Difference between revisions of "DPS921/ A Crash Course on Processors"
Mschumacher (talk | contribs) |
Mschumacher (talk | contribs) |
||
| (One intermediate revision by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
=== What a Processor Consists of & How it’s Made=== | === What a Processor Consists of & How it’s Made=== | ||
A processor is made up of many parts. These parts include: | A processor is made up of many parts. These parts include: | ||
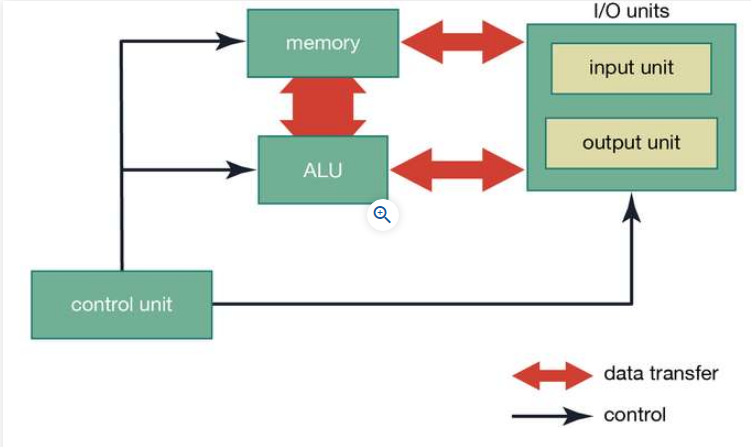
| − | Control Unit: retrieves, breaks down and executes instructions. | + | *Control Unit: retrieves, breaks down and executes instructions. |
| − | Logic Gates: Controls the flow of information | + | *Logic Gates: Controls the flow of information |
| − | Arithmetic and Logic Unit: Performs arithmetic and logical operations on data. | + | *Arithmetic and Logic Unit: Performs arithmetic and logical operations on data. |
| − | Internal Clock: ensures circuits work together at the same time. | + | *Internal Clock: ensures circuits work together at the same time. |
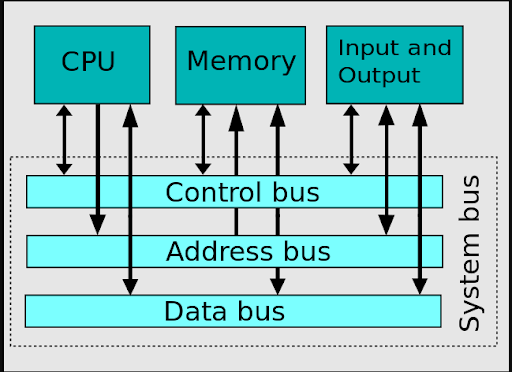
| − | Internal Buses: connects and interacts with internal computer components. | + | *Internal Buses: connects and interacts with internal computer components. |
| − | Registers: Stores data, waiting for instructions for them to be executed. The main component of a processor is silicon and the second main component is the transistor. Silicon is a natural element found in the earth's crust and has the characteristics to make it a semiconductor. A transistor is an electrical component which can play two roles, an amplifier or a switch. The first step in the process of creating a processor is to melt silicon with electrical active elements such as arsenic, boron, phosphorus or antimony. | + | *Registers: Stores data, waiting for instructions for them to be executed. |
| + | The main component of a processor is silicon and the second main component is the transistor. Silicon is a natural element found in the earth's crust and has the characteristics to make it a semiconductor. A transistor is an electrical component which can play two roles, an amplifier or a switch. The first step in the process of creating a processor is to melt silicon with electrical active elements such as arsenic, boron, phosphorus or antimony. | ||
| Line 110: | Line 111: | ||
=== Modern & Future Processors === | === Modern & Future Processors === | ||
| − | In the modern day, when hearing of processors two big giants come to play: AMD & Intel. With the advanced modern technology and the highly complex needs of most applications, the CPU’s and GPU’s are being developed at its highest engineered levels. The newest line of chips from Intel | + | In the modern day, when hearing of processors two big giants come to play: AMD & Intel. With the advanced modern technology and the highly complex needs of most applications, the CPU’s and GPU’s are being developed at its highest engineered levels. The newest line of chips from Intel and AMD provide an extremely high quality product which guarantees to tackle any task thrown at them. The new AMD Ryzen 9 3950X comes equipped with 16 cores, 32 threads, and a base clock of 3.5GHZ. While the Intel Core i9-10900k Series provides a 10 core, 20 thread 3.7 GHZ chip. It is everyone's goal to make the next processor the best performing and fastest. New technology is being researched with the use of fiber optics to replace capacitors. A photonic crystal is a slab of silicon with holes drilled in it which allows light to travel through the holes. So far, the researchers managed to reach speeds of data transmission at 40GB/S. With new developments always in the making, it is exciting to see what the future holds for computational processing. |
Latest revision as of 11:54, 7 April 2021
Contents
Group Members
1. Glib Zayarnyy
2. Matthew Schumacher
A Crash Course on Processors
A central processing unit (CPU) is a piece of hardware that is responsible for allowing your computer to interact with the applications and programs installed on it. The amount of cores within a processor determines how much information can be transmitted at a time and as well as how quickly that information can be transmitted. A processor core are individual units within a CPU. Each core is responsible for its own individual tasks requested by the user. Clock speed is the unit of measurement that determines the duration it takes for a CPU to retrieve and interpret instructions. The unit of measurement for clock speed is gigahertz (GHz). The higher the gigahertz, the faster the clock speed. A modern processor can handle upto a trillion calculations per second. Most computers sold today either come equipped with either an Intel, AMD or Apple processors. While CPU’s handle the inputs and outputs of applications within a computer, a GPU processor is designed to handle graphical outputs on your monitor. Both CPU and GPU are the main components that make up a computer.
Different Types of Processors
CPU’s come in a few types in the modern age and for most pc’s they come in 32 and 64 bit respectively. The difference between 32 and 64 bit processors refers to the amount of computational values they can store. Additionally 32 bit processors cap out at handing 4gb of ram. “A 64 bit processor has 4 billion times the physical memory of a 32-bit processor.”
Overclocking (CPU,GPU):
Overclocking refers to increasing the clock rate of a CPU or GPU so it runs faster than the manufacturer had originally set. The benefits of overclocking are increased performance, although most individuals would not notice these marginal increases.
MicroProcessors
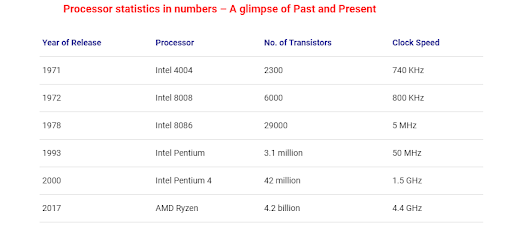
The very first microprocessor was the Intel 4004. It was only 4-bits. designed by Marcian Hoff and Federico Faggin in 1969. This microprocessor was found in simple electronic devices such as cash registers and calculators. It was able to perform 92600 operations per second.
In 1972 the Intel 8008 was released. This was the first 8-bit microprocessor. This microprocessor was found in bottling machines and microcomputers.
In 1979 the Intel 8088 was released and this was a 16-bit processor.
Motorola released the 68000 and came in a 16-32 bit processor. These processors began to make their way into apple products as well as Sega arcade systems.
Jumping ahead to 1987 the first Scalable Processor Architecture was used. This offered faster execution rates and would be found in mainframes.
Intel in 1993 released a processor called the Intel Pentium, this had 3.1 million transistors and ran at 60hz.
In 2001 IBM released the first multi core processor called the power 4. This began a new journey that would change the way people used technology and what people could do with technology. It had 174 million transistors and could clock at 1.3Ghz.
2017 Amd Releases the first Ryzen series Processors to compete with Intel.
2021 AMD released the Ryzen 9 5950x which has 19.2 billion transistors. It is a 64-bit microprocessor.
Looking through the years from 1969 to 2021, several technological advancements can be seen, the increase from 4 bits to 64 bits, the increase from 2,300 to 19.2 billion transistors in just 52 years. Additionally the transition from single to multicore processors increased computing in a variety of ways that will be later discussed.
What a Processor Consists of & How it’s Made
A processor is made up of many parts. These parts include:
- Control Unit: retrieves, breaks down and executes instructions.
- Logic Gates: Controls the flow of information
- Arithmetic and Logic Unit: Performs arithmetic and logical operations on data.
- Internal Clock: ensures circuits work together at the same time.
- Internal Buses: connects and interacts with internal computer components.
- Registers: Stores data, waiting for instructions for them to be executed.
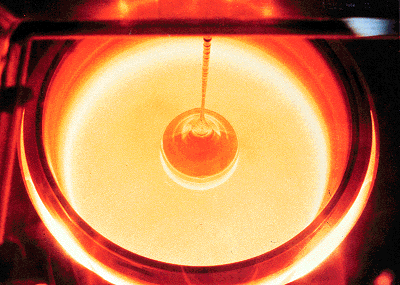
The main component of a processor is silicon and the second main component is the transistor. Silicon is a natural element found in the earth's crust and has the characteristics to make it a semiconductor. A transistor is an electrical component which can play two roles, an amplifier or a switch. The first step in the process of creating a processor is to melt silicon with electrical active elements such as arsenic, boron, phosphorus or antimony.
Next, once the desired temperatures are reached, a silicon seed crystal is inserted within the compound. Once the seed is in place, it begins to grow. As the seed grows exponentially it is also extracted simultaneously from the melt as an ingot. At this stage, many factors come to play to ensure sufficient electrical properties of the silicon such as concentration, temperature and speed of the melt. Once around 6 inches of ingot is extracted, it is cut to the proper diameter.
They are then polished to produce a flat, mirror like surface. Lastly, the compound is inspected and heated if needed to remove any defects.
Transistors are made from a complex chemical formula and step process that involves diffusing acceptor atoms (Boron) in silicon dioxide. These transistors are used in the microprocessors and memory.
Nowadays, most of the process is automated under strict supervision of the technicians. The labs must be kept extremely clean as one spec of dust can ruin the entire chip. It may take up to three full months to completely create and test a processor.
Single Core vs Multi Core
Processors began as single core, this means that at any time they only had a single processing unit on them. This was the case until 2001 when the first multi core processor was released. This increased performance because instead of one processing unit executing one task, now there are multiple processors executing multiple tasks increasing efficiency and speed. This allows the multi core processors to run multiple programs or processes at once. An added benefit was the physical CPU did not increase in size, only one physical CPU chip was inserted into the motherboard.
Two definitions we should clarify before we continue.
Process: A process is a task, like an application. A process can be made up of two or more threads.
Thread: A thread is a chunk of data from a program that a processor would manage. All programs create single or multiple threads.
Multithreading: Multiple threads exist within a process and execute independently, but share resources.
When it comes to multi core processors, they excel at being able to execute more than one thread at the same time. Each core is able to process a separate chunk of data, which increases performance and allows multiple applications to run at the same time.
Modern & Future Processors
In the modern day, when hearing of processors two big giants come to play: AMD & Intel. With the advanced modern technology and the highly complex needs of most applications, the CPU’s and GPU’s are being developed at its highest engineered levels. The newest line of chips from Intel and AMD provide an extremely high quality product which guarantees to tackle any task thrown at them. The new AMD Ryzen 9 3950X comes equipped with 16 cores, 32 threads, and a base clock of 3.5GHZ. While the Intel Core i9-10900k Series provides a 10 core, 20 thread 3.7 GHZ chip. It is everyone's goal to make the next processor the best performing and fastest. New technology is being researched with the use of fiber optics to replace capacitors. A photonic crystal is a slab of silicon with holes drilled in it which allows light to travel through the holes. So far, the researchers managed to reach speeds of data transmission at 40GB/S. With new developments always in the making, it is exciting to see what the future holds for computational processing.
Progress Report
- Update 1: Monday, March 15, 2021 - Began Research on Processors
- Update 2: Friday, March 19, 2021 - Developed a project structure
- Update 3: Sunday, March 21, 2021 - Completed What is Processors section
- Update 4: Monday March 29, 2021 - Completed Different Types & How it’s made section
- Update 5: Monday, April 5, 2021 - Completed Modern & Future work section.
References
- A. (2020, June 20). Multi-Core Processor: Is More Always Better? Streamer Builds. https://www.streamerbuilds.com/multi-core-processor/
- Both, D. (2020, July 23). The central processing unit (CPU): Its components and functionality. Enable Sysadmin. https://www.redhat.com/sysadmin/cpu-components-functionality
- Computer Hope. (2020, April 30). What is BIT (Binary DigIT)? Https://Www.Computerhope.Com/Jargon/b/Bit.Htm.
- Fonseka, A. (2020, November 8). Evolution of Computer Processors. Zzoomit. https://www.zzoomit.com/evolution-of-computer-processors/
- HP. HP TECH TAKES. https://www.hp.com/us-en/shop/tech-takes/what-is-processor-speed#:~:text=What%20is%20a%20PC%20processor,you're%20using%20a%20computer.
- Intel 4004 | Computer Wiki | Fandom. (n.d.-b). Computer Wiki. https://computer.fandom.com/wiki/Intel_4004
- Lee, C. (2019, April 19). The future of high-speed computing may be larger CPUs with optics. Ars Technica. https://arstechnica.com/science/2019/04/the-future-of-high-speed-computing-may-be-larger-cpus-with-optics/
- Martindale, J. (2021, March 19). 32-bit vs. 64-bit: Understanding what these options really mean. Digital Trends. https://www.digitaltrends.com/computing/32-bit-vs-64-bit-operating-systems/
- M68000. (2019, June 14). Sega Retro. https://segaretro.org/M68000
- Techopedia. (2011, December 8). Scalable Processor Architecture (SPARC). Techopedia.Com. https://www.techopedia.com/definition/26753/scalable-processor-architecture-sparc
- The CPUShack . How a cpu microprocessor is made. http://www.cpushack.com/EtchingWafers.html
- Thomas, B. (2021, March 19). Best processors 2021: the best CPUs for your PC from Intel and AMD. TechRadar. https://www.techradar.com/news/best-processors