Difference between revisions of "Unbinding MAC Addresses on Fedora"
Chris Tyler (talk | contribs) (Created page with '{{Admon/note|Fedora 12|These instructions are written for Fedora 12 but should apply to other Fedora releases.}} By default, Fedora binds ethernet interfaces (such as eth0) to a...') |
Chris Tyler (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | {{Admon/note|Fedora 12|These instructions are written for Fedora 12 but should apply to other Fedora releases.}} | + | [[Category:Fedora]][[Category:OPS235]]{{Admon/note|Fedora 12|These instructions are written for Fedora 12 but should apply to other Fedora releases.}} |
By default, Fedora binds ethernet interfaces (such as eth0) to a MAC address (specific network interface card/NIC). This is useful, because if a NIC is added, it will be assigned a new ethernet interface (instead of bumping the existing eth0 to eth1). However, this causes problems when you use a removable disk drive and move it from one computer to another. | By default, Fedora binds ethernet interfaces (such as eth0) to a MAC address (specific network interface card/NIC). This is useful, because if a NIC is added, it will be assigned a new ethernet interface (instead of bumping the existing eth0 to eth1). However, this causes problems when you use a removable disk drive and move it from one computer to another. | ||
Revision as of 10:45, 26 January 2010
By default, Fedora binds ethernet interfaces (such as eth0) to a MAC address (specific network interface card/NIC). This is useful, because if a NIC is added, it will be assigned a new ethernet interface (instead of bumping the existing eth0 to eth1). However, this causes problems when you use a removable disk drive and move it from one computer to another.
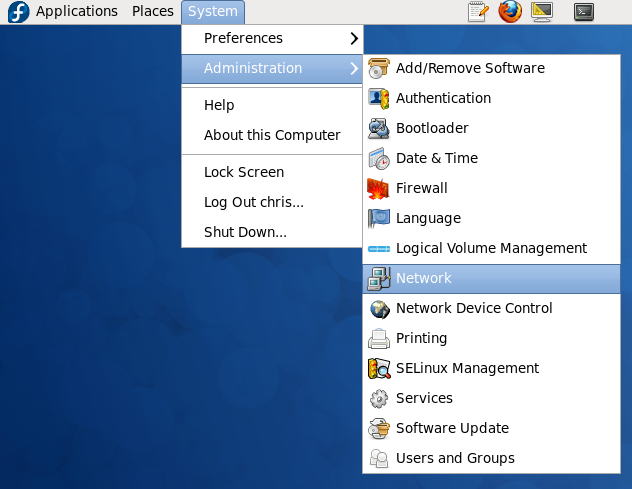
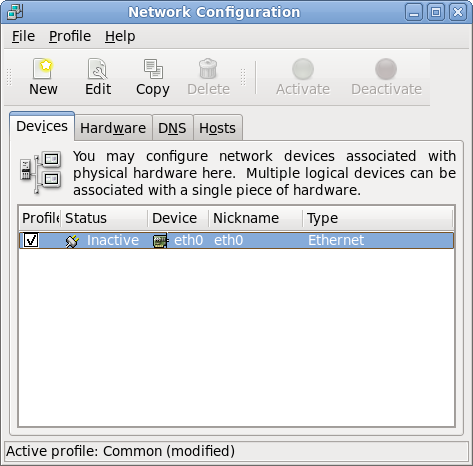
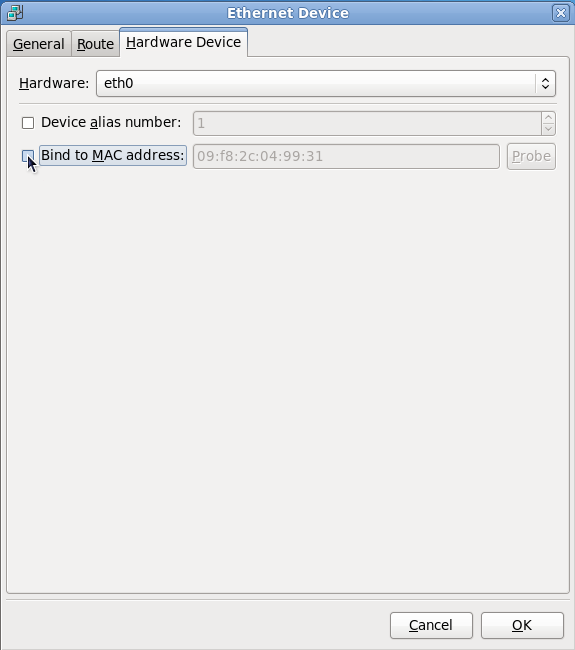
To unbind the interace from the MAC address: