VM Details:
- VM Name (and hostname): centos2
- Boot media: Network installation
- Installation source URL: http://belmont.senecac.on.ca/centos/7/os/x86_64/
- VM Image Pathname: /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos2.img
- Memory: 2048MB
- Disk space: 20GB
- CPUs: 1
- Create the VM (called centos2) as you did with the c7host machine, except for the following differences:
- Select Network Installation using the installation source URL displayed above.
- When customizing your partitions, do the same operation that you did in centos1, but after automatically creating the partitions, reduce the size of the root LVM partition to 8000 MB and add an LVM partition with a size of 2000 MB (mount point: /home, name: home, and make certain root and /home partitions have ext4 file system).
- Don't forget to install the GNOME desktop here as you will need a GUI for Centos2
- Complete the installation. Login to your regular user account, and perform a yum update for the centos2 VM (reboot if required). Make certain to adjust your screen-saver settings if desired.
- Repeat the steps as you did to start the SSH service, set iptables to accept connections via ssh, test connections between centos2 and c7host, and disable SELinux (refer to lab1).
- Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations. Record your findings in the Installation Comparison chart in lab2 logbook.
Answer the Investigation 2 observations / questions in your lab log book.
Part 3: Installing from a Network using a Kickstart File
- VM Details:
- VM Name (and hostname): centos3
- Boot media: Network installation
- Installation source URL: http://belmont.senecac.on.ca/centos/7/os/x86_64/
- Kickstart File URL: http://matrix.senecac.on.ca/~andrew.smith/ops235/centos7-kickstart-v01.cfg
- VM Image Pathname: /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos3.img
- Memory: 2048MB
- Disk space: 15GB
- CPUs: 1
- Create the VM as you did with the centos2 virtual machine, specifying a network install as before, but specify the kickstart location under the "options section" for network install. What do you think is the purpose of this kickstart file?
- Observe the installation. How is it different from booting from a downloaded image?
- Complete the installation. Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations.
If the during the installation, you see the message at the bottom Pane is Dead, click the Virtual Machine menu at the top, select Shut Down -> Force Off, right-click on centos3 in the virtual manager window and select Delete. Redo the VM setup for a new instance of the centos3 VM. - What happens when the installation is finished?
- Take a look at the kickstart file (eg. view url in a webj-browser) to determine the root password as well as the name and password for the first user account!
- Boot the virtual machine and log in (use the user ID and password information from the previous step). Compare the experience to the first time you booted the other virtual machines. Record this information in the table contained in Investigation 4.
- Repeat the steps as you did to start the SSH service, set iptables to accept connections via ssh, test connections between centos3 and c7host, and disable SELinux (refer to lab1).
- Remember that centos3 is text-based interface only (no graphics). To recover from a blank screen, press a key (like the SPACE key) to return to the screen display.
- Record the time taken to install, and compare this to the time taken by the previous installations. Record your findings in the Installation Comparison chart in lab2 logbook.
INVESTIGATION 2: MANAGING VIRTUAL MACHINES
Part 1: Managing Virtual Machines from the Command Line
- Start the centos1 virtual machine, and stop the centos2 and centos3 virtual machines.
- Switch to the c7host machine, and open a shell terminal.
- Enter these admin commands into your c7host machine and note the result:
-
virsh list -
virsh list --all -
virsh list --inactive
-
- Now, shut-down your centos1 VM normally, and close the centos1 VM window.
- Switch to your terminal and issue the command:
virsh start centos1 - Using the appropriate command check to see if your centos1 VM is now running.
- There are other commands that can be used (such as suspend, or shutdown). The "shutdown" command may not always work since it relies on the guest handling a particular ACPI event. Why do you think it is useful to have commands to manipulate VMs?
- Since this is a text-based version of Linux, you do not need to turn off the screen-saver.
Answer all observations / questions in your lab log book.
Part 2: Backing Up Virtual Machines
- Shut down all of the virtual machines.
- Change to the directory
/var/lib/libvirt/images/. Note the size of the files in this directory. What do these files contain? - Make a compressed backup of the centos3.img file to your home directory with this command:
gzip < centos3.img > ~YourUserId/centos3.img.backup.gz
(Note: Make certain to use the redirection signs "<" and ">" properly in the command!) - Compare the size of the compressed and original files (hint: use ls -lh). If file is very large (like 15GB), you didn't compress it and you need to remove that file and perform the previous step until you get it right!
- Start the centos3 VM.
- Make certain that you are in your VM and not in your main system!
- Wreck only your centos3 system! Try this command inside the centos3 virtual machine:
rm -rf /*(ignore error messages). - Shut down the centos3 VM. If you tried to start the centos3 VM, it would not boot since all system files have been removed!
- Restore the original image from the backup in your home directory by typing this command:
gunzip < ~YourUserId/centos3.img.backup.gz > centos3.img - Restart the VM. Is it working normally?
- Create compressed backups of your other virtual machines (ie. centos1 and centos2).
- You should make a copy of the xml configuration file in case you "wipe" and re-install the host machine, and want to add a restored VM backups to the virtual machine manager list. We will demonstrate using the centos3 xml configuration file, and prove that a "clone" can be added to your list.Please perform the following step:
- Execute the following command:
virsh dumpxml centos3 > centos3.xml - Examine the file
centos3.xml. What does it contain? What format is it in? - We will now learn how to download a compressed image file and xml configuration file and add it as a VM to the virtual manager menu.
- Issue the following commands:
- Copy these files to the /var/lib/libvirt/images directory and decompress the image
- Make certain your present working directory is: /var/lib/libvirt/images
- Issue the command:
virsh define practical1.xml - What happened in the virtual manager window? To remove a VM entry in the Virtual Manager window, simply issue the command: virsh undefine vm_name (without the .xml file extension)
- Launch the VM to see if it boots-up
- Can you log into this VM? Perhaps your instructor will give you a clue in week #7... >;p
- For the remainder of these labs, it is assumed that you will backup both the images and xml configuration files for all Virtual machines, when asked to backup your virtual machines. It is also highly recommended to backup these files to an external storage device (eg. USB key) in case the host machine gets "wiped" and you need to rebuild your HOST machine and then restore your Virtual Machines...
- Answer this question in your log book:
- In order to fully back up a virtual machine, what information should be saved in addition to the virtual machine image?
- A previous OPS235 student graciously created a shell script that you can download and run to check to see how you performed this lab (to see if you are on the right track).
Simply issue the command:wget http://matrix.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/ops235/lab2check2.bashand run on your c7host machine.
If the shell script indicates any major errors, please inform your OPS235 instructor or lab assistant to advise what to do.
Answer the Investigation observations / questions in your lab log book.
INVESTIGATION 3: LOOKING AHEAD
Part 1: Automating Routine Tasks (Shell Scripting)
You will continue our use of Bash Shell scripting by first creating a Bash Shell script that will allow the Linux sysadmin to select their created VMs for backup to root's home directory. Afterwards you will download, view and run a couple Bash Shell scripts that use the virsh command to start and stop your virtual machines.
If you require additional practice in creating shell scripts using logic, loops and mathematical operations, run the commands in your Matrix account:- /home/murray.saul/scripting-2
- /home/murray.saul/scripting-3
Perform the following steps in your c7host machine:
- Open a Bash shell terminal and login as root.
- Use a text editor (such as
viornano) to create a Bash Shell script called:backupVM.bashin /root's home directory. - Enter the following text content into your text-editing session:
#!/bin/bash
# backupVM.bash
# Purpose: Creates system info report
#
# USAGE: ./report.bash
#
# Author: *** INSERT YOUR NAME ***
# Date: *** CURRENT DATE ***
if [ $PWD != "/root" ] # only runs if in root's directory
then
echo "You must be located in /root" >&2
exit 1
fi
- Save your editing session, but remain in the text editor.
- This shell script is designed particularly for your centos1, centos2, and centos3 VMS.
- The code displayed below will prompt the user if they wish for all VMs to be backed-up; otherwise, allow the user the option of specifying which VMs to be backed-up. Add the following code
read -p "Backup all VMs? (y|n):" answer # prompt if all VMs to be backed-up
if [ "$answer" = "y" ] # Backup all VMs if answer is yes
then
for num in 1 2 3 # Determinant loop for 3 arguments: 1, 2, and 3
do
echo "Backing up VM #$num"
gzip < /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos$num.img > /root/centos$num.img.backup.gz
echo "VM #$num BACKUP DONE"
done
elif [ "$answer" = "n" ]
then
read -p "Which VM should be backed up? (1/2/3): " numanswer
until echo $numanswer | grep "^[123]$" >> /dev/null # Look for match of single digit: 1,2, or 3
do
read -p "Invalid Selection. Select 1, 2, or 3: " numanswer
done
echo "Backing up VM #$numanswer"
gzip < /var/lib/libvirt/images/centos$numanswer.img > /root/centos$numanswer.img.backup.gz
echo "VM #$numanswer BACKUP DONE":
else
echo "Invalid Selection... Aborting program"
exit 2
fi
- Save, set permissions, and then run that shell script to backup centos1. Confirm that this script did backup this image to root's home directory
- Use the
wgetcommand to download, study, and run the following shell scripts on-line:https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/vm-start-text.bash
https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/vm-stop-text.bashhttps://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/vm-start.bash
https://scs.senecac.on.ca/~murray.saul/vm-stop.bash - Try to understand what these Bash Shell scripts do.
- You have completed lab2. Proceed to Completing The Lab, and follow the instructions for "lab sign-off".
Answer all observations / questions in your lab log book.
LAB 2 SIGN-OFF (SHOW INSTRUCTOR)
Arrange proof of the following on the screen:
- ✓ All VMs:
- Working virtual machines created and running
- Disk layout and size correct on all virtual machines
- Proof of yum updates
- All virtual machines backed-up (eg. usb stick and/or home directory)
- ✓c7host machine:
- Correct VM image filenames contained in /var/lib/libvirt/images directory
- Creation of your bash shell script called backupVM.bash
- A list of your iptables rules (command: iptables -L)
- ✓ Lab2 logbook notes and Installation Comparison chart completed
Practice For Quizzes, Tests, Midterm & Final Exam
- What is the name of the CentOS installation program?
- What is the name of the file created by the CentOS installation program?
- Which type of installation works best for confirming compatibility with hardware before installation? Why?
- Which type of installation works best for installing large numbers of computers? Why?
- How can you reduce the number of software updates required immediately after installation?
- How do you start and stop virtual machines?
- How do you SSH into your virtual machines?
- What is procedure to backup your VM images (and XML config files) to your USB key?
- The kickstart installation (centos3) was a network installation. Can a kickstart file be used with a DVD installation?
- The kickstart installation (centos3) was fairly fast. Why? Under what circumstances would it take a long time, even on a fast network?