Difference between revisions of "DPS915/M-N-M"
Mohamed Baig (talk | contribs) (→Final version's errors, warnings and observations) |
|||
| (30 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 147: | Line 147: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
==== Muhammad Ahsan: Prime Number Generator( 1,000,000,000 primes) ==== | ==== Muhammad Ahsan: Prime Number Generator( 1,000,000,000 primes) ==== | ||
| Line 161: | Line 160: | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| + | /** {{{ http://code.activestate.com/recipes/576559/ (r2) */ | ||
| + | /* | ||
| + | Copyright (c) 2008 Florian Mayer | ||
| − | + | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy | |
| − | + | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal | |
| − | + | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights | |
| − | + | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell | |
| − | + | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is | |
| − | + | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions: | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in | ||
| + | all copies or substantial portions of the Software. | ||
| + | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR | ||
| + | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, | ||
| + | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE | ||
| + | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER | ||
| + | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, | ||
| + | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN | ||
| + | THE SOFTWARE. | ||
| + | */ | ||
| − | + | #include <iostream> | |
| − | + | #include <vector> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | #include < | ||
| − | |||
| − | #include < | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
#include <string.h> | #include <string.h> | ||
| − | + | using namespace std; | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | vector<unsigned long> get_primes(unsigned long max){ | ||
| + | vector<unsigned long> primes; | ||
| + | char *sieve; | ||
| + | sieve = new char[max/8+1]; | ||
| + | // Fill sieve with 1 | ||
| + | memset(sieve, 0xFF, (max/8+1) * sizeof(char)); | ||
| + | for(unsigned long x = 2; x <= max; x++) | ||
| + | if(sieve[x/8] & (0x01 << (x % 8))){ | ||
| + | primes.push_back(x); | ||
| + | // Is prime. Mark multiplicates. | ||
| + | for(unsigned long j = 2*x; j <= max; j += x) | ||
| + | sieve[j/8] &= ~(0x01 << (j % 8)); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | delete[] sieve; | ||
| + | return primes; | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | int main(void){ | |
| − | + | vector<unsigned long> primes; | |
| − | + | primes = get_primes(1000000000); | |
| − | + | // return 0; | |
| − | + | // Print out result. | |
| − | + | vector<unsigned long>::iterator it; | |
| − | + | for(it=primes.begin(); it < primes.end(); it++) | |
| − | + | cout << *it << " "<<endl; | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | cout << endl; | |
| − | + | return 0; | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
| + | /** end of http://code.activestate.com/recipes/576559/ }}} */ | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | ==== Nitin Prakash Panicker: LZW File Compression ==== | ||
| − | + | <pre> | |
| + | Flat profile: | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. | |
| − | + | % cumulative self self total | |
| + | time seconds seconds calls ns/call ns/call name | ||
| + | 99.46 48.19 48.19 CLZWCompressFile::Compress(char*, char*) | ||
| − | + | 0.33 48.35 0.16 17122488 9.34 9.34 CLZWCompressFile::getc_src() | |
| − | + | 0.21 48.45 0.10 7095561 14.09 14.09 CLZWCompressFile::putc_comp(int) | |
| − | + | </pre> | |
| + | ==== Source Code for LZW File Compression ==== | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[lzw.cpp]] | |
| + | [[lzw.h]] | ||
| + | === Assignment 2 === | ||
| + | ==== Source code for prime number generator we will be putting on the gpu ==== | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| − | / | + | # include <cmath> // This library enable the use of sqrt. |
| + | # include <iostream> | ||
| + | |||
| + | using namespace std; | ||
| + | |||
| + | void primenum(long double); // Prototype... | ||
| + | |||
| + | int c = 0; | ||
| + | |||
| + | int main(){ | ||
| + | long double x = 0; | ||
| + | cout<<"\n This program will generate all prime numbers up to the" | ||
| + | <<"\n number you have entered below...\n"; | ||
| + | cout<<"\n Please enter a number: "; | ||
| + | cin>> x; | ||
| + | cout<<"\n Here are all the prime numbers up to "<<x<<".\n"; | ||
| + | primenum(x); //function invocation... | ||
| + | cout<<endl<<"\nThere are "<<c | ||
| + | <<" prime numbers less than or equal to "<<x<<".\n\n"; | ||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | // This function will determine the primenumbers up to num. | ||
| + | void primenum(long double x){ | ||
| + | bool prime = true; // Calculates the square-root of 'x' | ||
| + | int number2; | ||
| + | number2 =(int) floor (sqrt (x)); | ||
| + | for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++){ | ||
| + | for ( int j = 2; j <= number2; j++){ | ||
| + | if ( i!=j && i % j == 0 ){ | ||
| + | prime = false; | ||
| + | break; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | if (prime){ | ||
| + | cout <<" "<<i<<" "; | ||
| + | c += 1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | prime = true; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | getchar(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | </pre> | |
| + | ==== Version of prime generator running on GPU ==== | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| − | / | + | # include <cmath> // This library enable the use of sqrt. |
| + | # include <iostream> | ||
| + | # include <cuda_runtime.h> | ||
| + | |||
| + | using namespace std; | ||
| + | |||
| + | void primenum(long double); // Prototype... | ||
| + | |||
| + | int c = 0; | ||
| + | |||
| + | int main(){ | ||
| + | long double x = 0; | ||
| + | cout<<"\n This program will generate all prime numbers up to the" | ||
| + | <<"\n number you have entered below...\n"; | ||
| + | cout<<"\n Please enter a number: "; | ||
| + | cin>> x; | ||
| + | cout<<"\n Here are all the prime numbers up to "<<x<<".\n"; | ||
| + | primenum(x); //function invocation... | ||
| + | cout<<endl<<"\nThere are "<<c | ||
| + | <<" prime numbers less than or equal to "<<x<<".\n\n"; | ||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | // This function will determine the primenumbers up to num. | ||
| + | void primenum(long double x){ | ||
| + | //Array to hold generated primes on host | ||
| + | int *primes_h = new int[x]; | ||
| + | //Device array to hold the primes on the device | ||
| + | int *primes_d = new int[x]; | ||
| + | //allocate device memory and initialize device memory | ||
| + | cudaMalloc((void**)&primes_d, x * sizeof(int)); | ||
| + | cudaMemset(&primes_d,sizeof(int),x * sizeof(int); | ||
| + | |||
| + | //Kernal goes here | ||
| + | //error checking | ||
| + | |||
| + | //copy the array holding primes from device to host | ||
| + | cudaMemcpy(primes_h, primes_d, x * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); | ||
| + | |||
| + | //display the primes | ||
| + | for(int i=0; i<x ; i++){ | ||
| + | cout<<primes_h[i]<<endl; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | //free allocated memory | ||
| + | delete [] primes_h; | ||
| + | cudaFree(primes_d); | ||
| + | |||
| + | getchar(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | </pre> | |
| + | ==== Almost Final version ==== | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | # include <cmath> // This library enable the use of sqrt. | ||
| − | + | # include <iostream> | |
| − | + | # include <ctime> | |
| − | + | #include<iomanip> | |
| − | + | #include<cstdlib> | |
| + | # include <cuda_runtime.h> | ||
| + | //#include <times.h> | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | using namespace std; | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | inline clock_t getMilliSecs() { | |
| − | + | return clock() / (CLOCKS_PER_SEC / 1000); | |
| + | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | __global__ void primegen(bool prime, int number2,int x,int *primes_d) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | int c = 0; | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | for ( int j = 2; j <= number2; j++) | ||
| + | { | ||
| − | + | if ( i!=j && i % j == 0 ) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | prime = false; | |
| + | break; | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | if (prime) | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{ | { | ||
| − | + | primes_d[c]=i; | |
| − | + | c += 1; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | prime = true; | |
| − | + | } | |
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | void primenum(long double); // Prototype... | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | int main() | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | long double x = 0; | |
| − | + | cout<<"\n This program will generate all prime numbers up to the"<<"\n number you have entered below...\n"; | |
| − | + | cout<<"\n Please enter a number: "; | |
| + | cin>> x; | ||
| + | cout<<"\n Here are all the prime numbers up to "<<x<<".\n"; | ||
| − | + | primenum(x); //function invocation... | |
| − | + | //cout<<endl<<"\nThere are "<<c | |
| − | + | //<<" prime numbers less than or equal to "<<x<<".\n\n"; | |
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | // This function will determine the primenumbers up to num. | |
| − | + | void primenum(long double x) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | bool prime = true; | |
| − | + | //struct tms start_time, stop_time; | |
| − | int | + | int number2; |
| − | + | number2 =(int) floor (sqrt (x)); | |
| − | + | clock_t start = getMilliSecs(); | |
| − | + | //Array to hold generated primes on host | |
| + | int *primes_h = new int[(int)x]; | ||
| + | //Device array to hold the primes on the device | ||
| − | + | int *primes_d = new int[(int)x]; | |
| − | + | //allocate device memory and initialize device memory | |
| − | + | cudaMalloc((void**)&primes_d, (int)x * sizeof(int)); | |
| − | + | // cudaMalloc((void**)&c_d, sizeof(int)); | |
| − | + | cudaMemset(&primes_d,0,x * sizeof(int)); | |
| − | + | //error checking | |
| − | + | cudaError_t error ; | |
| − | + | //Kernal goes here | |
| − | + | primegen<<<1,1>>>(prime,number2,(int)x,primes_d); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | // extract error code from the kernel's execution | |
| − | + | error = cudaGetLastError(); | |
| − | + | if (error != cudaSuccess) { | |
| − | + | cout << cudaGetErrorString(error) << endl; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | //copy the array holding primes from device to host | |
| + | error =cudaMemcpy(primes_h, primes_d, ((int)x) * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | if (error != cudaSuccess) { | |
| − | + | cout << cudaGetErrorString(error) << endl; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | // cudaMemcpy(c_h, c_d, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); | |
| − | + | //display the primes | |
| + | for(int i=0; i<(int)x ; i++){ | ||
| + | if(primes_h[i]>=2 && primes_h[i]<=(int)x){ | ||
| − | + | cout<<primes_h[i]<<endl; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | cout << "Elapsed time: " << (getMilliSecs() - start) << "ms" << endl; | |
| − | + | // cout<< "time: "<< (stop_s-start_s)/double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC)<<endl; | |
| − | / | + | //free allocated memory |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | delete [] primes_h; | |
| − | + | cudaFree(primes_d); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | getchar(); | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| − | + | === Assignment 3 === | |
| − | + | ==== Cuda Version:First Attempt ==== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | # include <cmath> // This library enable the use of sqrt. | ||
| − | + | # include <iostream> | |
| − | + | # include <ctime> | |
| − | + | #include<iomanip> | |
| − | + | #include<cstdlib> | |
| − | + | # include <cuda_runtime.h> | |
| − | / | + | //#include <times.h> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | using namespace std; | |
| − | + | ||
| + | inline clock_t getMilliSecs() { | ||
| − | + | return clock() / (CLOCKS_PER_SEC / 1000); | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
| Line 982: | Line 600: | ||
| − | + | __global__ void primegen(bool prime, int number2,int x,int *primes_d) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | int c = 0; | |
| + | int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | for ( int i=1; i <= x; i++) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | if( i!= idx && i%idx == 0 ) | |
| + | { | ||
| + | prime = false; | ||
| − | + | break; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | if(prime) | |
| − | + | { | |
| + | primes_d[c]=i; | ||
| + | c += 1; | ||
| − | + | } | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | prime = true; | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | /*for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++) | |
| + | { | ||
| + | for ( int j = 2; j <= number2; j++) | ||
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | if ( i!=j && i % j == 0 ) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | prime = false; | |
| − | + | break; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | if (prime) | |
| − | + | { | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | primes_d[c]=i; | |
| − | + | c += 1; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | prime = true; | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | } */ | |
| + | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | void primenum(long double); // Prototype... | |
| − | + | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| − | + | int main() | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
{ | { | ||
| − | + | long double x = 0; | |
| − | + | cout<<"\n This program will generate all prime numbers up to the"<<"\n number you have entered below...\n"; | |
| − | + | cout<<"\n Please enter a number: "; | |
| + | cin>> x; | ||
| + | cout<<"\n Here are all the prime numbers up to "<<x<<".\n"; | ||
| − | + | primenum(x); //function invocation... | |
| + | //cout<<endl<<"\nThere are "<<c | ||
| + | //<<" prime numbers less than or equal to "<<x<<".\n\n"; | ||
| − | + | return 0; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| + | // This function will determine the primenumbers up to num. | ||
| + | void primenum(long double x) | ||
| − | + | { | |
| − | + | int n = x; | |
| − | + | int d; | |
| − | + | bool prime = true; | |
| − | + | //struct tms start_time, stop_time; | |
| − | + | int number2; | |
| − | + | number2 =(int) floor (sqrt (x)); | |
| − | + | clock_t start = getMilliSecs(); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | cudaDeviceProp prop; | |
| − | + | cudaGetDevice(&d); | |
| − | + | cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, d); | |
| − | + | int nThreads = prop.maxThreadsDim[0]; | |
| − | + | int n_max = nThreads * prop.maxGridSize[0]; | |
| − | + | if ( n> n_max) { | |
| − | + | n = n_max; | |
| − | + | cout << "n reduced to " << n << endl; | |
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | //Array to hold generated primes on host | |
| − | + | int *primes_h = new int[(int)x]; | |
| − | + | ||
| + | //Device array to hold the primes on the device | ||
| + | int *primes_d = new int[(int)x]; | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | //allocate device memory and initialize device memory | |
| + | cudaMalloc((void**)&primes_d, (int)x * sizeof(int)); | ||
| + | |||
| − | + | // cudaMalloc((void**)&c_d, sizeof(int)); | |
| − | + | cudaMemset(&primes_d,0,x * sizeof(int)); | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ||
| + | //error checking | ||
| + | cudaError_t error ; | ||
| − | + | ||
| + | //Kernal goes here | ||
| + | primegen<<<(n + nThreads - 1) / nThreads, nThreads>>>(prime,number2,(int)x,primes_d); | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | // extract error code from the kernel's execution | |
| − | + | ||
| + | error = cudaGetLastError(); | ||
| + | if (error != cudaSuccess) { | ||
| − | + | cout << cudaGetErrorString(error) << endl; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | //copy the array holding primes from device to host | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | error =cudaMemcpy(primes_h, primes_d, ((int)x) * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | if (error != cudaSuccess) { | |
| − | + | cout << cudaGetErrorString(error) << endl; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | + | // cudaMemcpy(c_h, c_d, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); | |
| − | + | //display the primes | |
| + | for(int i=0; i<(int)x ; i++){ | ||
| + | if(primes_h[i]>=2 && primes_h[i]<=(int)x){ | ||
| − | + | cout<<primes_h[i]<<endl; | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
} | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | cout << "Elapsed time: " << (getMilliSecs() - start) << "ms" << endl; | ||
| − | + | // cout<< "time: "<< (stop_s-start_s)/double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC)<<endl; | |
| − | + | //free allocated memory | |
| − | + | ||
| + | delete [] primes_h; | ||
| + | cudaFree(primes_d); | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | getchar(); | |
| + | } | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | ==== Conclusion: Logical Error ==== | ||
| − | + | [[Image:gpuA3error.png|thumb|widthpx| ]] | |
| − | + | The prime number generated seems to have run into some logical error. It does not generate the prime numbers correctly. Instead spits out all numbers. | |
| − | + | ==== Cuda Version: Attempt Two ==== | |
| + | Gives a run time error "invalid argument". Logical error still persists. | ||
| − | + | ==== Final Cuda version ==== | |
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | #include <cstdio> | ||
| + | #include <cstdlib> | ||
| + | #include <iostream> | ||
| + | #include <ctime> | ||
| + | #include <cuda_runtime.h> | ||
| − | + | using namespace std; | |
| − | + | /** | |
| + | * This macro checks return value of the CUDA runtime call and exits | ||
| + | * the application if the call failed. | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | #define CUDA_CHECK_RETURN(value) { \ | ||
| + | cudaError_t _m_cudaStat = value; \ | ||
| + | if (_m_cudaStat != cudaSuccess) { \ | ||
| + | fprintf(stderr, "Error %s at line %d in file %s\n", \ | ||
| + | cudaGetErrorString(_m_cudaStat), __LINE__, __FILE__); \ | ||
| + | exit(1); \ | ||
| + | } } | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| + | * Kernel code to generate and detect primes | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | __global__ void prime(int *num, int blockNum, int threadNum, int size) { | ||
| + | const int tid = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; | ||
| + | const int bid = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y; | ||
| + | __syncthreads(); | ||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * Generate prime numbers and store them in the array. | ||
| + | * The first element is always 2 | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | if(tid == 0) { | ||
| + | num[tid] = 2; | ||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | num[tid] = 2 * tid + 1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | int tmp = bid * threadNum + tid; | ||
| − | + | int step1 = 2 * tmp + 3; | |
| + | int step2 = tmp + 1; | ||
| − | + | while(tmp < size) { | |
| + | int i = 1; | ||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * Check if an element is not prime, if it isn't set it to 0. | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | while((step1 * i + step2) < size) { | ||
| + | num[step1 * i + step2] = 0; | ||
| + | i++; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | tmp += blockNum * threadNum; | ||
| + | __syncthreads(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { | |
| + | if(argc != 2) { | ||
| + | cout << "Incorrect no of arguments" << endl; | ||
| + | return 1; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | int n = atoi(argv[1]); | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| + | * variable declarations | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | int *device; | ||
| + | int host[n]; | ||
| + | int d; | ||
| + | cudaDeviceProp prop; | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| + | * Get the properties of the device in use | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | cudaGetDevice(&d); | ||
| + | cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, d); | ||
| + | int numberOfBlocks = 8; | ||
| + | int maxThreadsPerBlock = prop.maxThreadsPerBlock; | ||
| + | int numberOfThreads = maxThreadsPerBlock/numberOfBlocks; | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| + | * Start timer | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | clock_t cb, ce; | ||
| + | cb = clock(); | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| + | * Allocate memory on the device | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | CUDA_CHECK_RETURN(cudaMalloc((void**) &device, sizeof(int) * n)); | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| + | * Call kernel with appropriate grid and thread size | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | prime<<<numberOfBlocks, numberOfThreads>>>(device, numberOfBlocks, numberOfThreads, n); | ||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * Copy results back to host | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | CUDA_CHECK_RETURN(cudaMemcpy(&host, device, sizeof(int) * n, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost)); | ||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * Free memory on device | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | CUDA_CHECK_RETURN(cudaFree(device)); | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| + | * Output values | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) | ||
| + | if (host[i] != 0) | ||
| + | cout << host[i] << endl; | ||
| − | + | /** | |
| − | + | * Stop timer | |
| − | + | */ | |
| − | + | ce = clock(); | |
| − | + | cout << "Prime generation - took " << double(ce - cb)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << " seconds" << endl; | |
| − | + | } | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | } | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | [[Image:manualDelete.png|thumb|200px|Manual Delete Warning]] | |
| + | ===== Final version's errors, warnings and observations ===== | ||
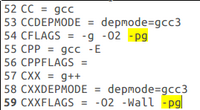
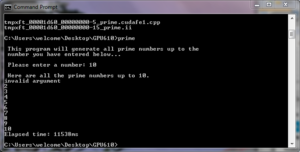
| + | * If a number over 515 is entered as the launch argument, the program will display random values at the end of the list of prime numbers | ||
| + | * When attempting to delete the host array manually in the program, a warning is displayed | ||
| + | [[Image:ManualCrash.png|thumb|200px|Manual Delete Crash]] | ||
| + | * The program crashes at the end if the host array is manually deleted | ||
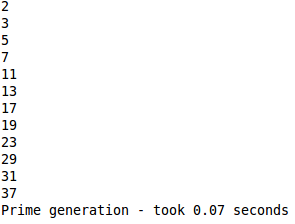
| − | === | + | ===== Successful run of Prime generation ===== |
| − | = | + | [[Image:PrimeSuccessfulRun.png]] |
Latest revision as of 16:55, 12 April 2013
GPU610/DPS915 | Student List | Group and Project Index | Student Resources | Glossary
Contents
[hide]Team: M-N-M
Team Members
Potential Projects
| Project Name | Project Description | Status |
|---|---|---|
| C Compiler | Take the compilation process and transfer it to the GPU | failed |
| Galactic Collision Simulation | A 2D simulation of two galaxies colliding, with fully simulated gravity effects. | cannot benefit from parallel computing,already fast enough |
| Isomorphism of graphs | Check if two graphs are isomorphic in nature. This is a very straight forward program. | failed |
| Image Processing | Mathematical operations applied to images for colour negation, rotation, blurring effects, etc. | scrapped |
| Facial Recognition system | Speed up time taken to match face with database | already CUDA enabled |
| Steganography | Speed up the process of encrypting one type of file into another | Profiled |
| Prime number generator | Generate prime numbers | Profiled |
| LZW File compression | Compress files using Lempel-Ziv-Welch algorithm | Profiled |
Progress
Assignment 1
Mohamed Baig: Steganography using Steghide
- Steghide has certain dependencies that it uses to complete its function.
- Dependencies:
- libmash
- libcrypt
- libjpeg
- zlib
- Ran the Configure file to see if I have all the Dependencies
- Installed the all the dependencies
- Ran Configure again to generate Makefile in the src folder
- Altered the Makefile to enable profiling
- Altered some source files to avoid errors
AuSampleValues.cc
#include "AuSampleValues.h" // AuMuLawSampleValue template <> //My change const BYTE AuMuLawSampleValue::MinValue = 0 ; template <> //My change const BYTE AuMuLawSampleValue::MaxValue = BYTE_MAX ; // AuPCM8SampleValue template <> //My change const SBYTE AuPCM8SampleValue::MinValue = SBYTE_MIN ; template <> //My change const SBYTE AuPCM8SampleValue::MaxValue = SBYTE_MAX ; // AuPCM16SampleValue template <> //My change const SWORD16 AuPCM16SampleValue::MinValue = SWORD16_MIN ; template <> //My change const SWORD16 AuPCM16SampleValue::MaxValue = SWORD16_MAX ; // AuPCM32SampleValue template <> //My change const SWORD32 AuPCM32SampleValue::MinValue = SWORD32_MIN ; template <> //My change const SWORD32 AuPCM32SampleValue::MaxValue = SWORD32_MAX ;
AuData.h
#ifndef SH_AUDATA_H
#define SH_AUDATA_H
#include "BinaryIO.h"
#include "AudioData.h"
// AuMuLawAudioData
typedef AudioDataImpl<AuMuLaw,BYTE> AuMuLawAudioData ;
template <> //My change
inline BYTE AuMuLawAudioData::readValue (BinaryIO* io) const { return (io->read8()) ; }
template <> //My change
inline void AuMuLawAudioData::writeValue (BinaryIO* io, BYTE v) const { io->write8(v) ; }
// AuPCM8AudioData
typedef AudioDataImpl<AuPCM8,SBYTE> AuPCM8AudioData ;
template <> //My change
inline SBYTE AuPCM8AudioData::readValue (BinaryIO* io) const { return ((SBYTE) io->read8()) ; }
template <> //My change
inline void AuPCM8AudioData::writeValue (BinaryIO* io, SBYTE v) const { io->write8((BYTE) v) ; }
// AuPCM16AudioData
typedef AudioDataImpl<AuPCM16,SWORD16> AuPCM16AudioData ;
template <> //My change
inline SWORD16 AuPCM16AudioData::readValue (BinaryIO* io) const { return ((SWORD16) io->read16_be()) ; }
template <> //My change
inline void AuPCM16AudioData::writeValue (BinaryIO* io, SWORD16 v) const { io->write16_be((UWORD16) v) ; }
// AuPCM32AudioData
typedef AudioDataImpl<AuPCM32,SWORD32> AuPCM32AudioData ;
template <> //My change
inline SWORD32 AuPCM32AudioData::readValue (BinaryIO* io) const { return ((SWORD32) io->read32_be()) ; }
template <> //My change
inline void AuPCM32AudioData::writeValue (BinaryIO* io, SWORD32 v) const { io->write32_be((UWORD32) v) ; }
#endif // ndef SH_AUDATA_H
- The result of embedding kilobytes of text data into an image
Flat profile: Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls s/call s/call name 13.38 0.21 0.21 1318276 0.00 0.00 Selector::idxX(unsigned int, unsigned int, unsigned int*) const 11.47 0.39 0.18 4054789 0.00 0.00 Vertex::getDegree() const 9.55 0.54 0.15 659139 0.00 0.00 Selector::calculate(unsigned int) 7.64 0.66 0.12 659141 0.00 0.00 JpegFile::getEmbeddedValue(unsigned int) const 7.01 0.77 0.11 659139 0.00 0.00 __gnu_cxx::hashtable<std::pair<unsigned int const, unsigned int>, unsigned int, __gnu_cxx::hash<unsigned int>, std::_Select1st<std::pair<unsigned int const, unsigned int> >, std::equal_to<unsigned int>, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::resize(unsigned long) 6.37 0.87 0.10 328293 0.00 0.00 JpegFile::getSampleValue(unsigned int) const 5.73 0.96 0.09 1 0.09 0.09 Selector::~Selector() 3.82 1.02 0.06 1 0.06 0.09 JpegFile::read(BinaryIO*)
- The result of attempting to embed 1.7 GB of data into an image
Flat profile: Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls s/call s/call name 54.43 21.52 21.52 1192388169 0.00 0.00 BitString::_append(bool) 16.79 28.15 6.64 593200712 0.00 0.00 BitString::operator[](unsigned long) const 9.30 31.83 3.68 74898412 0.00 0.00 BitString::append(unsigned char, unsigned short) 4.78 33.72 1.89 3 0.63 6.41 BitString::append(BitString const&) 3.50 35.10 1.39 BitString::BitString(unsigned long) 1.91 35.86 0.76 BitString::clear() 1.29 36.37 0.51 1 0.51 37.26 Embedder::Embedder() 1.20 36.84 0.48 37823336 0.00 0.00 BinaryIO::eof() const
Muhammad Ahsan: Prime Number Generator( 1,000,000,000 primes)
Flat profile Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls Ts/call Ts/call name 100.00 53.83 53.83 get_primes(unsigned long) 0.00 53.83 0.00 27 0.00 0.00 void std::vector<unsigned long, std::allocator<unsigned long> >::_M_emplace_back_aux<unsigned long const&>(unsigned long const&&&) 0.00 53.83 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__Z10get_primesm
/** {{{ http://code.activestate.com/recipes/576559/ (r2) */
/*
Copyright (c) 2008 Florian Mayer
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in
all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN
THE SOFTWARE.
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
vector<unsigned long> get_primes(unsigned long max){
vector<unsigned long> primes;
char *sieve;
sieve = new char[max/8+1];
// Fill sieve with 1
memset(sieve, 0xFF, (max/8+1) * sizeof(char));
for(unsigned long x = 2; x <= max; x++)
if(sieve[x/8] & (0x01 << (x % 8))){
primes.push_back(x);
// Is prime. Mark multiplicates.
for(unsigned long j = 2*x; j <= max; j += x)
sieve[j/8] &= ~(0x01 << (j % 8));
}
delete[] sieve;
return primes;
}
int main(void){
vector<unsigned long> primes;
primes = get_primes(1000000000);
// return 0;
// Print out result.
vector<unsigned long>::iterator it;
for(it=primes.begin(); it < primes.end(); it++)
cout << *it << " "<<endl;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
/** end of http://code.activestate.com/recipes/576559/ }}} */
Nitin Prakash Panicker: LZW File Compression
Flat profile: Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls ns/call ns/call name 99.46 48.19 48.19 CLZWCompressFile::Compress(char*, char*) 0.33 48.35 0.16 17122488 9.34 9.34 CLZWCompressFile::getc_src() 0.21 48.45 0.10 7095561 14.09 14.09 CLZWCompressFile::putc_comp(int)
Source Code for LZW File Compression
Assignment 2
Source code for prime number generator we will be putting on the gpu
# include <cmath> // This library enable the use of sqrt.
# include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void primenum(long double); // Prototype...
int c = 0;
int main(){
long double x = 0;
cout<<"\n This program will generate all prime numbers up to the"
<<"\n number you have entered below...\n";
cout<<"\n Please enter a number: ";
cin>> x;
cout<<"\n Here are all the prime numbers up to "<<x<<".\n";
primenum(x); //function invocation...
cout<<endl<<"\nThere are "<<c
<<" prime numbers less than or equal to "<<x<<".\n\n";
return 0;
}
// This function will determine the primenumbers up to num.
void primenum(long double x){
bool prime = true; // Calculates the square-root of 'x'
int number2;
number2 =(int) floor (sqrt (x));
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++){
for ( int j = 2; j <= number2; j++){
if ( i!=j && i % j == 0 ){
prime = false;
break;
}
}
if (prime){
cout <<" "<<i<<" ";
c += 1;
}
prime = true;
}
getchar();
}
Version of prime generator running on GPU
# include <cmath> // This library enable the use of sqrt.
# include <iostream>
# include <cuda_runtime.h>
using namespace std;
void primenum(long double); // Prototype...
int c = 0;
int main(){
long double x = 0;
cout<<"\n This program will generate all prime numbers up to the"
<<"\n number you have entered below...\n";
cout<<"\n Please enter a number: ";
cin>> x;
cout<<"\n Here are all the prime numbers up to "<<x<<".\n";
primenum(x); //function invocation...
cout<<endl<<"\nThere are "<<c
<<" prime numbers less than or equal to "<<x<<".\n\n";
return 0;
}
// This function will determine the primenumbers up to num.
void primenum(long double x){
//Array to hold generated primes on host
int *primes_h = new int[x];
//Device array to hold the primes on the device
int *primes_d = new int[x];
//allocate device memory and initialize device memory
cudaMalloc((void**)&primes_d, x * sizeof(int));
cudaMemset(&primes_d,sizeof(int),x * sizeof(int);
//Kernal goes here
//error checking
//copy the array holding primes from device to host
cudaMemcpy(primes_h, primes_d, x * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
//display the primes
for(int i=0; i<x ; i++){
cout<<primes_h[i]<<endl;
}
//free allocated memory
delete [] primes_h;
cudaFree(primes_d);
getchar();
}
Almost Final version
# include <cmath> // This library enable the use of sqrt.
# include <iostream>
# include <ctime>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstdlib>
# include <cuda_runtime.h>
//#include <times.h>
using namespace std;
inline clock_t getMilliSecs() {
return clock() / (CLOCKS_PER_SEC / 1000);
}
__global__ void primegen(bool prime, int number2,int x,int *primes_d)
{
int c = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++)
{
for ( int j = 2; j <= number2; j++)
{
if ( i!=j && i % j == 0 )
{
prime = false;
break;
}
}
if (prime)
{
primes_d[c]=i;
c += 1;
}
prime = true;
}
}
void primenum(long double); // Prototype...
int main()
{
long double x = 0;
cout<<"\n This program will generate all prime numbers up to the"<<"\n number you have entered below...\n";
cout<<"\n Please enter a number: ";
cin>> x;
cout<<"\n Here are all the prime numbers up to "<<x<<".\n";
primenum(x); //function invocation...
//cout<<endl<<"\nThere are "<<c
//<<" prime numbers less than or equal to "<<x<<".\n\n";
return 0;
}
// This function will determine the primenumbers up to num.
void primenum(long double x)
{
bool prime = true;
//struct tms start_time, stop_time;
int number2;
number2 =(int) floor (sqrt (x));
clock_t start = getMilliSecs();
//Array to hold generated primes on host
int *primes_h = new int[(int)x];
//Device array to hold the primes on the device
int *primes_d = new int[(int)x];
//allocate device memory and initialize device memory
cudaMalloc((void**)&primes_d, (int)x * sizeof(int));
// cudaMalloc((void**)&c_d, sizeof(int));
cudaMemset(&primes_d,0,x * sizeof(int));
//error checking
cudaError_t error ;
//Kernal goes here
primegen<<<1,1>>>(prime,number2,(int)x,primes_d);
// extract error code from the kernel's execution
error = cudaGetLastError();
if (error != cudaSuccess) {
cout << cudaGetErrorString(error) << endl;
}
//copy the array holding primes from device to host
error =cudaMemcpy(primes_h, primes_d, ((int)x) * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (error != cudaSuccess) {
cout << cudaGetErrorString(error) << endl;
}
// cudaMemcpy(c_h, c_d, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
//display the primes
for(int i=0; i<(int)x ; i++){
if(primes_h[i]>=2 && primes_h[i]<=(int)x){
cout<<primes_h[i]<<endl;
}
}
cout << "Elapsed time: " << (getMilliSecs() - start) << "ms" << endl;
// cout<< "time: "<< (stop_s-start_s)/double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC)<<endl;
//free allocated memory
delete [] primes_h;
cudaFree(primes_d);
getchar();
}
Assignment 3
Cuda Version:First Attempt
# include <cmath> // This library enable the use of sqrt.
# include <iostream>
# include <ctime>
#include<iomanip>
#include<cstdlib>
# include <cuda_runtime.h>
//#include <times.h>
using namespace std;
inline clock_t getMilliSecs() {
return clock() / (CLOCKS_PER_SEC / 1000);
}
__global__ void primegen(bool prime, int number2,int x,int *primes_d)
{
int c = 0;
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
for ( int i=1; i <= x; i++)
{
if( i!= idx && i%idx == 0 )
{
prime = false;
break;
}
if(prime)
{
primes_d[c]=i;
c += 1;
}
prime = true;
}
}
/*for (int i = 1; i <= x; i++)
{
for ( int j = 2; j <= number2; j++)
{
if ( i!=j && i % j == 0 )
{
prime = false;
break;
}
}
if (prime)
{
primes_d[c]=i;
c += 1;
}
prime = true;
} */
void primenum(long double); // Prototype...
int main()
{
long double x = 0;
cout<<"\n This program will generate all prime numbers up to the"<<"\n number you have entered below...\n";
cout<<"\n Please enter a number: ";
cin>> x;
cout<<"\n Here are all the prime numbers up to "<<x<<".\n";
primenum(x); //function invocation...
//cout<<endl<<"\nThere are "<<c
//<<" prime numbers less than or equal to "<<x<<".\n\n";
return 0;
}
// This function will determine the primenumbers up to num.
void primenum(long double x)
{
int n = x;
int d;
bool prime = true;
//struct tms start_time, stop_time;
int number2;
number2 =(int) floor (sqrt (x));
clock_t start = getMilliSecs();
cudaDeviceProp prop;
cudaGetDevice(&d);
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, d);
int nThreads = prop.maxThreadsDim[0];
int n_max = nThreads * prop.maxGridSize[0];
if ( n> n_max) {
n = n_max;
cout << "n reduced to " << n << endl;
}
//Array to hold generated primes on host
int *primes_h = new int[(int)x];
//Device array to hold the primes on the device
int *primes_d = new int[(int)x];
//allocate device memory and initialize device memory
cudaMalloc((void**)&primes_d, (int)x * sizeof(int));
// cudaMalloc((void**)&c_d, sizeof(int));
cudaMemset(&primes_d,0,x * sizeof(int));
//error checking
cudaError_t error ;
//Kernal goes here
primegen<<<(n + nThreads - 1) / nThreads, nThreads>>>(prime,number2,(int)x,primes_d);
// extract error code from the kernel's execution
error = cudaGetLastError();
if (error != cudaSuccess) {
cout << cudaGetErrorString(error) << endl;
}
//copy the array holding primes from device to host
error =cudaMemcpy(primes_h, primes_d, ((int)x) * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (error != cudaSuccess) {
cout << cudaGetErrorString(error) << endl;
}
// cudaMemcpy(c_h, c_d, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
//display the primes
for(int i=0; i<(int)x ; i++){
if(primes_h[i]>=2 && primes_h[i]<=(int)x){
cout<<primes_h[i]<<endl;
}
}
cout << "Elapsed time: " << (getMilliSecs() - start) << "ms" << endl;
// cout<< "time: "<< (stop_s-start_s)/double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC)<<endl;
//free allocated memory
delete [] primes_h;
cudaFree(primes_d);
getchar();
}
Conclusion: Logical Error
The prime number generated seems to have run into some logical error. It does not generate the prime numbers correctly. Instead spits out all numbers.
Cuda Version: Attempt Two
Gives a run time error "invalid argument". Logical error still persists.
Final Cuda version
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
using namespace std;
/**
* This macro checks return value of the CUDA runtime call and exits
* the application if the call failed.
*/
#define CUDA_CHECK_RETURN(value) { \
cudaError_t _m_cudaStat = value; \
if (_m_cudaStat != cudaSuccess) { \
fprintf(stderr, "Error %s at line %d in file %s\n", \
cudaGetErrorString(_m_cudaStat), __LINE__, __FILE__); \
exit(1); \
} }
/**
* Kernel code to generate and detect primes
*/
__global__ void prime(int *num, int blockNum, int threadNum, int size) {
const int tid = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
const int bid = blockIdx.y * blockDim.y + threadIdx.y;
__syncthreads();
/**
* Generate prime numbers and store them in the array.
* The first element is always 2
*/
if(tid == 0) {
num[tid] = 2;
} else {
num[tid] = 2 * tid + 1;
}
int tmp = bid * threadNum + tid;
int step1 = 2 * tmp + 3;
int step2 = tmp + 1;
while(tmp < size) {
int i = 1;
/**
* Check if an element is not prime, if it isn't set it to 0.
*/
while((step1 * i + step2) < size) {
num[step1 * i + step2] = 0;
i++;
}
tmp += blockNum * threadNum;
__syncthreads();
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
if(argc != 2) {
cout << "Incorrect no of arguments" << endl;
return 1;
}
int n = atoi(argv[1]);
/**
* variable declarations
*/
int *device;
int host[n];
int d;
cudaDeviceProp prop;
/**
* Get the properties of the device in use
*/
cudaGetDevice(&d);
cudaGetDeviceProperties(&prop, d);
int numberOfBlocks = 8;
int maxThreadsPerBlock = prop.maxThreadsPerBlock;
int numberOfThreads = maxThreadsPerBlock/numberOfBlocks;
/**
* Start timer
*/
clock_t cb, ce;
cb = clock();
/**
* Allocate memory on the device
*/
CUDA_CHECK_RETURN(cudaMalloc((void**) &device, sizeof(int) * n));
/**
* Call kernel with appropriate grid and thread size
*/
prime<<<numberOfBlocks, numberOfThreads>>>(device, numberOfBlocks, numberOfThreads, n);
/**
* Copy results back to host
*/
CUDA_CHECK_RETURN(cudaMemcpy(&host, device, sizeof(int) * n, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost));
/**
* Free memory on device
*/
CUDA_CHECK_RETURN(cudaFree(device));
/**
* Output values
*/
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
if (host[i] != 0)
cout << host[i] << endl;
/**
* Stop timer
*/
ce = clock();
cout << "Prime generation - took " << double(ce - cb)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC << " seconds" << endl;
}
Final version's errors, warnings and observations
- If a number over 515 is entered as the launch argument, the program will display random values at the end of the list of prime numbers
- When attempting to delete the host array manually in the program, a warning is displayed
- The program crashes at the end if the host array is manually deleted