Difference between revisions of "Common Windows Operations"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | == Window Elements == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:calc.png|right|800px ]] | ||
| + | |||
The majority of windows operations in Linux is identical to MS Windows. | The majority of windows operations in Linux is identical to MS Windows. | ||
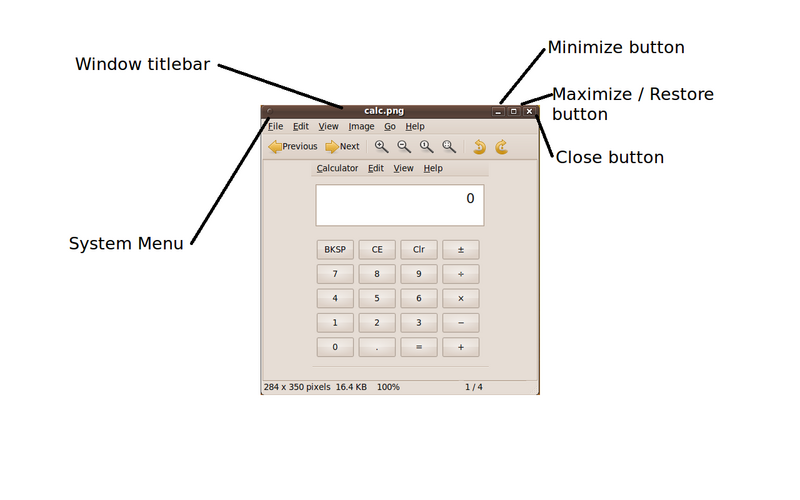
The typical Linux application window consists of a window boundary, and a window titlebar. On the window titlebar, there is a system menu on the left-hand-side and three buttons on the right-hand-side to minimize, maximize and close the window. Sometimes the availability of these buttons differ based on the application and how it was created. | The typical Linux application window consists of a window boundary, and a window titlebar. On the window titlebar, there is a system menu on the left-hand-side and three buttons on the right-hand-side to minimize, maximize and close the window. Sometimes the availability of these buttons differ based on the application and how it was created. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Common Window Operations == | == Common Window Operations == | ||
Revision as of 10:56, 5 November 2009
Contents
Window Elements
The majority of windows operations in Linux is identical to MS Windows.
The typical Linux application window consists of a window boundary, and a window titlebar. On the window titlebar, there is a system menu on the left-hand-side and three buttons on the right-hand-side to minimize, maximize and close the window. Sometimes the availability of these buttons differ based on the application and how it was created.