Difference between revisions of "GPU621/Apache Spark Fall 2022"
(→RDD Overview) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ==Group Information== | + | ==Group 3 Information== |
Alan Huang; | Alan Huang; | ||
Jianchang Yu; | Jianchang Yu; | ||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
==Apache Spark Introduction== | ==Apache Spark Introduction== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file: Spark_2022.png|600px]] | ||
Apache Spark is an open source cluster computing framework pioneered by Matei Zaharia at the University of California, Berkeley's AMPLab in 2009 and released open source in 2010 under the BSD license.Spark uses in-memory computing technology to analyze data in memory while it is still being written to the hard disk. Spark allows users to load data into cluster memory and query it multiple times, making it ideal for machine learning algorithms. | Apache Spark is an open source cluster computing framework pioneered by Matei Zaharia at the University of California, Berkeley's AMPLab in 2009 and released open source in 2010 under the BSD license.Spark uses in-memory computing technology to analyze data in memory while it is still being written to the hard disk. Spark allows users to load data into cluster memory and query it multiple times, making it ideal for machine learning algorithms. | ||
| − | |||
==Spark features== | ==Spark features== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 14: | ||
==Spark Ecosystem== | ==Spark Ecosystem== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file: Spark_component_2022.png|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
===1. Spark Core=== | ===1. Spark Core=== | ||
| − | The Spark core is the project's foundation, providing distributed task | + | The Spark core is the project's foundation, providing distributed task scheduling, and basic I/O functionality. The underlying program abstraction is called Resilient Distributed Datasets, or RDDs, which is a collection of data that can be manipulated in parallel through fault-tolerant mechanisms. The abstraction of RDDs is presented through language integration APIs in Scala, Java, and Python, simplifying programming complexity and allowing applications to manipulate RDDs in a manner similar to manipulating native datasets. |
===2. Spark SQL=== | ===2. Spark SQL=== | ||
| Line 26: | Line 30: | ||
===4. MLlib=== | ===4. MLlib=== | ||
| − | MLlib is a distributed machine learning framework on Spark | + | MLlib is a distributed machine learning framework on Spark. |
===5. GraphX=== | ===5. GraphX=== | ||
| Line 32: | Line 36: | ||
==Spark Application== | ==Spark Application== | ||
| − | |||
===1. The iterative operations and the multiple operations of the specific data sets === | ===1. The iterative operations and the multiple operations of the specific data sets === | ||
Spark is developed based on a memory-based iterative computing framework, so Spark has the advantage that the amount of read data will increase as the number of iterations increases. In the case of where iterative operations are applied or specific data sets need to be operated multiple times, Spark is very effective. | Spark is developed based on a memory-based iterative computing framework, so Spark has the advantage that the amount of read data will increase as the number of iterations increases. In the case of where iterative operations are applied or specific data sets need to be operated multiple times, Spark is very effective. | ||
| Line 56: | Line 59: | ||
===Work Flow Chart=== | ===Work Flow Chart=== | ||
[[File:Cluster-overview.png]] | [[File:Cluster-overview.png]] | ||
| + | ===The implementation of Spark requires the following Components=== | ||
| + | ====1.Driver Program (SparkContext)==== | ||
| + | SparkContext is the main entry point for all Spark functions. | ||
| + | ====2.Cluster Manager==== | ||
| + | The cluster manager is used for resource management of applications. | ||
| + | ====3. Worker node==== | ||
| + | Work nodes are used to submit tasks to executors, report executor status information, cpu and memory information to the cluster manager. | ||
| + | ====4. Executor==== | ||
| + | Components that perform computational tasks. It is a process responsible for running tasks, saving data and returning result data. | ||
| − | + | ===The implementation of Spark has the following steps=== | |
| + | *1. The SparkContext applies for computing resources from the Cluster Manager. | ||
| + | *2. The Cluster Manager receives the request and start allocating the resources. (Creates and activates the executor on the worker node.) | ||
| + | *3. The SparkContext sends the program/application code (jar package or python file, etc.) and task to the Executor. Executor executes the task and saves/returns the result | ||
| + | *4. The SparkContext will collect the results. | ||
==Apache Spark Core API== | ==Apache Spark Core API== | ||
===RDD Overview=== | ===RDD Overview=== | ||
| − | One of the most important concepts in Spark is a resilient distributed dataset (RDD). RDD is a collection of elements partitioned across the nodes of the cluster that can be operated in parallel. | + | |
| + | [[file:RDD_Spark.jpg|800px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | One of the most important concepts in Spark is a resilient distributed dataset (RDD). RDD is a collection of elements partitioned across the nodes of the cluster that can be operated in parallel. Spark is normally used to handle huge data, and RDD is what makes it possible for Spark to split the input data into different nodes. RDD also provides useful APIs for the programmer to call. We will introduce some key APIs provided by Spark Core 2.2.1 using Java 8. You can find more information about the RDD here. https://spark.apache.org/docs/2.2.1/rdd-programming-guide.html | ||
===Spark Library Installation Using Maven=== | ===Spark Library Installation Using Maven=== | ||
| Line 122: | Line 142: | ||
===RDD APIs=== | ===RDD APIs=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[file: Actions_RDD.png|800px]] | ||
Basically there are types of APIs. Transformations and Actions. Transformation APIs are functions that could return another RDD set. Using these APIs, we can create child RDD from parent RDD. Actions are the functions we want to perform onto the actual dataset. They will not return new RDDs. | Basically there are types of APIs. Transformations and Actions. Transformation APIs are functions that could return another RDD set. Using these APIs, we can create child RDD from parent RDD. Actions are the functions we want to perform onto the actual dataset. They will not return new RDDs. | ||
| Line 428: | Line 450: | ||
https://data-flair.training/blogs/spark-rdd-operations-transformations-actions/ | https://data-flair.training/blogs/spark-rdd-operations-transformations-actions/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://www.databricks.com/glossary/what-is-spark-streaming#:~:text=Spark%20Streaming%20is%20an%20extension,%2C%20databases%2C%20and%20live%20dashboards | ||
| + | |||
| + | https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/streaming-programming-guide.html | ||
https://hevodata.com/learn/spark-batch-processing/ | https://hevodata.com/learn/spark-batch-processing/ | ||
| − | https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/ | + | https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/cluster-overview.html |
Latest revision as of 13:44, 7 December 2022
Contents
Group 3 Information
Alan Huang; Jianchang Yu; Tim Lin;
Apache Spark Introduction
Apache Spark is an open source cluster computing framework pioneered by Matei Zaharia at the University of California, Berkeley's AMPLab in 2009 and released open source in 2010 under the BSD license.Spark uses in-memory computing technology to analyze data in memory while it is still being written to the hard disk. Spark allows users to load data into cluster memory and query it multiple times, making it ideal for machine learning algorithms.
Spark features
Spark has a great future. It can scale to over 8000 nodes. Spark Streaming is scalable, high-throughput, and fault-tolerant for processing instant data streams.Spark SQL supports structured and relational query processing SQL.MLlib high-end library for machine learning algorithms and Graphx graphics processing algorithms.
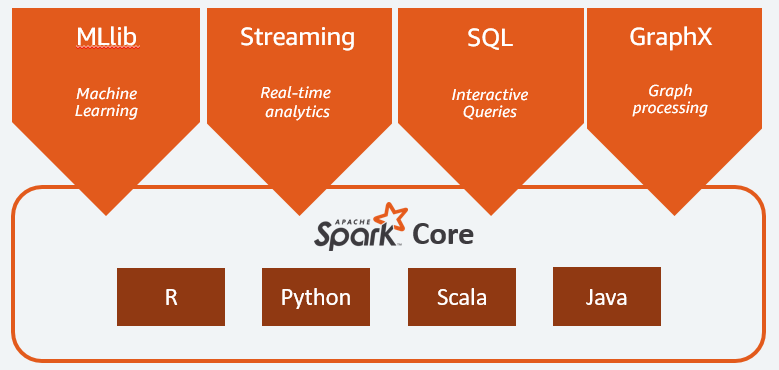
Spark Ecosystem
1. Spark Core
The Spark core is the project's foundation, providing distributed task scheduling, and basic I/O functionality. The underlying program abstraction is called Resilient Distributed Datasets, or RDDs, which is a collection of data that can be manipulated in parallel through fault-tolerant mechanisms. The abstraction of RDDs is presented through language integration APIs in Scala, Java, and Python, simplifying programming complexity and allowing applications to manipulate RDDs in a manner similar to manipulating native datasets.
2. Spark SQL
Spark SQL brings a data abstraction concept called SchemaRDD to the Spark core to provide support for structured and semi-structured data. Spark SQL provides domain-specific languages, and you can manipulate SchemaRDDs using Scala, Java, or Python. It also supports the use of the SQL language using the command line interface and ODBC/JDBC server.
3. Spark Streaming
Spark Streaming takes advantage of Spark's core fast scheduling capabilities to perform stream analysis. It intercepts small batches of information and performs RDD transformations on them. This design allows streaming analysis to use the same set of application code written for batch analysis within the same engine.
4. MLlib
MLlib is a distributed machine learning framework on Spark.
5. GraphX
GraphX is a distributed graph processing framework on Spark. It provides a set of APIs for expressing graph computations and can emulate Pregel abstraction. graphX also provides optimized runs for this abstraction.
Spark Application
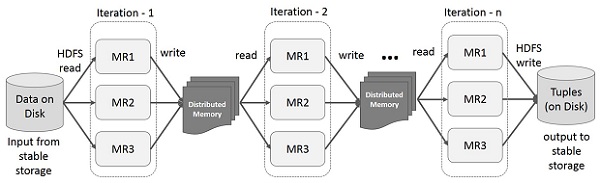
1. The iterative operations and the multiple operations of the specific data sets
Spark is developed based on a memory-based iterative computing framework, so Spark has the advantage that the amount of read data will increase as the number of iterations increases. In the case of where iterative operations are applied or specific data sets need to be operated multiple times, Spark is very effective.
2. Real-time calculation
With the batch processing capability of Spark Streaming, Spark has the advantage of large throughput in real-time statistical analysis calculations.
3. Batch data processing
Spark has the ability to process massive data
- With the advantage of high throughput with Spark Streaming, Spark can also process massive data in real time.
Spark cluster mode
1. Local mode
For local development and testing, it is usually divided into local single-thread and local-cluster multi-thread.
2. Standalone cluster mode
Running on the Standalone cluster manager, Standalone is responsible for resource management, Spark is responsible for task scheduling and calculation
3. Hadoop YARN cluster mode
Running on the Hadoop YARN cluster manager, Hadoop YARN is responsible for resource management, Spark is responsible for task scheduling and calculation
4. Apache Mesos cluster mode
Running on the Apache Mesos cluster manager, Apache Mesos is responsible for resource management, Spark is responsible for task scheduling and computing
5. Kubernetes cluster mode
Running on the Kubernetes cluster manager, Kubernetes is responsible for resource management, and Spark is responsible for task scheduling and computing
Spark Implementation
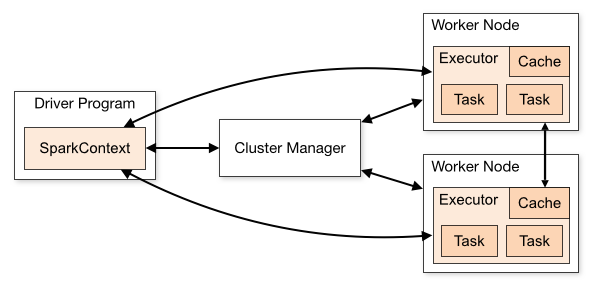
Work Flow Chart
The implementation of Spark requires the following Components
1.Driver Program (SparkContext)
SparkContext is the main entry point for all Spark functions.
2.Cluster Manager
The cluster manager is used for resource management of applications.
3. Worker node
Work nodes are used to submit tasks to executors, report executor status information, cpu and memory information to the cluster manager.
4. Executor
Components that perform computational tasks. It is a process responsible for running tasks, saving data and returning result data.
The implementation of Spark has the following steps
- 1. The SparkContext applies for computing resources from the Cluster Manager.
- 2. The Cluster Manager receives the request and start allocating the resources. (Creates and activates the executor on the worker node.)
- 3. The SparkContext sends the program/application code (jar package or python file, etc.) and task to the Executor. Executor executes the task and saves/returns the result
- 4. The SparkContext will collect the results.
Apache Spark Core API
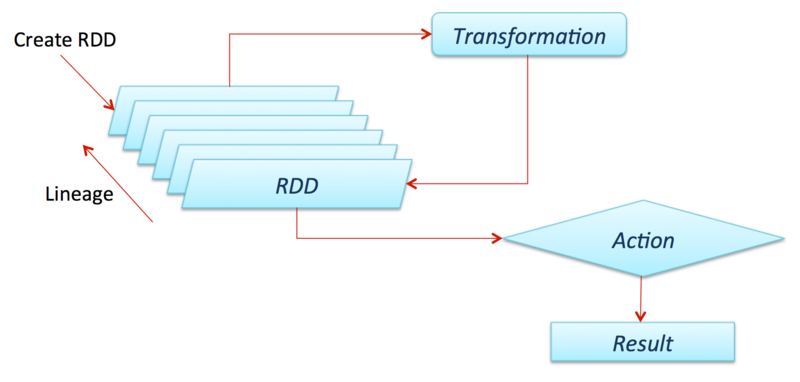
RDD Overview
One of the most important concepts in Spark is a resilient distributed dataset (RDD). RDD is a collection of elements partitioned across the nodes of the cluster that can be operated in parallel. Spark is normally used to handle huge data, and RDD is what makes it possible for Spark to split the input data into different nodes. RDD also provides useful APIs for the programmer to call. We will introduce some key APIs provided by Spark Core 2.2.1 using Java 8. You can find more information about the RDD here. https://spark.apache.org/docs/2.2.1/rdd-programming-guide.html
Spark Library Installation Using Maven
An Apache Spark application can be easily instantiated using Maven. To add the required libraries, you can copy and paste the following code into the "pom.xml".
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-core_2.10</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.spark</groupId>
<artifactId>spark-sql_2.10</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hadoop</groupId>
<artifactId>hadoop-hdfs</artifactId>
<version>2.2.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
Create And Set Up Spark
Spark needs to be set up in a cluster so first we need to create a JavaSparkContext object, which tells Spark how to access a cluster. To create a SparkContext you first need to build a SparkConf object that contains information about your application. We will talk about how to set up a spark in a cluster later. Now let's try to create a spark locally. To do that, we will need the following code:
//create and set up spark
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("HelloSpark").setMaster("local[*]");
JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
sc.setLogLevel("WARN");
Create RDDs
There are two ways to create RDDs: parallelizing an existing collection in your driver program, or referencing a dataset in an external storage system, such as a shared filesystem, HDFS, HBase, or any data source offering a Hadoop InputFormat.
1. Parallelized Collections
Let’s start with some Java collections by calling JavaSparkContext’s parallelize method on an existing Collection in your driver program. The elements of the collection are copied to form a distributed dataset that can be operated on in parallel.
//create input data list
List<Integer> inputData = new ArrayList<>();
inputData.add(11);
inputData.add(22);
inputData.add(33);
inputData.add(44);
//use RDD to run create RDDS
JavaRDD<Integer> javaRDD = sc.parallelize(inputData);
2. External Datasets
The other way is to create RDD from any storage source supported by Hadoop, including your local file system, HDFS, Amazon S3, etc. Text file RDDs can be created using SparkContext’s textFile method. This method takes an URI for the file (either a local path on the machine, or a hdfs://, s3n://, etc URI) and reads it as a collection of lines.
//From local file
JavaRDD<String> sentences = sc.textFile("src/main/resources/subtitles/input.txt");
//From a S3 file
JavaRDD<String> sentences = sc.textFile("s3://gpu621-demo/input.txt");
RDD APIs
Basically there are types of APIs. Transformations and Actions. Transformation APIs are functions that could return another RDD set. Using these APIs, we can create child RDD from parent RDD. Actions are the functions we want to perform onto the actual dataset. They will not return new RDDs.
1. Transformations
1.1 map(func)
The map function iterates over every line in RDD and split into new RDD. It receives a function, and will use that function to each line and create new RDD.
//create input data list
List<Integer> inputData = new ArrayList<>();
inputData.add(11);
inputData.add(22);
inputData.add(33);
inputData.add(44);
//create RDD
JavaRDD<Integer> javaRDD = sc.parallelize(inputData);
// map from one RDD to another RDD
JavaRDD<Double> mapRDD = javaRDD.map(value -> Math.sqrt(value));
//Output: 3.3166247903554, 4.69041575982343, 5.744562646538029, 6.6332495807108
mapRDD.foreach(value->System.out.println(value));
1.2 filter(func)
filter() is used when we only want some elements that meet the conditions. When we use this function, we need to pass another predicate function.
//create input data list
List<Integer> inputData = new ArrayList<>();
inputData.add(11);
inputData.add(22);
inputData.add(33);
inputData.add(44);
// create RDD
JavaRDD<Integer> javaRDD = sc.parallelize(inputData);
//use filter
JavaRDD<Double> filterRDD = javaRDD.filter(value ->value>=30);
//Output: 33 44
filterRDD.foreach(value->System.out.println(value));
1.3 flatMap(func)
flatMap is similar to map, but the difference is that flatMap could return multiple elements from one input.
//create input data list
List<String> inputData = new ArrayList<>();
inputData.add("WARN: Monday 1 May 0101");
inputData.add("ERROR: Monday 1 May 0102");
inputData.add("WARN: Monday 2 May 0301");
inputData.add("ERROR: Monday 3 May 0401");
inputData.add("FATAL: Monday 4 May 0406");
// create RDD
JavaRDD<String> sentencesRDD = sc.parallelize(inputData);
JavaRDD<String> wordsRDD = sentencesRDD.flatMap(value -> Arrays.asList(value.split(" ")).iterator());
1.4 mapToPair()
It is similar to map transformation; however, this transformation produces PairRDD, that is, an RDD consisting of key and value pairs. This transformation is specific to Java RDDs. With other RDDs, map transformation can perform both (map and mapToPair()) of the tasks.
List<String> inputData = new ArrayList<>();
inputData.add("WARN: Monday 1 May 0101");
inputData.add("ERROR: Monday 1 May 0102");
inputData.add("WARN: Monday 2 May 0301");
inputData.add("ERROR: Monday 3 May 0401");
inputData.add("FATAL: Monday 4 May 0406");
// create RDD
JavaRDD<String> logMessages = sc.parallelize(inputData);
//use Fluent API
JavaPairRDD<String, Long> levelRDD= logMessages.mapToPair(value ->new Tuple2<>(value.split(":")[0], 1L));
// (WARN,1) (ERROR,1) (ERROR,1) (FATAL,1) (WARN,1)
levelRDD.foreach(tuple2->System.out.println(tuple2));
1.5 reduceByKey(func)
When we use reduceByKey on a dataset (K, V), the pairs on the same machine with the same key are combined.
List<String> inputData = new ArrayList<>();
inputData.add("WARN: Monday 1 May 0101");
inputData.add("ERROR: Monday 1 May 0102");
inputData.add("WARN: Monday 2 May 0301");
inputData.add("ERROR: Monday 3 May 0401");
inputData.add("FATAL: Monday 4 May 0406");
// create RDD
JavaRDD<String> logMessages = sc.parallelize(inputData);
//use Fluent API
JavaPairRDD<String, Long> levelRDD= logMessages.mapToPair(value ->new Tuple2<>(value.split(":")[0], 1L));
// (WARN,2) (ERROR,2) (FATAL,1)
levelRDD.reduceByKey ((a,b)->a+b).forEach(t->System.out.println(t))
1.6 sortByKey()
When we apply the sortByKey() function on a dataset of (K, V) pairs, the data is sorted according to the key K in another RDD.
2. Actions
When the action is triggered after the result, new RDD is not formed like transformation. Thus, Actions are Spark RDD operations that give non-RDD values. The values of action are stored to drivers or to the external storage system. It brings laziness of RDD into motion. reduce(func)
2.1 Reduce()
Aggregate the elements of the dataset using a function func (which takes two arguments and returns one).
//create input data list
List<Integer> inputData = new ArrayList<>();
inputData.add(11);
inputData.add(22);
inputData.add(33);
inputData.add(44);
//use RDD to run reduce function
JavaRDD<Integer> javaRDD = sc.parallelize(inputData);
Integer result = javaRDD.reduce((Integer a, Integer b) -> a + b);
//output: 110
System.out.println(result);
2.2 Count()
count() returns the number of elements in RDD.
2.3 take(n)
The action take(n) returns n number of elements from RDD. It tries to cut the number of partition it accesses, so it represents a biased collection. We cannot presume the order of the elements.
2.4 collect()
The action collect() is the common and simplest operation that returns our entire RDDs content to driver program.
2.5 foreach()
When we have a situation where we want to apply operation on each element of RDD, but it should not return value to the driver. In this case, foreach() function is useful.
Useful Case
Scenario: If you have a video caption script, you want to sort all the word by frequency. How should we do it?
//create and set up spark
SparkConf conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("HelloSpark").setMaster("local[*]");
JavaSparkContext sc = new JavaSparkContext(conf);
sc.setLogLevel("WARN");
//read data from text file
//note that for production mode, we should not use file from local machine
//should use S3 or other resources
JavaRDD<String> sentences = sc.textFile("src/main/resources/subtitles/input.txt");
//remove the time stamp
JavaRDD<String> lettersOnlyRDD = sentences.map(sentence -> sentence.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z\\s]", "").toLowerCase());
//remove the blank line
JavaRDD<String> removeBlankLineRDD = lettersOnlyRDD.filter(sentence -> sentence.trim().length() > 0);
//map to only words
JavaRDD<String> wordsRDD = removeBlankLineRDD.flatMap(sentence -> Arrays.asList(sentence.split(" ")).iterator());
//create pair RDD
JavaPairRDD<String, Long> pairRDD = wordsRDD.mapToPair(word -> new Tuple2<>(word, 1L));
//get frequency
JavaPairRDD<String, Long> totals = pairRDD.reduceByKey((a, b) -> a + b);
//make frequency as the key
JavaPairRDD<Long, String> reversedMap = totals.mapToPair(t -> new Tuple2(t._2, t._1));
//sort the rdd
List<Tuple2<Long, String>> results = reversedMap.sortByKey(false).collect();
//print out the result
results.forEach(t->System.out.println(t));
//close
sc.close();
Deploy Apache Spark Application On AWS
Amazon EMR is a cloud big data solution for petabyte-scale data processing, interactive analytics, and machine learning using open-source frameworks such as Apache Spark, Apache Hive, and Presto provided by AWS cloud service. EMR is easy to use and it has low cost, so it’s a great start for spark beginners.
Prerequisite
From here, I will assume you have an AWS service account and that you have basic knowledge about AWS services like how to use S3 bucket, or how to add role or policy to services.
Also, you will need to have basic knowledge about SSH and Linux commands.
Create an EMR cluster
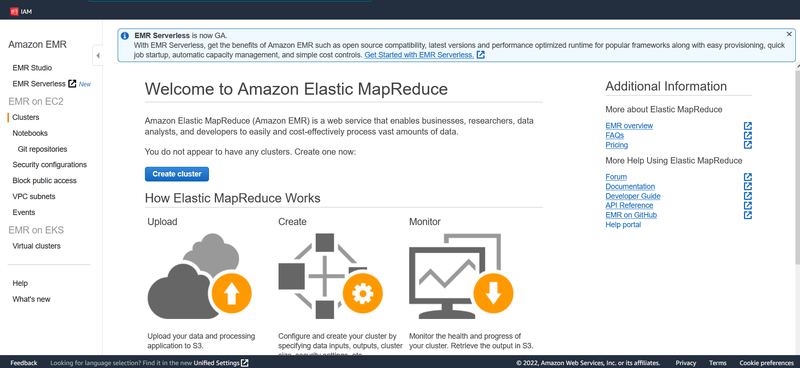
Search and choose EMR on AWS service panel.
Click the Create Cluster button.
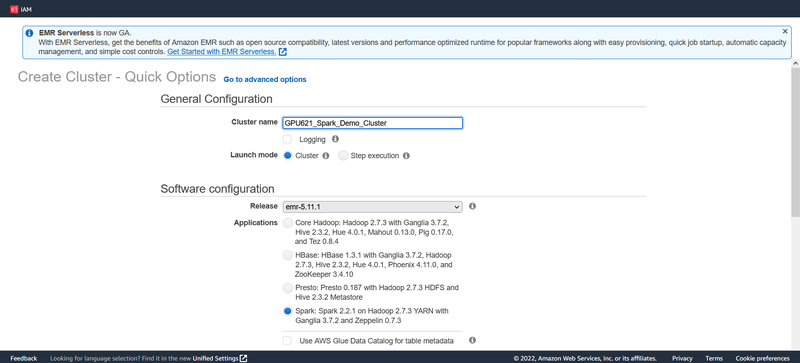
Enter as cluster name and choose a release version. Here I will choose the EMR-5.11.1 for the Release version. For the application, you can see that there are many options, we will choose Spark as this is our main topic.
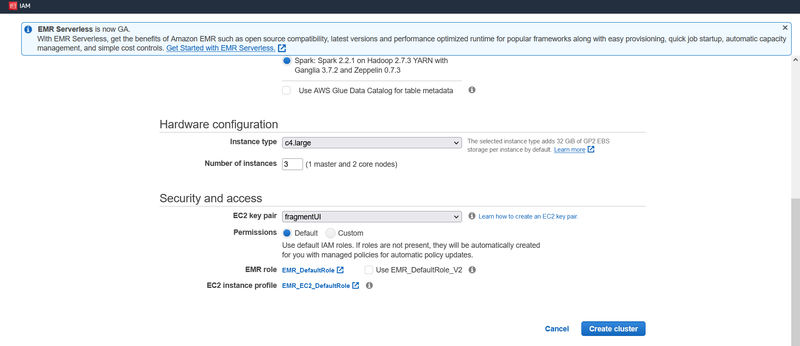
Next, we need to choose an instance type. As you may know, the cluster will run on multiple EC2 instances and different EC2 instances have different features. Please note, different EC2 types cost differently. Please refer to the EC2 type table to check the prices. Here I will choose c4.large type as it’s the most inexpensive one. For the number of instances, I will choose 3, that is, one master and 2 nodes.
For the security part. Please choose an EC2 key pair you already used for other services before, or create a new one.
Click Create Cluster button to wait for the cluster to be set up.
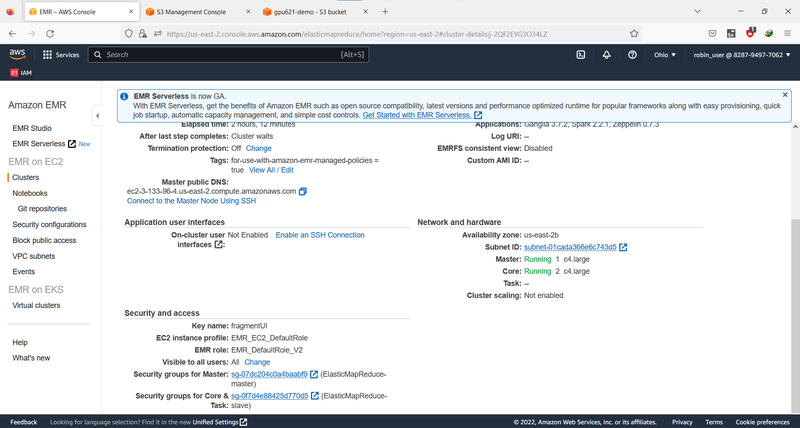
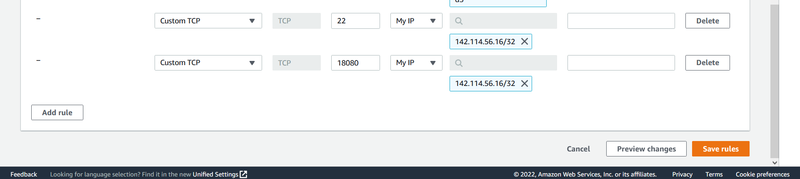
You will see a page like this. Next, we need to change the security group for Master, which acts like a firewall to add an inbound rule.
We need to open port 22 and port 18080 for your IP so that you can visit the Master EC2.
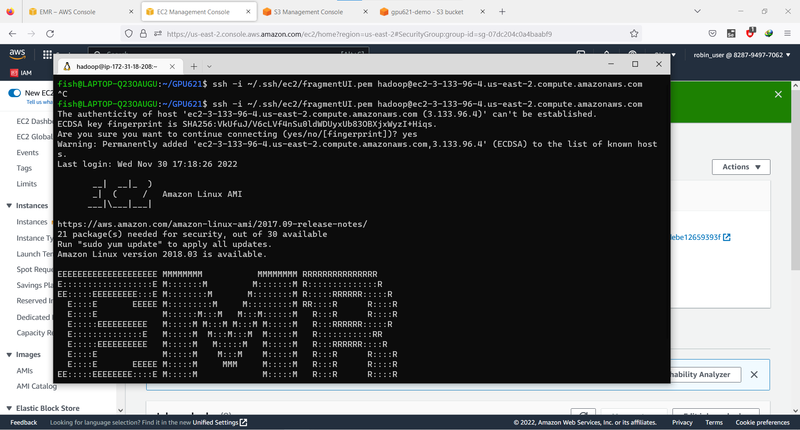
Then, you can try to ssh to the master node by using
ssh -I <private_key.pem> hadoop@<MasterPublicDNS>
You should see a welcome page like this:
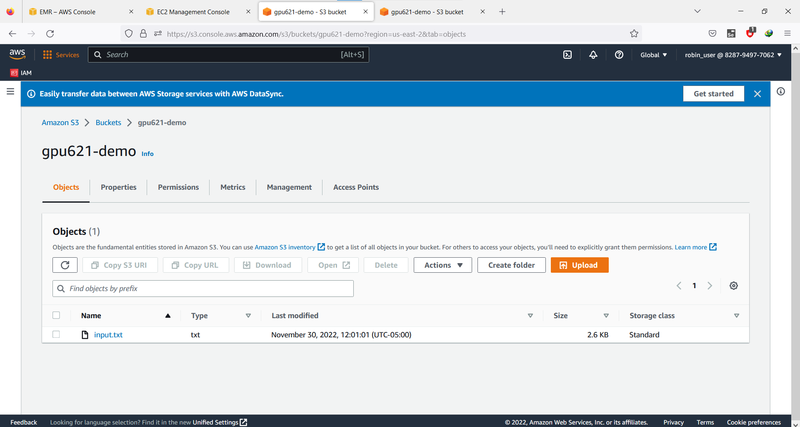
Create an S3 bucket
Unlike the previous case where we run on a solo computer, now we need to run the application on different nodes. It makes no sense to read the file from a local hard disk because most of the time the file will be too big for one node to handle. We need to put the file onto something that all nodes can share, and we can use aN S3 file as the input file. S3 is another service AWS provides. The size of a single file on S3 can be as large as 5TB. I will skip this part and please search how to create a new bucket to hold both the input file and the application package. Please make the bucket open to the public so you will not have permission issue later on.
Build the application
1. Change code
In order to run it on the cloud cluster, we need to do some modifications to the code. First, let’s change the file path from a local position to the s3.
From
JavaRDD<String> sentences = sc.textFile("src/main/resources/subtitles/input.txt");
To
JavaRDD<String> sentences = sc.textFile("s3://gpu621-demo/input.txt");
Also, add the entry point class to the pom file:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.0.2</version>
<configuration>
<archive>
<manifest>
<mainClass>ca.wonderfish.spark8.Main</mainClass>
</manifest>
</archive>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
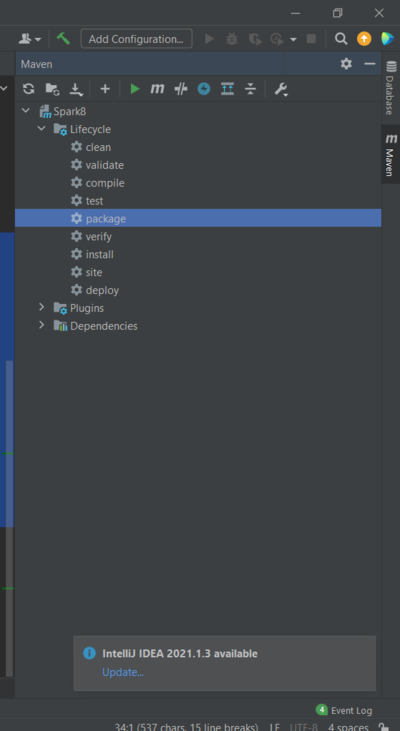
2. Build the package
Build the package using command line or the IDE. If you are using Idea, click the package under lifecycle Tab of maven
You will get a jar file under the target folder.
Upload the jar file to your S3 bucket
Upload the jar file into the S3 bucket you created before.
Run the application on the cluster
Ssh into the master node of the cluster. Then issue a copy command to copy the jar file to the master node using:
aws s3 cp <s3://yourbucket/jarFileName.jar> .
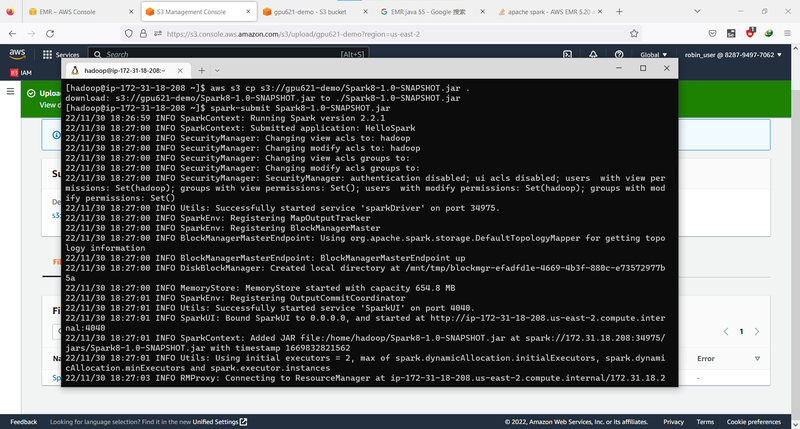
Then you can run the app using:
spark-submit <jarFileName.jar>
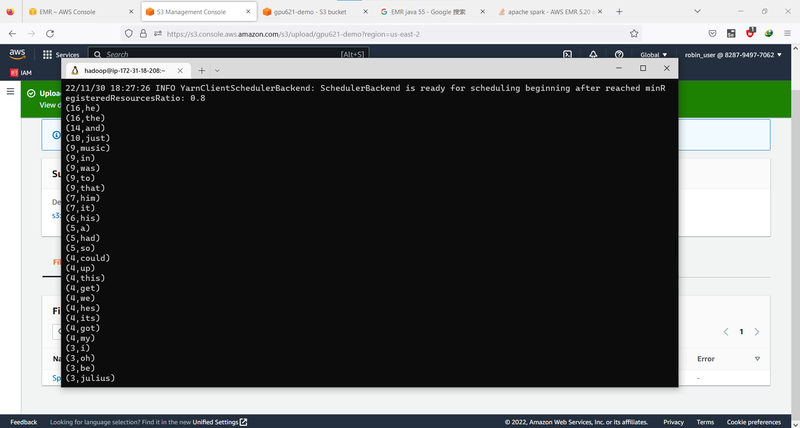
You should see the log info and the output of your application.
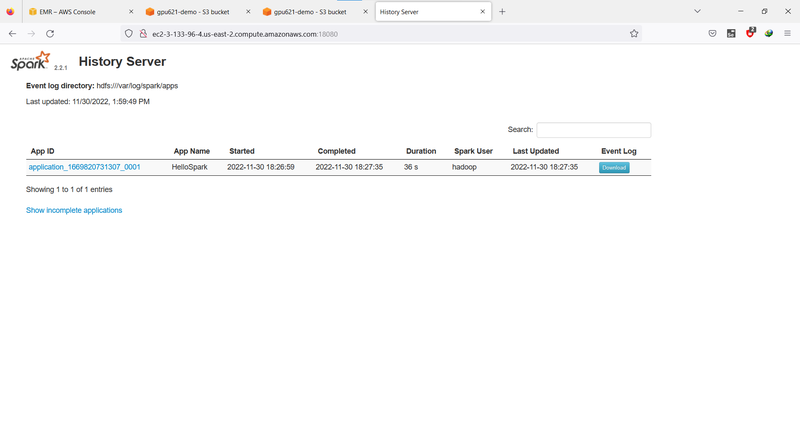
Check cluster status
Spark provides a simple dash board to check the status of the cluster. Visit <your_cluster_master_DNS>:18080, you will see the dash board.
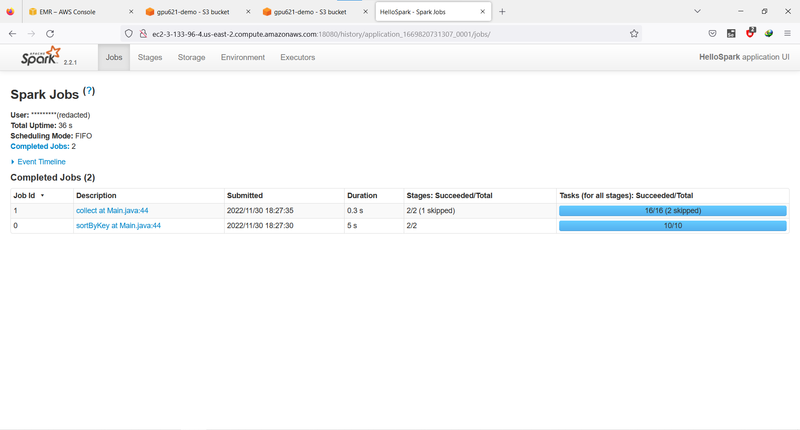
Click the application id, you can see more details like job descriptions.
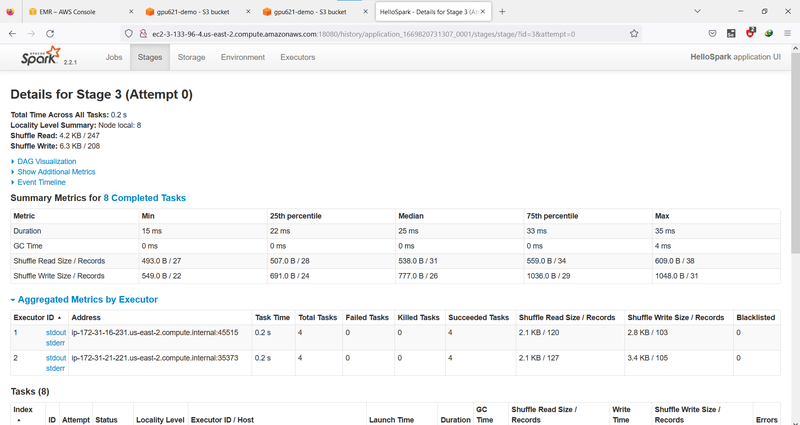
Or the stage descriptions.
Conclusion
With Amazon EMR you can set up a cluster to process and analyze data with big data frameworks in just a few minutes. You can install Spark on an Amazon EMR cluster along with other Hadoop applications, and it can also leverage the EMR file system (EMRFS) to directly access data in Amazon S3.
References
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/emr/latest/ReleaseGuide/emr-spark.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/emr/latest/ManagementGuide/emr-gs.html
https://data-flair.training/blogs/spark-rdd-operations-transformations-actions/
https://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/streaming-programming-guide.html