Difference between revisions of "OPS335 Lab 1"
m (libvirtd now managed by Systemd.) |
m (Added link to systemd cheatsheet) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==Instructions== | ==Instructions== | ||
===Managing services using systemd=== | ===Managing services using systemd=== | ||
| − | + | Before you start, it you were more familiar with the chkconfig or service commands, you may wish to review the [http://fedoraproject.org/wiki/SysVinit_to_Systemd_Cheatsheet SysVinit to Systemd Cheatsheet]. | |
Boot up your Fedora 17 x86_64 system, login with your learn id and use Firefox to authenticate yourself on Senenet so you can download and install new software. | Boot up your Fedora 17 x86_64 system, login with your learn id and use Firefox to authenticate yourself on Senenet so you can download and install new software. | ||
*Open a terminal window and su to root. | *Open a terminal window and su to root. | ||
Revision as of 15:59, 18 December 2012
Configuring a Linux Gateway
This lab will show you how to set up a simple intranet using one Fedora PC as a gateway. The same Fedora PC will be a host a small group of Fedora 17 VM's (Virtual Machine) which will act as PC's inside an intranet. Here is a diagram of your setup.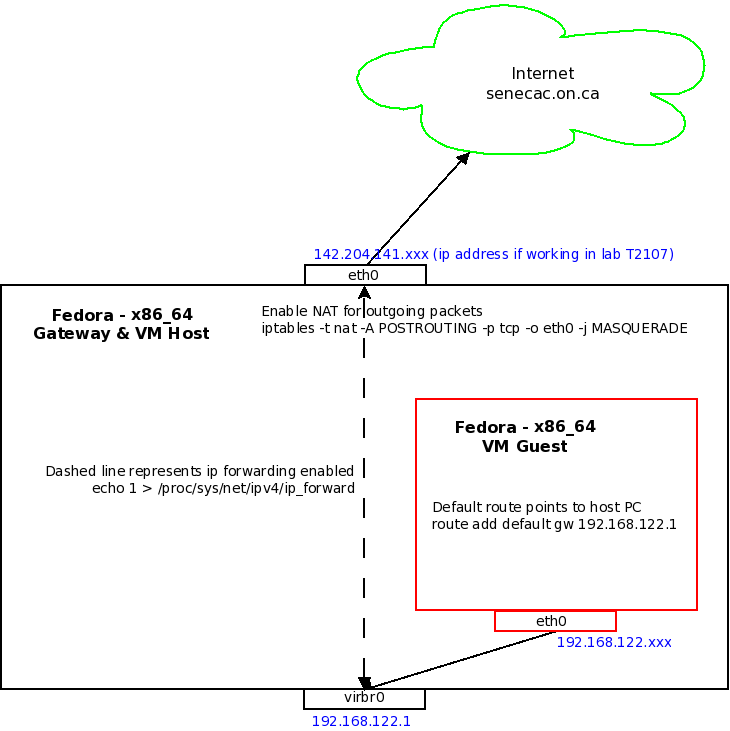
Instructions
Managing services using systemd
Before you start, it you were more familiar with the chkconfig or service commands, you may wish to review the SysVinit to Systemd Cheatsheet. Boot up your Fedora 17 x86_64 system, login with your learn id and use Firefox to authenticate yourself on Senenet so you can download and install new software.
- Open a terminal window and su to root.
- Ensure your system date and time are correct.
- Ensure your system is up to date
yum update
- Start your ssh server
service sshd start Redirecting to /bin/systemctl start sshd.service
- Notice that your command was redirected to
'systemctl', the command executed was'systemctl start sshd.service'. Record this in your lab book. - Enable sshd to start at boot
chkconfig sshd on Note: Forwarding request to 'systemctl enable sshd.service'. ln -s '/lib/systemd/system/sshd.service' '/etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/sshd.service'
- Again notice your command was redirected to
'systemctl', the command executed was'systemctl enable sshd.service'. A symbolic link was created as well, explain its purpose in your lab book. - Install the virtualization software
yum groupinstall virtualization
- Start the libvirt daemon using
'systemctl'
systemctl start libvirtd.service
- Enable libvirtd to start at boot using
'systemctl'
systemctl enable libvirtd.service
- You may occasionally encounter services that have not yet been moved to Systemd. In those cases Systemd will redirect the command to the appropriate older method. e.g.
systemctl enable serviceName.service serviceName.service is not a native service, redirecting to /sbin/chkconfig. Executing /sbin/chkconfig serviceName on Warning: unit files do not carry install information. No operation executed.
How to change the default runlevel using systemd
Fedora 17 does not use '/etc/inittab' to set the default run level but rather uses targets as a more flexible replacement. Note the output of the following command:
ll /etc/systemd/system/*.target lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 36 Dec 3 09:35 /etc/systemd/system/default.target -> /lib/systemd/system/runlevel5.target
and
ll /lib/systemd/system/*.target
Systemd uses symbolic links to point to the default runlevel in use. To change the default runlevel you must first remove the existing symlink.
rm /etc/systemd/system/default.target
To change your system to boot in Graphical mode by default:
ln -s /lib/systemd/system/graphical.target /etc/systemd/system/default.target
Make note of the command that would be needed to change the default 'runlevel' (or 'target' as it is now referred to when using systemd) to multiuser or runlevel 3.
Create your personal network
Observe and record the output of the following command:
iptables -t nat -L
Start Virtual Machine Manager through Gnome or through command line. You will need to enter your root password.
virt-manager
Right click 'localhost (QEMU)' and select 'Details'. Click on the 'Virtual Networks' tab and use the plus sign to add a new virtual network using the following options.
- Name your virtual network 'ops335'
- Use the last two digits of your student number for the third octet of network IP address. Example, if your student number is 000-000-090, the network address would be 192.168.90.0/24.
- Ensure the DHCP range will allow you to assign at least 3 static IP addresses.
- Choose 'Forwarding to physical network' radio button, 'Destination: Any physical device' and 'Mode: NAT'
- Ensure the network is started at boot.
Once completed open a terminal and observe and record the output of the following command:
iptables -t nat -L
Installing the first guest machine
With the virtualization software installed and your personal network created, you are now ready to create your first "Virtual Machine". Use the Fedora 17 x86 64 bit disk to install, or download an iso from Belmont (these links will only work at school).
wget http://belmont.senecac.on.ca/fedora/releases/17/Live/x86_64/Fedora-17-x86_64-Live-Desktop.iso or wget http://belmont.senecac.on.ca/fedora/releases/17/Live/x86_64/Fedora-17-x86_64-Live-KDE.iso
- Click on the icon "Create a new virtual machine" to begin.
- Name your machine "f17-vm01" and choose your installation method - "Local install media". Choose the desired option to install from either the CD or iso. For "OS type" select "Linux" and for Version select "Fedora 17" then click on the "Forward" button.
- Use the default memory and CPU options for use with lab computers (Depending available hardware these settings can be adjusted). Then click on the "Forward" button to proceed.
- Leave the disk image size set at 8GB, ensure "Allocate entire disk now" is checked, then click on the "Forward" button.
- At the "Ready to begin installation" window click on 'Advanced options' arrow to review available options.
- Select the Virtual Network named 'ops335'. Make note of the other available options.
Once your Fedora Live CD boots up you will see a message that Gnome 3 has failed to load and is currently running in fallback mode. This is normal for a VM. Close the dialog window and click on the Applications menu.
- Select Applications -> System Tools -> Install to Hard Disk
- Click the "Next" button to begin your Fedora installation. Select the appropriate default options.
- Set your hostname to "vm01.localdomain".
- Click the "Next" button to begin your Fedora installation. Select the appropriate default options.
During Firstboot create a user with the same name as your learn ID and the first user created on your host machine. This is important to ensure future labs work. Now login and open a terminal window. Switch to root and update your VM guest machine
yum update
This could take a long time and you should reboot after it's done. Ensure your VM guest has internet access
host cbc.ca
Minimizing your VM's footprint
Since all VMs used in this course are intended to be servers, the presence of a GUI in not recommended - servers are typically managed from the command line. Conduct relevant research to complete the following for your Fedora VM:
- Make it boot by default to the command line only
- Remove the Gnome/KDE environment
Test your VM to make sure that it boots correctly before moving on to the next step.
Creating additional Clone VM's
To quickly create additional VM's shutdown 'f17-vm01', right click and select 'Clone...'. Use the following options:
- Name: f17-vm02
- Storage:
- Click the drop down menu below 'f17-vm01.img', choose details and rename the image to the f17-vm02.img
Once successfully created boot the new VM and correct the host name. This can be done using the GUI or command line.
- Record in your notes how each is done.
- After creating f17-vm02 repeat the above steps to create f17-vm03 and correct the host name.
- Check for connectivity.
host cbc.ca
Testing Connectivity
- Test connectivity by pinging each of your VM's.
- Ping matrix and google from each of your VM's to ensure you can reach the outside world. (you will need to be authenticated on your host machine).
- Start the ssh server using 'systemctl'
systemctl start sshd.service
- Enable the ssh server at startup on all machines
systemctl enable sshd.service
- Try to ssh from the guest to the host machine.
- Try to ssh from the host to the guest machine.
- Try to ssh to your Matrix account from both the host and guest machines.
- Try to ssh from your Matrix account back to your host and guest machines.
- Use system-config-firewall on your VM, so it accepts incoming ssh connections.
- Restart iptables using systemctl
systemctl restart iptables.service
- Backup your new firewall rules
iptables-save > /etc/sysconfig/iptables.backup
- Ensure changes are still present
iptables -L
- Try to ssh from the host to the guest machine.
Completing the Lab
Answer the following questions in your logbook.
- How can you tell if a service is native or non-native to 'systemd'?
- Explain the iptables rules displayed when you ran the command 'iptables -t nat -L'. How did they differ after creating your personal network.
- Explain the output displayed when you enabled sshd to start at boot by running the command 'chkconfig sshd on'.
- What file was edited to change the host name on your VM's?
- What iptables rule was added to allow NEW ssh connections to the guest vm's?
- How are ping and ssh affected (on both machines) when you run the following command on the host machine?
- echo 0 > /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward
- Change the default target on vm02 and vm03 to multiuser.
- What command(s) was used?
- What option can be added to reduce this to a single command?
- Edit each of your VM's to use a static IP address. VM01 should use the first available address in the subnet, VM02 the second and VM03 the third.
- This should be done using the command line on all 3 virtual machines. Make note of the files used and entries required.
- Ensure connectivity from all VM's after the change.