Difference between revisions of "OPS335 Lab 4b"
(→Testing the connection to the Postfix Service) |
(→INVESTIGATION 1: INSTALL THUNDERBIRD (MUA) and SETUP A REFERENCE CLIENT) |
||
| (167 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | [[Category:OPS335]][[Category:OPS335 Labs]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == OVERVIEW== |
| + | {{Admon/important|Warning|Your lab 4a must be complete before you can start this lab.}} | ||
| − | + | In Lab 4a, you configured and ran the '''Postfix''' application for our MTA (a.k.a. SMTP server) on your '''vm2''' and '''vm3''' machines. | |
| − | * | + | That setup has some major drawbacks: |
| − | * | + | :* It required an SMTP server ('''MTA''') to be configured on each machine. |
| + | :* The Message Store ('''MS''') would also be unique to each machine - what a user received on one server would not exist on any other. | ||
| + | In this lab you will centralize some of this information, so that a user can send email from any machine in the network, and have incoming mail sent to a centralized messages store. | ||
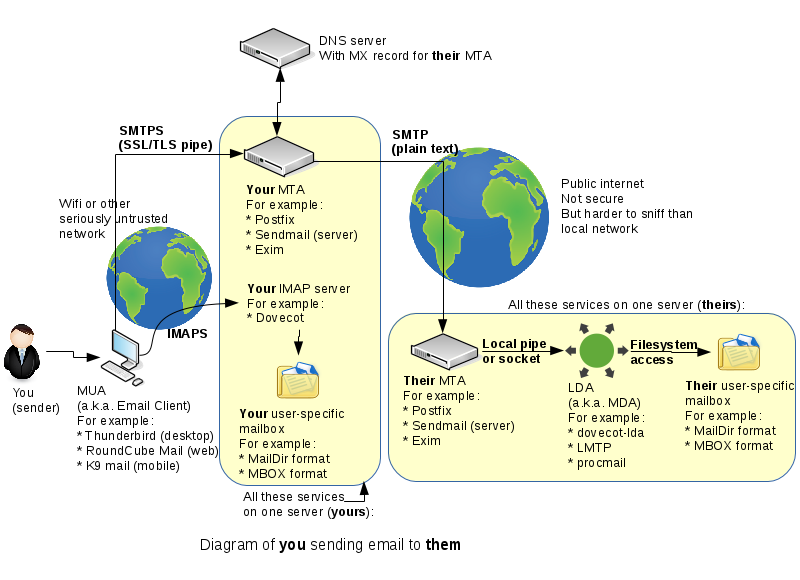
| − | + | '''The a diagram below (duplicate to lab 4a) shows your basic setup of your email system:''' | |
| − | |||
[[Image:Email-servers.png]] | [[Image:Email-servers.png]] | ||
| − | + | You will begin by modifying the existing '''Postfix''' ('''MTA''') servers to make mail they send come from your domain (instead of each machine). Then you will add a record to your DNS server to allow mail to be sent to the domain itself, instead of the individual machines. Next, you will add a Local Delivery Agent ('''LDA''') to your '''vm3''' by installing '''dovecot-lda''', configure it, and test it to make sure that is is working correctly. | |
| − | + | Finally, you will set up an '''IMAP''' server called '''Dovecot''' on your '''vm3''' machine, so you can read your email from an MUA such as ''Thunderbird'' or a ''Webmail'' application. You will set up a webmail application called '''Roundcube''' in a later lab). | |
| − | === Services | + | === Learning About the Services Involved in an Email Delivery === |
| − | In reality, the terms '''MTA''', '''MDA''', '''MUA''', '''LDA''' can actually be considered misleading since some of those services can be combined together to form a single entity (application), while other applications may operate as separate entities. There may be overlap, so if you don't find those acronyms helpful, don't worry too much about them. On the other hand, when referred to in diagrams, they can help to visualize those processes when | + | In reality, the terms '''MTA''', '''MDA''', '''MUA''', '''LDA''' can actually be considered misleading since some of those services can be combined together to form a single entity (application), while other applications may operate as separate entities. There may be overlap, so if you don't find those acronyms helpful, don't worry too much about them. On the other hand, when referred to in diagrams, they can help to visualize those processes when trying to understand how an e-mail system works. |
| − | [http://wiki.dovecot.org/MailServerOverview Here | + | [http://wiki.dovecot.org/MailServerOverview Here is an overview] of those terms (from the Dovecot wiki). It is worth viewing this link. |
In the diagram displayed above, the elements include: | In the diagram displayed above, the elements include: | ||
| − | * | + | * '''User Account'''. The individual who wants to send or receive mail messages. |
| − | * | + | * '''MUA''' (email client). This is the application that the individual uses to send or receive mail messages. It can be a '''native application''' or a '''web application'''. You will learn how to setup and use both types of these applications throughout the remainder of this course. |
| − | * Two ''' | + | * Two '''MTA''' servers. These are the servers responsible for getting your emails to the <u>destination</u> server. |
** They are similar to routers (which route packets) but work on the <u>application</u> layer rather than the <u>network</u> layer. | ** They are similar to routers (which route packets) but work on the <u>application</u> layer rather than the <u>network</u> layer. | ||
** In our example, there are only two MTAs - but there can be several. | ** In our example, there are only two MTAs - but there can be several. | ||
** You connect to your MTA over a <u>secure</u> connection, so your emails can't be read by the operators of the network you're connected to. | ** You connect to your MTA over a <u>secure</u> connection, so your emails can't be read by the operators of the network you're connected to. | ||
** The mail message then travels the rest of the way to the destination MTA <u>unencrypted</u>, so anyone with access to the routers in-between can read all your emails. That is why many organizations will refuse to send you confidential information over email. | ** The mail message then travels the rest of the way to the destination MTA <u>unencrypted</u>, so anyone with access to the routers in-between can read all your emails. That is why many organizations will refuse to send you confidential information over email. | ||
| − | * | + | * '''LDA/MDA''' Server. This server will receive the email from the MTA, and will store it on disk in some format. '''MailDir''' and '''MBOX''' are the most popular mailbox formats. |
| − | * When sending an email, you send it to the destination using your MTA, but you also want to save it in your '''"Sent"''' folder for yourself. This is accomplished by a separate connection to your '''IMAP''' or '''POP3''' server. | + | * '''IMAP/POP3''' server(s). When sending an email, you send it to the destination using your MTA, but you also want to save it in your '''"Sent"''' folder for yourself. This is accomplished by a separate connection to either your '''IMAP''' or '''POP3''' server. |
** Thus, a situation can occur that although you sent your email successfully, it may never make it to your "Sent" folder - the <u>second</u> connection to your IMAP server is quite unrelated to the first connection to the '''SMTP''' server. | ** Thus, a situation can occur that although you sent your email successfully, it may never make it to your "Sent" folder - the <u>second</u> connection to your IMAP server is quite unrelated to the first connection to the '''SMTP''' server. | ||
| − | * | + | * '''DNS''' Server. A DNS server is also involved - it is needed to retrieve the address of the email server responsible for email for a particular domain. This is done with '''MX''' records. |
| − | === | + | ===Online References=== |
| − | + | * [https://help.ubuntu.com/community/Dovecot Dovecot Community Documentation] | |
| + | * [http://wiki.dovecot.org/LDA Dovecot-lda] | ||
| + | * [http://wiki.dovecot.org/LDA/Postfix Configuring dovecot-lda with postfix] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == INVESTIGATION 1: INSTALL THUNDERBIRD (MUA) and SETUP A REFERENCE CLIENT== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Unlike the '''mailx''' (MUA) application you installed and used in Lab 4a, this lab will be using the '''Thunderbird''' (MUA) application instead which is a graphical application that uses a '''centralized Message Store''' (MS) to retrieve and read mail messages. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Although we will be eventually setting up the Thunderbird application to perform all the mail operations discussed above, you need to learn to '''"walk before you can run"'''. Eventually, you are going to set up all those mail services, but to begin with, you will set up an email client to connect to an already working server which is the '''Seneca email server'''. Once we learn how to do this for our Seneca email account, then we can use it for our mail servers for our VM2 and VM3. | ||
'''Perform the following steps:''' | '''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
#Switch to your '''host''' machine, and install the '''Thunderbird''' email application. | #Switch to your '''host''' machine, and install the '''Thunderbird''' email application. | ||
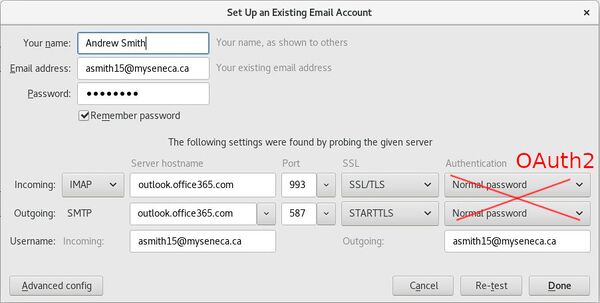
| − | #When you | + | #When you first launch the Thunderbird application, a configuration dialog should appear as shown in the diagram below: |
| − | [[Image:Seneca-student-thunderbird-email-setup.png|600px]] | + | <br> |
| + | ::[[Image:Seneca-student-thunderbird-email-setup.png|600px]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <ol><li value="3">Use the data in the table below to configure the Thunderbird settings dialog box for YOUR Seneca e-mail account:</li></ol> | ||
| − | :: | + | {| class="wikitable" border="1" style="margin-left:40px;" |
| + | ! Setting !! '''Incoming: IMAP''' !! '''Outgoing: SMTP''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''Username'''|| yoursenecauserid@myseneca.ca || yoursenecauserid@myseneca.ca | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''servername''' || outlook.office365.com || outlook.office365.com | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''port''' || 993 || 587 | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''security''' || SSL/TLS || STARTTLS | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | '''References''' | ||
| + | | colspan="2" | [1] [https://employees.senecacollege.ca/spaces/77/it-services/wiki/view/2394/other-email-clients ITS - Configuring other Email Clients] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | :: | + | ::Note that your username is your full email address(<em>yourid@myseneca.ca</em>) and not just <em>yourid</em>. |
| − | |||
| + | {{Admon/important |Unencrypted Options|Notice that there are <u>unencrypted</u> options available to connect to your SMTP/IMAP servers but those are rarely used these days - the potential for abuse is too great. On a free wifi network, the operator would be able to not only read your email, but also obtain your password without any password/encryption cracking tools. In fact, even on a private wired network, it is not uncommon for an employer to use a packet sniffer utility to monitor all the traffic going over their network (Packet Sniffing applications were actually found to be legally acceptable practice if used by the management of organizations)}} | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <ol><li value="3">After you create your '''Thunderbird''' account, you should be able to read your existing email and send new email within the Thunderbird application.</li><li>Take time to view your ''Account Settings'' and ''Preferences'' to get a feel for what settings exist. For example:<ul><li>How often will Thunderbird check for new messages?</li><li>Will the messages you write be in HTML or plain text?</li><li>How do you change your SMTP server settings? Why are they in a different section?</li></ul></li><li>The main objective of this section was to learn how to setup your Thunderbird application to read your Seneca email, so in the next section you can use the exact type of setup for your own email server.</li></ol> | ||
| − | + | '''Record steps, commands, and your observations in INVESTIGATION 1 in your OPS335 lab log-book''' | |
| − | == INVESTIGATION | + | == INVESTIGATION 2: SETUP A CENTRALIZED MESSAGE STORE == |
| − | + | === Setup Your MTA to Use Correct Domain=== | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | In Lab 4a, both of your email servers were sending mail messages addressed from users of the actual machines themselves. This would be confusing for the receiver who might get emails from the same user @vm1, vm2, and vm3. Which would they respond to? To avoid this problem from occurring, we can make all servers make the sent mail appear to come from a central location (usually the '''domain'''), and make incoming email sent to that address to be accessible from machines within our network. | |
'''Perform the following steps:''' | '''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
| − | # | + | # Issue the '''mail''' command to view the email messages you sent between your '''vm2''' and '''vm3''' in your lab 4a. Notice that each is addressed from root on whichever machine sent it. |
| − | # | + | # On both machines (vm2 and vm3), edit the '''/etc/postfix/main.cf''' file to change the '''myorigin''' parameter from '''$myhostname''' to '''$mydomain'''. Restart the '''postfix''' service. |
| − | + | # Now, send emails messages (via the '''mail''' command) between both of your vm2 and vm3 machines, and view the mail messages by issuing '''mail''' in each vm. The sender address should now read that the received mail messages came from '''root@yourdomain.ops'''. | |
| − | # | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ::The next step is to configure what addresses that the server will receive email for. This is done using postfix by setting the '''mydestination''' parameter (configuration variable) to include '''$mydomain''' (this is assuming you've set up '''mydomain''', '''myorigin''' , and '''inet_interfaces''' properly). | |
| − | |||
| − | ''' | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | ::''' | + | <ol><li value="4">Edit the '''/etc/postfix/main.cf''' file for '''vm3 ONLY''', scroll down to the line containing: '''mydestination''' and change line to the text shown below:<br><source>mydestination = $mydomain, $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost</source>'''Note:''' Even though your machine's name is ''vm3.yoursenecaid.ops'', your postfix MTA will also receive emails addressed to the domain called: yoursenecaid.ops</li></ol> |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ::In order for this to work, we need to add a DNS record that will point mail sent to the domain towards one of the SMTP servers configured to accept it. | ||
| − | <ol><li value=" | + | <ol><li value="5">Add an '''MX''' record to the forward lookup zone on '''host''' so that all incoming mail addressed to the domain is sent to your vm3.</li><li>Restart the service and use the '''dig''' command to confirm that it works.</li><li>Send an email from your '''vm2''' to '''root@yourdomain.ops'''</li><li>Confirm that it arrives on your '''vm3''' machine</li></ol> |
| − | <li> | ||
| − | <li> | ||
| − | === | + | === Relay Email Through Another Server=== |
| − | + | When email is sent from either vm, it is addressed from the domain, but receiving MTAs might query why mail sent from vm2 doesn't match the address of the MX record for the domain. This would be a red-flag for potential spam. To avoid this, we can relay all mail sent from vm2 (or any other machine in our network) through vm3 so that it properly appears to come from the mail server that matches the MX record for the domain. | |
'''Perform the following steps:''' | '''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
| − | # | + | # Move to your vm2 machine. |
| − | # | + | # Direct your '''vm2''' MTA to relay mail through vm3, by making the following editing change for the '''/etc/postfix/main.cf''' file:<br><source>relayhost = vm3.<yourdomain>.ops</source> |
| − | + | # Restart the '''postfix''' service. | |
| + | # Next, you must instruct your '''vm3''' machine to allow your vm2 machine to pass email through it by making the following editing change to the '''/etc/postfix/main.cf''' file:<br><source>mynetworks = 192.168.X.0/24</source>NOTE: Substitute in your '''own network''' for X<br><br> | ||
| + | # Restart the '''postfix''' service. | ||
| − | + | All mail is now being delivered to a centralized location (and also appears to be coming from that same location), but a user would still have to access that server to retrieve it. | |
| − | === | + | === Install and Configure the Local Delivery Agent (LDA/MDA) === |
| − | + | Postfix is capable of performing the function of an LDA, but its LDA capabilities are limited, thus postfix is generally not used for that purpose. Currently, the most popular LDA is ''LMTP'', but we will be installing, configuring, and using an LDA called '''Dovecot''' since it is also popular and we will setting up Dovecot as an '''IMAP''' server later in this lab. Using both Postfix and Dovecot will actually increase the performance of our IMAP server. | |
'''Perform the following steps:''' | '''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
| − | # | + | #Move to your '''vm3''' machine. |
| − | + | #Dovecot is not installed when you installed your Virtual machines in previous labs.<br>Install the Dovecot application by issuing the following command:<br><source>yum install dovecot</source> | |
| + | #Edit your '''/etc/postfix/main.cf''' file and scroll down to (or search for) '''mailbox_command'''. Add the following line:<br><source>mailbox_command = /usr/libexec/dovecot/dovecot-lda -f "$SENDER" -a "$RECIPIENT"</source> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ::NOTE: Do <u>'''not'''</u> replace any variables, those are set automatically by Postfix when it runs the LDA. If you are interested in learning more about the Dovecot application, you can read about dovecot-lda [http://wiki.dovecot.org/LDA/Postfix here] and [http://wiki.dovecot.org/LDA here]. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <ol><li value="4">Finally, edit the '''/etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf''' file and indicate where you want your mail delivered by including the following line:<source>mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir</source></li> | ||
| + | <li>Restart your postfix service.</li><li>While the emails are still stored only on VM3, they will now be easier for other machines/services to access.</li> | ||
| + | <li>Due to permissions on the directories where mail will now be stored, root will no longer receive mail. Check the logs for an indication as to why.</li></ol> | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Record steps, commands, and your observations in INVESTIGATION 2 in your OPS335 lab log-book''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==INVESTIGATION 3: USING THUNDERBIRD (MUA) FOR VM2 and VM3 MACHINES == | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Accessing Received Mail Messages on VM3 VIA IMAP === | ||
| − | + | First, we will set up the IMAP server so we can read email. The current way we have configured our mail server on our VM3 machine should allow all the email for anyaccount@yoursenecaid.ops should be delivered to our '''vm3''' machine. We will set up Dovecot with IMAP to get easy access to that email. | |
| − | ''' | + | '''Perform the following steps:''' |
| − | + | #The configuration file for the Dovecot service (which is not the same thing as dovecot-lda) is: '''/etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf'''. Modify the '''protocols''' option so that Dovecot will work with IMAP connections, no POP3 or LMTP. | |
| + | # Start the dovecot service, and ensure it will always start automatically when the machine boots. | ||
| + | # Use the '''ss''' command to confirm the service is listening, and use '''nc''' on the '''host''' to confirm you can connect to it. | ||
| + | # You'll probably fail, so using the information gathered from '''ss''', modify the firewall on vm3 to allow IMAP connections from your local network and try '''nc''' again. Once it works, do not forget to save this change so it will still be there the next time you reboot. | ||
| + | #If you can connect - it's now time to do something wrong, that is allow connections to our IMAP server over an unencrypted connection. | ||
| + | # Edit the '''/etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf''' file and set '''disable_plaintext_auth''' to '''no'''. | ||
| + | # Then edit the '''/etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-ssl.conf''' file and set '''ssl''' to '''yes'''.<br><br>'''Note:''' This combination of parameters will allow your username and password to be sent over the internet in plain text, for anyone interested to look at. In a later lab we'll set up secure SMTP and IMAP connections, for now this is all we have time for.<br><br> | ||
| + | # Restart dovecot so the changes take effect. | ||
| − | + | === Connecting to IMAP Servers Using Thunderbird=== | |
| − | |||
'''Perform the following steps:''' | '''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
| − | #On your host machine, return to the Mail Account Setup dialog box (eg. near top of lab). | + | #On your '''host''' machine, return to the Mail Account Setup dialog box (eg. near top of lab). |
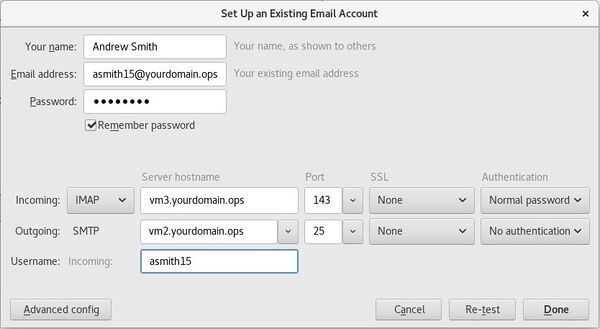
| − | # Set up | + | # Set up a '''new email account'''. You will be using account settings to connect to your '''vm2''' for '''SMTP''' and '''vm3''' for '''IMAP'''. Use <u>no</u> encryption, and use normal password authentication for IMAP. Refer to the diagram below for reference: |
[[Image:ops335-email-step1.png|600px]] | [[Image:ops335-email-step1.png|600px]] | ||
| − | + | <ol><li value="3">Try to connect to your IMAP server with Thunderbird by clicking on your '''Inbox'''.</li> | |
| + | <li>If nothing happens, then check the Thunderbird Activity Manager for any errors. If the connection is successful, you should see the '''Trash''' box <u>appear</u> below Inbox.</li> | ||
| + | <li>Use the Thunderbird application to send an email to your myseneca address. If you've done everything right, it will send the message successfully</li><li>Verify that your message has been sent. Check your myseneca email and look at '''/var/log/maillog''' on vm2 (your email server).</li></ol> | ||
| − | + | === Sending a Mail Message from VM2 (Using Thunderbird)=== | |
| + | '''Perform the following steps:''' | ||
| − | ''' | + | #Use the '''ss''' and '''nc''' commands (like you did in lab 4a) to confirm your service is listening on the correct ports/interfaces. You will probably have to open the appropriate firewall port on '''vm3''' to allow incoming '''SMTP''' connections.<br><br>'''Note:''' You should be able to send email to any regular user <u>on</u> '''vm3''' using the email address '''yourusername@yoursenecaid.ops''' using the Thunderbird application on your host machine (which is configured to use the account on your vm2).<br><br> |
| + | |||
| + | <ol><li value="2">Create a new account on your '''vm3''' machine using only your <u>first</u> name. We will use this account as a one-time "test" if the mail message has been received on your VM3 machine (from your VM2 machine).<br><br>'''Note:''' It is <u>'''important'''</u> that you '''<u>don't</u>''' create this same account name on your vm2 machine, since you want to easily identify the difference between the sending and receiving SMTP servers.<br /><br /></li></ol> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <ol><li value="3">Use the new account in Thunderbird to send an email to '''firstname@yoursenecaid.ops''' and then check the contents of '''/home/firstname/Maildir/new/''' on your '''vm3''' machine. There should be a file there with the contents of your email.</li><li>If there is no file, then check the log file '''/var/log/maillog''' to see what went wrong.</li><li>If you can see a file in the '''/home/firstname/Maildir/new/''' directory, then review the procedures on how you got the email server working (since you have performed many steps and set up many services).</li><li>Refer to the diagram at the top of this lab. Which services have you currently set up? Record your findings in your lab Logbook.</li></ol> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Admon/important |Encountering error messages when sending email|If you cannot properly receive sent e-mail messages, check the '''/var/log/syslog''' file for errors.<br><br> If you locate an error message in that file such as: '''Fatal: Error reading configuration: Invalid settings...''', then add the following <u>parameter</u> in '''/etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf''':<br />'''postmaster_address <nowiki>=</nowiki> DOMAIN''' (where DOMAIN is actually <u>your</u> domain).<br /><br />After you have saved those changes, then '''restart''' your dovecot service. This problem can also be resolved by properly setting the hostname of your machine to include the domain.}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Admon/important |Backup your VMs!|You MUST perform a '''full backup''' of ALL of your VMs whenever you complete your '''OPS335 labs''' or when working on your '''OPS335 assignments'''. You should be using the dump or rsync command, and you should use the Bash shell script that you were adviced to create in order to backup all of your VMs.}} | ||
| + | '''Record steps, commands, and your observations in INVESTIGATION 3 in your OPS335 lab log-book''' | ||
== COMPLETING THE LAB == | == COMPLETING THE LAB == | ||
| − | + | ===Online Submission=== | |
| + | Follow the instructions for lab 4b on blackboard. | ||
| + | <!-- | ||
| + | ===Andrew's sections=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | You may choose to: | ||
| + | * Submit screenshots of your work on Blackboard, in which case you don't need to come to the lab. | ||
| + | * Or come to the lab, show me your work, and talk to me about it. I want to hear what you've learned and answer any questions you have. | ||
| − | ' | + | You'll get the same grade regardless of how you choose to submit your work. |
::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>Status and configuration of your Postfix service on vm2. | ::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>Status and configuration of your Postfix service on vm2. | ||
| Line 151: | Line 204: | ||
::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>Your Thunderbird configuration. | ::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>Your Thunderbird configuration. | ||
::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>The email you sent to your myseneca account. | ::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>The email you sent to your myseneca account. | ||
| − | + | ::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>Download and run '''wget https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~andrew.smith/ops335/labcheck4b.bash''' on your '''c7host''' machine. | |
| − | + | ::<span style="color:green;font-size:1.5em;">✓</span>Completed Lab4b log-book notes. | |
| + | --> | ||
==EXPLORATION QUESTIONS== | ==EXPLORATION QUESTIONS== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
# What is the purpose of the Thunderbird application? | # What is the purpose of the Thunderbird application? | ||
| − | # List the steps to configure your DNS to | + | # List the steps to configure your DNS to allow your Thunderbird application to connect to your mail server. |
| + | # What is the purpose of the '''Dovecot''' package? | ||
| + | # What is the purpose of the '''mydestination''' parameter contained in the '''/etc/postfix/main.cf''' file? | ||
| + | # Why are '''IMAP''' and '''POP''' email servers placed on separate machines (vms)? | ||
| + | # What is the purpose of the '''mail_location''' parameter contained in the '''/etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf''' file? | ||
| + | # Why is root not able to receive mail with the changed mail location? What could you change to allow mail to be sent to root again? | ||
Latest revision as of 01:37, 12 March 2021
Contents
OVERVIEW
In Lab 4a, you configured and ran the Postfix application for our MTA (a.k.a. SMTP server) on your vm2 and vm3 machines.
That setup has some major drawbacks:
- It required an SMTP server (MTA) to be configured on each machine.
- The Message Store (MS) would also be unique to each machine - what a user received on one server would not exist on any other.
In this lab you will centralize some of this information, so that a user can send email from any machine in the network, and have incoming mail sent to a centralized messages store.
The a diagram below (duplicate to lab 4a) shows your basic setup of your email system:
You will begin by modifying the existing Postfix (MTA) servers to make mail they send come from your domain (instead of each machine). Then you will add a record to your DNS server to allow mail to be sent to the domain itself, instead of the individual machines. Next, you will add a Local Delivery Agent (LDA) to your vm3 by installing dovecot-lda, configure it, and test it to make sure that is is working correctly.
Finally, you will set up an IMAP server called Dovecot on your vm3 machine, so you can read your email from an MUA such as Thunderbird or a Webmail application. You will set up a webmail application called Roundcube in a later lab).
Learning About the Services Involved in an Email Delivery
In reality, the terms MTA, MDA, MUA, LDA can actually be considered misleading since some of those services can be combined together to form a single entity (application), while other applications may operate as separate entities. There may be overlap, so if you don't find those acronyms helpful, don't worry too much about them. On the other hand, when referred to in diagrams, they can help to visualize those processes when trying to understand how an e-mail system works.
Here is an overview of those terms (from the Dovecot wiki). It is worth viewing this link.
In the diagram displayed above, the elements include:
- User Account. The individual who wants to send or receive mail messages.
- MUA (email client). This is the application that the individual uses to send or receive mail messages. It can be a native application or a web application. You will learn how to setup and use both types of these applications throughout the remainder of this course.
- Two MTA servers. These are the servers responsible for getting your emails to the destination server.
- They are similar to routers (which route packets) but work on the application layer rather than the network layer.
- In our example, there are only two MTAs - but there can be several.
- You connect to your MTA over a secure connection, so your emails can't be read by the operators of the network you're connected to.
- The mail message then travels the rest of the way to the destination MTA unencrypted, so anyone with access to the routers in-between can read all your emails. That is why many organizations will refuse to send you confidential information over email.
- LDA/MDA Server. This server will receive the email from the MTA, and will store it on disk in some format. MailDir and MBOX are the most popular mailbox formats.
- IMAP/POP3 server(s). When sending an email, you send it to the destination using your MTA, but you also want to save it in your "Sent" folder for yourself. This is accomplished by a separate connection to either your IMAP or POP3 server.
- Thus, a situation can occur that although you sent your email successfully, it may never make it to your "Sent" folder - the second connection to your IMAP server is quite unrelated to the first connection to the SMTP server.
- DNS Server. A DNS server is also involved - it is needed to retrieve the address of the email server responsible for email for a particular domain. This is done with MX records.
Online References
INVESTIGATION 1: INSTALL THUNDERBIRD (MUA) and SETUP A REFERENCE CLIENT
Unlike the mailx (MUA) application you installed and used in Lab 4a, this lab will be using the Thunderbird (MUA) application instead which is a graphical application that uses a centralized Message Store (MS) to retrieve and read mail messages.
Although we will be eventually setting up the Thunderbird application to perform all the mail operations discussed above, you need to learn to "walk before you can run". Eventually, you are going to set up all those mail services, but to begin with, you will set up an email client to connect to an already working server which is the Seneca email server. Once we learn how to do this for our Seneca email account, then we can use it for our mail servers for our VM2 and VM3.
Perform the following steps:
- Switch to your host machine, and install the Thunderbird email application.
- When you first launch the Thunderbird application, a configuration dialog should appear as shown in the diagram below:
- Use the data in the table below to configure the Thunderbird settings dialog box for YOUR Seneca e-mail account:
| Setting | Incoming: IMAP | Outgoing: SMTP |
|---|---|---|
| Username | yoursenecauserid@myseneca.ca | yoursenecauserid@myseneca.ca |
| servername | outlook.office365.com | outlook.office365.com |
| port | 993 | 587 |
| security | SSL/TLS | STARTTLS |
| References | [1] ITS - Configuring other Email Clients | |
- Note that your username is your full email address(yourid@myseneca.ca) and not just yourid.
- After you create your Thunderbird account, you should be able to read your existing email and send new email within the Thunderbird application.
- Take time to view your Account Settings and Preferences to get a feel for what settings exist. For example:
- How often will Thunderbird check for new messages?
- Will the messages you write be in HTML or plain text?
- How do you change your SMTP server settings? Why are they in a different section?
- The main objective of this section was to learn how to setup your Thunderbird application to read your Seneca email, so in the next section you can use the exact type of setup for your own email server.
Record steps, commands, and your observations in INVESTIGATION 1 in your OPS335 lab log-book
INVESTIGATION 2: SETUP A CENTRALIZED MESSAGE STORE
Setup Your MTA to Use Correct Domain
In Lab 4a, both of your email servers were sending mail messages addressed from users of the actual machines themselves. This would be confusing for the receiver who might get emails from the same user @vm1, vm2, and vm3. Which would they respond to? To avoid this problem from occurring, we can make all servers make the sent mail appear to come from a central location (usually the domain), and make incoming email sent to that address to be accessible from machines within our network.
Perform the following steps:
- Issue the mail command to view the email messages you sent between your vm2 and vm3 in your lab 4a. Notice that each is addressed from root on whichever machine sent it.
- On both machines (vm2 and vm3), edit the /etc/postfix/main.cf file to change the myorigin parameter from $myhostname to $mydomain. Restart the postfix service.
- Now, send emails messages (via the mail command) between both of your vm2 and vm3 machines, and view the mail messages by issuing mail in each vm. The sender address should now read that the received mail messages came from root@yourdomain.ops.
- The next step is to configure what addresses that the server will receive email for. This is done using postfix by setting the mydestination parameter (configuration variable) to include $mydomain (this is assuming you've set up mydomain, myorigin , and inet_interfaces properly).
- Edit the /etc/postfix/main.cf file for vm3 ONLY, scroll down to the line containing: mydestination and change line to the text shown below:Note: Even though your machine's name is vm3.yoursenecaid.ops, your postfix MTA will also receive emails addressed to the domain called: yoursenecaid.ops
mydestination = $mydomain, $myhostname, localhost.$mydomain, localhost
- In order for this to work, we need to add a DNS record that will point mail sent to the domain towards one of the SMTP servers configured to accept it.
- Add an MX record to the forward lookup zone on host so that all incoming mail addressed to the domain is sent to your vm3.
- Restart the service and use the dig command to confirm that it works.
- Send an email from your vm2 to root@yourdomain.ops
- Confirm that it arrives on your vm3 machine
Relay Email Through Another Server
When email is sent from either vm, it is addressed from the domain, but receiving MTAs might query why mail sent from vm2 doesn't match the address of the MX record for the domain. This would be a red-flag for potential spam. To avoid this, we can relay all mail sent from vm2 (or any other machine in our network) through vm3 so that it properly appears to come from the mail server that matches the MX record for the domain.
Perform the following steps:
- Move to your vm2 machine.
- Direct your vm2 MTA to relay mail through vm3, by making the following editing change for the /etc/postfix/main.cf file:
relayhost = vm3.<yourdomain>.ops
- Restart the postfix service.
- Next, you must instruct your vm3 machine to allow your vm2 machine to pass email through it by making the following editing change to the /etc/postfix/main.cf file:NOTE: Substitute in your own network for X
mynetworks = 192.168.X.0/24
- Restart the postfix service.
All mail is now being delivered to a centralized location (and also appears to be coming from that same location), but a user would still have to access that server to retrieve it.
Install and Configure the Local Delivery Agent (LDA/MDA)
Postfix is capable of performing the function of an LDA, but its LDA capabilities are limited, thus postfix is generally not used for that purpose. Currently, the most popular LDA is LMTP, but we will be installing, configuring, and using an LDA called Dovecot since it is also popular and we will setting up Dovecot as an IMAP server later in this lab. Using both Postfix and Dovecot will actually increase the performance of our IMAP server.
Perform the following steps:
- Move to your vm3 machine.
- Dovecot is not installed when you installed your Virtual machines in previous labs.
Install the Dovecot application by issuing the following command:yum install dovecot
- Edit your /etc/postfix/main.cf file and scroll down to (or search for) mailbox_command. Add the following line:
mailbox_command = /usr/libexec/dovecot/dovecot-lda -f "$SENDER" -a "$RECIPIENT"
- Finally, edit the /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf file and indicate where you want your mail delivered by including the following line:
mail_location = maildir:~/Maildir
- Restart your postfix service.
- While the emails are still stored only on VM3, they will now be easier for other machines/services to access.
- Due to permissions on the directories where mail will now be stored, root will no longer receive mail. Check the logs for an indication as to why.
Record steps, commands, and your observations in INVESTIGATION 2 in your OPS335 lab log-book
INVESTIGATION 3: USING THUNDERBIRD (MUA) FOR VM2 and VM3 MACHINES
Accessing Received Mail Messages on VM3 VIA IMAP
First, we will set up the IMAP server so we can read email. The current way we have configured our mail server on our VM3 machine should allow all the email for anyaccount@yoursenecaid.ops should be delivered to our vm3 machine. We will set up Dovecot with IMAP to get easy access to that email.
Perform the following steps:
- The configuration file for the Dovecot service (which is not the same thing as dovecot-lda) is: /etc/dovecot/dovecot.conf. Modify the protocols option so that Dovecot will work with IMAP connections, no POP3 or LMTP.
- Start the dovecot service, and ensure it will always start automatically when the machine boots.
- Use the ss command to confirm the service is listening, and use nc on the host to confirm you can connect to it.
- You'll probably fail, so using the information gathered from ss, modify the firewall on vm3 to allow IMAP connections from your local network and try nc again. Once it works, do not forget to save this change so it will still be there the next time you reboot.
- If you can connect - it's now time to do something wrong, that is allow connections to our IMAP server over an unencrypted connection.
- Edit the /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-auth.conf file and set disable_plaintext_auth to no.
- Then edit the /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-ssl.conf file and set ssl to yes.
Note: This combination of parameters will allow your username and password to be sent over the internet in plain text, for anyone interested to look at. In a later lab we'll set up secure SMTP and IMAP connections, for now this is all we have time for. - Restart dovecot so the changes take effect.
Connecting to IMAP Servers Using Thunderbird
Perform the following steps:
- On your host machine, return to the Mail Account Setup dialog box (eg. near top of lab).
- Set up a new email account. You will be using account settings to connect to your vm2 for SMTP and vm3 for IMAP. Use no encryption, and use normal password authentication for IMAP. Refer to the diagram below for reference:
- Try to connect to your IMAP server with Thunderbird by clicking on your Inbox.
- If nothing happens, then check the Thunderbird Activity Manager for any errors. If the connection is successful, you should see the Trash box appear below Inbox.
- Use the Thunderbird application to send an email to your myseneca address. If you've done everything right, it will send the message successfully
- Verify that your message has been sent. Check your myseneca email and look at /var/log/maillog on vm2 (your email server).
Sending a Mail Message from VM2 (Using Thunderbird)
Perform the following steps:
- Use the ss and nc commands (like you did in lab 4a) to confirm your service is listening on the correct ports/interfaces. You will probably have to open the appropriate firewall port on vm3 to allow incoming SMTP connections.
Note: You should be able to send email to any regular user on vm3 using the email address yourusername@yoursenecaid.ops using the Thunderbird application on your host machine (which is configured to use the account on your vm2).
- Create a new account on your vm3 machine using only your first name. We will use this account as a one-time "test" if the mail message has been received on your VM3 machine (from your VM2 machine).
Note: It is important that you don't create this same account name on your vm2 machine, since you want to easily identify the difference between the sending and receiving SMTP servers.
- Use the new account in Thunderbird to send an email to firstname@yoursenecaid.ops and then check the contents of /home/firstname/Maildir/new/ on your vm3 machine. There should be a file there with the contents of your email.
- If there is no file, then check the log file /var/log/maillog to see what went wrong.
- If you can see a file in the /home/firstname/Maildir/new/ directory, then review the procedures on how you got the email server working (since you have performed many steps and set up many services).
- Refer to the diagram at the top of this lab. Which services have you currently set up? Record your findings in your lab Logbook.
Record steps, commands, and your observations in INVESTIGATION 3 in your OPS335 lab log-book
COMPLETING THE LAB
Online Submission
Follow the instructions for lab 4b on blackboard.
EXPLORATION QUESTIONS
- What is the purpose of the Thunderbird application?
- List the steps to configure your DNS to allow your Thunderbird application to connect to your mail server.
- What is the purpose of the Dovecot package?
- What is the purpose of the mydestination parameter contained in the /etc/postfix/main.cf file?
- Why are IMAP and POP email servers placed on separate machines (vms)?
- What is the purpose of the mail_location parameter contained in the /etc/dovecot/conf.d/10-mail.conf file?
- Why is root not able to receive mail with the changed mail location? What could you change to allow mail to be sent to root again?