Difference between revisions of "GPU610/DPS915 CUDA PI"
Peter Huang (talk | contribs) (→Progress) |
Peter Huang (talk | contribs) (→Conclusion) |
||
| (13 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== '''Progress''' == | == '''Progress''' == | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
=== '''Assignment 1''' === | === '''Assignment 1''' === | ||
==== '''Introduction''' ==== | ==== '''Introduction''' ==== | ||
| Line 23: | Line 26: | ||
==== '''Code Snippet''' ==== | ==== '''Code Snippet''' ==== | ||
| − | + | Serial Pi Calculation Algorithm | |
| − | + | ||
| − | for(i = 0; i < points; i++) | + | // loops through user amount of rounds of sets of points |
| − | { | + | for(i = 0; i < points; i++) |
| − | x = randNum(); | + | { |
| − | y = randNum(); | + | x = randNum(); |
| − | + | y = randNum(); | |
| − | // check if point resides within the circle | + | |
| − | if (((x*x) + (y*y)) <= 1.0) | + | // check if point resides within the circle |
| − | { | + | if (((x*x) + (y*y)) <= 1.0) |
| − | score++; | + | { |
| − | } | + | score++; |
| − | } | + | } |
| − | + | } | |
| − | // calculate pi | + | // calculate pi |
| − | pi = 4.0 * (float)score/(float)points; | + | pi = 4.0 * (float)score/(float)points; |
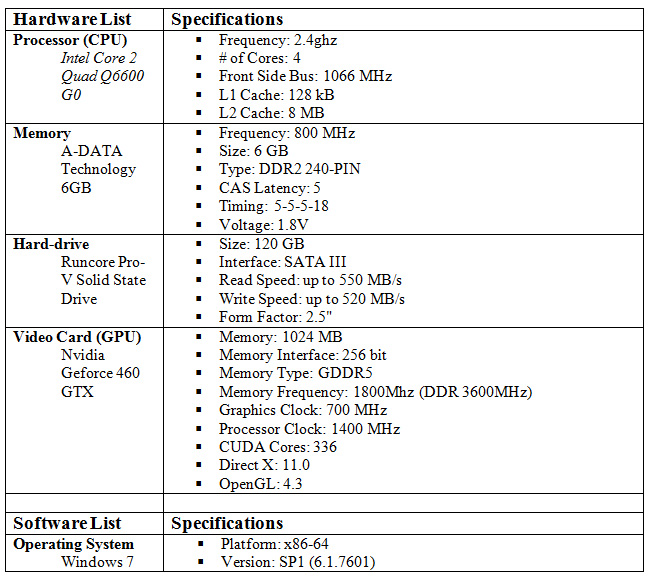
| + | ==== '''Software and Hardware''' ==== | ||
| + | [[File:Pi_software_and_hardware_list.jpg|border]] | ||
| + | ==== '''Program Execution Plan''' ==== | ||
| + | Pi serial tests would be conducted with sample counts up to 1 billion. Between 100 million and 1 billion, a sample count of 134217728 is sampled as that is the maximum sample value allowed for the Nvidia 460 GTX without generating memory allocation errors. | ||
==== '''Compilation and Running''' ==== | ==== '''Compilation and Running''' ==== | ||
| Line 47: | Line 54: | ||
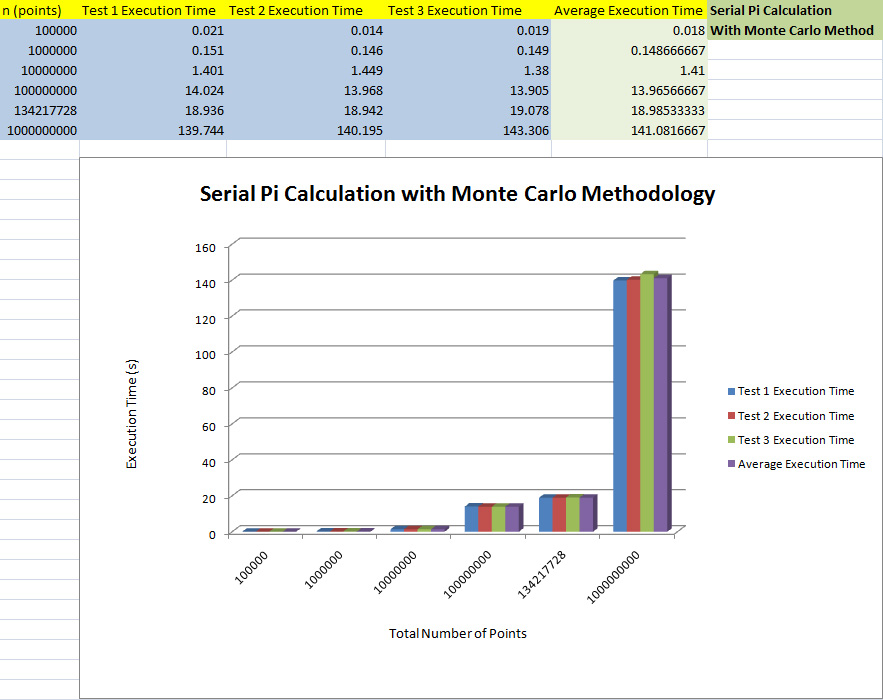
==== '''Serial Results''' ==== | ==== '''Serial Results''' ==== | ||
[[File:Pi_serial_results.jpg|border]] | [[File:Pi_serial_results.jpg|border]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== '''Conclusion''' ==== | ||
| + | As the sample count increases, the execution time of the program also increases. The Big-O Classification for ''pi_serial'' is O(1). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
=== '''Assignment 2''' === | === '''Assignment 2''' === | ||
==== '''Introduction''' ==== | ==== '''Introduction''' ==== | ||
In Phase 2, I've parallelized the serial program to run on a custom kernel on a CUDA-enabled device. | In Phase 2, I've parallelized the serial program to run on a custom kernel on a CUDA-enabled device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== '''Source File(s)''' ==== | ||
| + | Link: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B8GUuIUqdEJEbDBRNkhWYnpGSnM | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== '''Code Snippet''' ==== | ||
| + | Working Kernel Parallel CUDA Pi Calculation | ||
| + | |||
| + | __global__ void findPi(float *estimatedPi, curandState *states, unsigned int taskElements, float seed) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | unsigned int task_id = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x; // linear sequence of threads x-axis | ||
| + | int score = 0; | ||
| + | float xCoord; | ||
| + | float yCoord; | ||
| + | |||
| + | // 'random' generated value using curand, initialize curand using task_id, and seed parameter | ||
| + | curand_init(seed, task_id, 0, &states[task_id]); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // tally number of task elements | ||
| + | for(int i = 0; i < taskElements; i++) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |||
| + | // assigned each point coordinate values | ||
| + | xCoord = curand_uniform (&states[task_id]); | ||
| + | yCoord = curand_uniform (&states[task_id]); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // determine if coordinate is within the circle | ||
| + | if((xCoord*xCoord + yCoord*yCoord) <= 1.0f) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | score++; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // estimated value of pi for this particular task | ||
| + | estimatedPi[task_id] = (4.0f * score) / (float)taskElements; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== '''Software and Hardware''' ==== | ||
| + | [[File:Pi_software_and_hardware_list.jpg|border]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== '''Program Execution Plan''' ==== | ||
| + | Pi cuda tests would be conducted with sample counts starting at 100 thousand, with incremental multiplier of 10, to the maximum supported sample count of 134217728 (memory constraint on Nvidia 460 GTX). The blocks and threads values will be 128, 128 respectively throughout all the tests. | ||
==== '''Compilation and Running''' ==== | ==== '''Compilation and Running''' ==== | ||
| Line 60: | Line 114: | ||
==== '''Serial VS CUDA''' ==== | ==== '''Serial VS CUDA''' ==== | ||
[[File:Pi_serial_vs_cuda_results.jpg|border]] | [[File:Pi_serial_vs_cuda_results.jpg|border]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==== '''Conclusion''' ==== | ==== '''Conclusion''' ==== | ||
| − | + | Using CUDA technology and parallelizing the serial code in the original code, there is an enormous increase in performance (lower execution time) to calculate, as high as '''1372%'''. In the next (final) phase, an attempt to investigate if shared memory, optimal memory allocation, minimizing said memory access time, and other optimization factors would provide a further increase (lower execution time) in performance for ''pi_cuda''. | |
=== '''Assignment 3''' === | === '''Assignment 3''' === | ||
Latest revision as of 19:22, 4 November 2013
GPU610/DPS915 | Student List | Group and Project Index | Student Resources | Glossary
Contents
CUDA PI Calcuation (Monte Carlo)
Team Pi CUDA
Welcome to GPU610AA Fall 2013 Team Pi CUDA Page.
My name is Peter Huang and I'm a student in the GPU610 class for the Fall Semester of 2013. Having no background whatsoever in parallel programming, I've decided to choose something that is out of my scope of understanding and interest (video game programming) to challenge myself. Thus, I've decided to investigate the benefits of parallel programming applied to the Monte Carlo statistical method to approximating the value of pi.
Announcements
N/A
Team Members
Progress
Assignment 1
Introduction
For the initial profiling, I've decided to investigate the Monte Carlo Statistics Methodology of approximating the value of Pi. A brief explanation of Monte Carlo Pi calculation can be found here: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VJTFfIqO4TU
Source File(s)
Link: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B8GUuIUqdEJES3VEOGRnYmRNaEk
Code Snippet
Serial Pi Calculation Algorithm
// loops through user amount of rounds of sets of points
for(i = 0; i < points; i++)
{
x = randNum();
y = randNum();
// check if point resides within the circle
if (((x*x) + (y*y)) <= 1.0)
{
score++;
}
}
// calculate pi
pi = 4.0 * (float)score/(float)points;
Software and Hardware
Program Execution Plan
Pi serial tests would be conducted with sample counts up to 1 billion. Between 100 million and 1 billion, a sample count of 134217728 is sampled as that is the maximum sample value allowed for the Nvidia 460 GTX without generating memory allocation errors.
Compilation and Running
Serial Results
Conclusion
As the sample count increases, the execution time of the program also increases. The Big-O Classification for pi_serial is O(1).
Assignment 2
Introduction
In Phase 2, I've parallelized the serial program to run on a custom kernel on a CUDA-enabled device.
Source File(s)
Link: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B8GUuIUqdEJEbDBRNkhWYnpGSnM
Code Snippet
Working Kernel Parallel CUDA Pi Calculation
__global__ void findPi(float *estimatedPi, curandState *states, unsigned int taskElements, float seed)
{
unsigned int task_id = blockDim.x * blockIdx.x + threadIdx.x; // linear sequence of threads x-axis
int score = 0;
float xCoord;
float yCoord;
// 'random' generated value using curand, initialize curand using task_id, and seed parameter
curand_init(seed, task_id, 0, &states[task_id]);
// tally number of task elements
for(int i = 0; i < taskElements; i++)
{
// assigned each point coordinate values
xCoord = curand_uniform (&states[task_id]);
yCoord = curand_uniform (&states[task_id]);
// determine if coordinate is within the circle
if((xCoord*xCoord + yCoord*yCoord) <= 1.0f)
{
score++;
}
}
// estimated value of pi for this particular task
estimatedPi[task_id] = (4.0f * score) / (float)taskElements;
}
}
Software and Hardware
Program Execution Plan
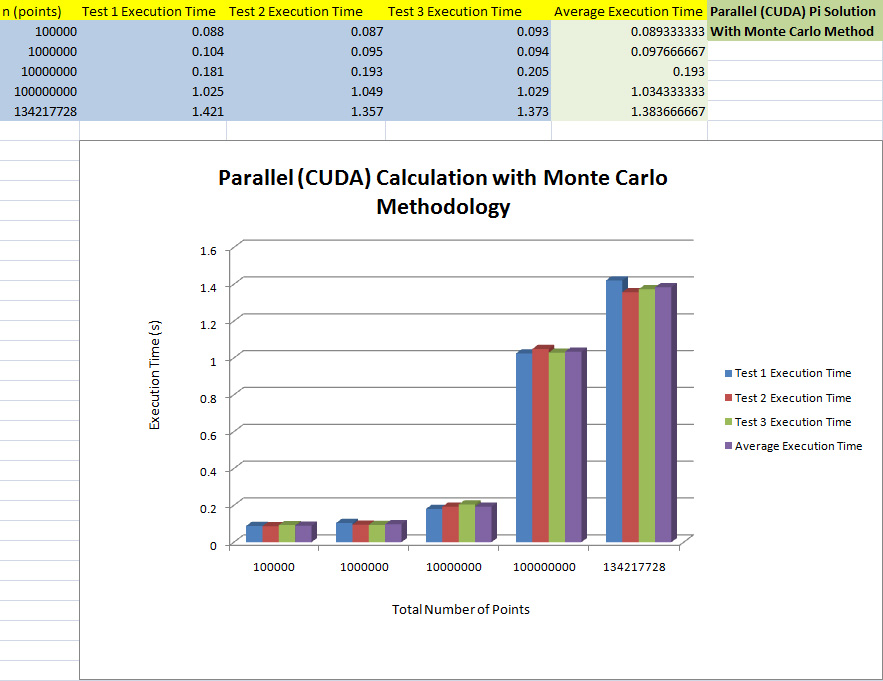
Pi cuda tests would be conducted with sample counts starting at 100 thousand, with incremental multiplier of 10, to the maximum supported sample count of 134217728 (memory constraint on Nvidia 460 GTX). The blocks and threads values will be 128, 128 respectively throughout all the tests.
Compilation and Running
Parallel (CUDA) Results
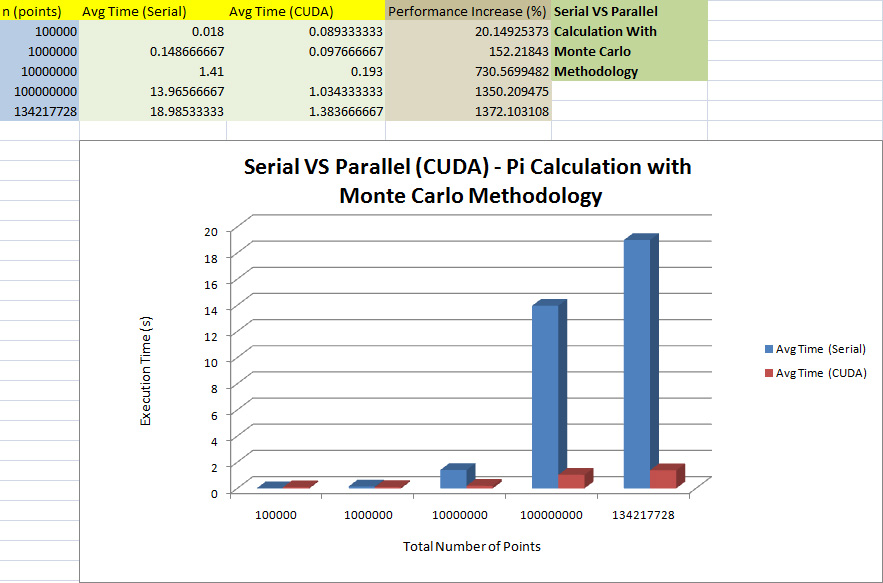
Serial VS CUDA
Conclusion
Using CUDA technology and parallelizing the serial code in the original code, there is an enormous increase in performance (lower execution time) to calculate, as high as 1372%. In the next (final) phase, an attempt to investigate if shared memory, optimal memory allocation, minimizing said memory access time, and other optimization factors would provide a further increase (lower execution time) in performance for pi_cuda.
Assignment 3
Agenda
N/A
Progress
N/A
Meetings
N/A
Discussion
N/A