Difference between revisions of "DPS921/Team team"
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
== Multitasking in C++11 == | == Multitasking in C++11 == | ||
C++ 11 introduced the ability to code using multitasking, a form of parallelism on shared memory instead of serial. This is known as “virtual parallelism” as it is not true parallelism (see figure 1). Every task created through “virtual parallelism” or multitasking in the Standard Template Library runs on one available core. If multiple tasks are created, they are split into minor tasks, and then split into an order of when they should be running. This means that you can have two tasks in progress at the same time, but they are never working at the same time. | C++ 11 introduced the ability to code using multitasking, a form of parallelism on shared memory instead of serial. This is known as “virtual parallelism” as it is not true parallelism (see figure 1). Every task created through “virtual parallelism” or multitasking in the Standard Template Library runs on one available core. If multiple tasks are created, they are split into minor tasks, and then split into an order of when they should be running. This means that you can have two tasks in progress at the same time, but they are never working at the same time. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:multitask_parallel.PNG |thumb|center|600px| ]] | ||
== What is provided? == | == What is provided? == | ||
| Line 142: | Line 144: | ||
Mutex’s are the lock mechanism mentioned above. The purpose of a mutex is to make an area of memory accessible only to the thread that has accessed it. Once a thread is done with its changes to the memory, the thread will unlock it, move on, and allow the next thread to make its changes.<br> | Mutex’s are the lock mechanism mentioned above. The purpose of a mutex is to make an area of memory accessible only to the thread that has accessed it. Once a thread is done with its changes to the memory, the thread will unlock it, move on, and allow the next thread to make its changes.<br> | ||
Mutex’s in C++ are introduced with the <Mutex> header file from the std::mutex class. A mutex has two main functions, std::mutex::lock() and std::mutex::unlock().<br> | Mutex’s in C++ are introduced with the <Mutex> header file from the std::mutex class. A mutex has two main functions, std::mutex::lock() and std::mutex::unlock().<br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Mutex code example: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | // mutex example | ||
| + | #include <iostream> // std::cout | ||
| + | #include <thread> // std::thread | ||
| + | #include <mutex> // std::mutex | ||
| + | #include <vector> | ||
| + | |||
| + | // THIS IS THE MUTEX LOCK EXAMPLE | ||
| + | std::mutex mtx; // mutex for critical section | ||
| + | |||
| + | void print_block(int n, char c) { | ||
| + | // critical section (exclusive access to std::cout signaled by locking mtx): | ||
| + | |||
| + | mtx.lock();//comment out these lines to remove mutex | ||
| + | |||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { std::cout << c; } | ||
| + | std::cout << '\n'; | ||
| + | |||
| + | mtx.unlock();//comment out these lines to remove mutex | ||
| + | } | ||
| − | + | int main() | |
| + | { | ||
| + | std::thread th1(print_block, 50, '*'); | ||
| + | std::thread th2(print_block, 50, '$'); | ||
| + | |||
| + | th1.join(); | ||
| + | th2.join(); | ||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | + | Results with the mutexes in place: | |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | + | $$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$ | |
| + | ************************************************** | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| − | <b>If the locks are removed the output will change every run | + | <b>If the locks are removed, the output will change every run. The results will look similar to:</b> |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
| − | + | $$$$$$$************************************************** | |
| + | $$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$ | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
| + | |||
=== Atomicity === | === Atomicity === | ||
The Atomic operations library throws out the concept of using locks and allows for lockless concurrent programming. The atomic class handles everything for you when it comes to making sure the memory space does not encounter bugs when running between multiple threads. | The Atomic operations library throws out the concept of using locks and allows for lockless concurrent programming. The atomic class handles everything for you when it comes to making sure the memory space does not encounter bugs when running between multiple threads. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Atomic code example: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | #include <iostream> // std::cout | ||
| + | #include <thread> // std::thread | ||
| + | #include <mutex> // std::mutex | ||
| + | #include <vector> | ||
| + | #include <atomic> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | //THIS IS THE ATOMIC CODE //Result is the same as if you were to use mutex locks. Wallet will contain 5000 | ||
| + | class Wallet | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | std::atomic<int> mMoney; | ||
| + | public: | ||
| + | Wallet() :mMoney(0) {} | ||
| + | int getMoney() { return mMoney; } | ||
| + | void addMoney(int money) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < money; ++i) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | mMoney++; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | int testMultithreadedWallet() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | Wallet walletObject; | ||
| + | std::vector<std::thread> threads; | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) { | ||
| + | threads.push_back(std::thread(&Wallet::addMoney, &walletObject, 1000)); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < threads.size(); i++) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | threads.at(i).join(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | return walletObject.getMoney(); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | int main() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | |||
| + | int val = 0; | ||
| + | for (int k = 0; k < 1000; k++) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | if ((val = testMultithreadedWallet()) != 5000) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | std::cout << "Error at count = " << k << " Money in Wallet = " << val << std::endl; | ||
| + | //break; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | std::cout << "Money in Wallet is: " << val << std::endl; | ||
| + | |||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | Results: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | Money in Wallet is: 5000 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
== Intel Threading Building Blocks == | == Intel Threading Building Blocks == | ||
| Line 635: | Line 734: | ||
== Case Studies between STL & TBB == | == Case Studies between STL & TBB == | ||
| − | Comparison of TBB parallel sort, STL sort | + | === <u>Comparison of TBB parallel sort, STL sort</u> === |
<pre> | <pre> | ||
#include <stddef.h> | #include <stddef.h> | ||
| Line 706: | Line 805: | ||
const auto startTime = high_resolution_clock::now(); | const auto startTime = high_resolution_clock::now(); | ||
// same sort call as above, but with par_unseq: | // same sort call as above, but with par_unseq: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
tbb::parallel_sort(sorted); | tbb::parallel_sort(sorted); | ||
| Line 720: | Line 817: | ||
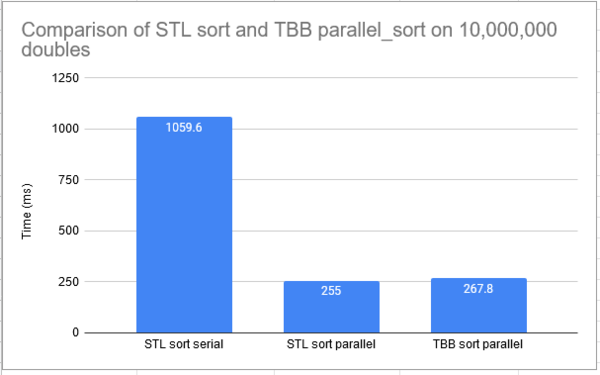
Results on an intel i7-3770k, average of 5 runs: | Results on an intel i7-3770k, average of 5 runs: | ||
[[File:sortcomparison.PNG |thumb|center|600px| Results of STL vs TBB sort algorithms]] | [[File:sortcomparison.PNG |thumb|center|600px| Results of STL vs TBB sort algorithms]] | ||
| + | STL parallel sort performed similarly to TBB parallel sort<br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | === <u>Comparison of TBB inclusive scan, STL inclusive scan</u> === | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | #include <functional> | ||
| + | #include <iostream> | ||
| + | #include <iterator> | ||
| + | #include <numeric> | ||
| + | #include <vector> | ||
| + | #include <random> | ||
| + | #include <chrono> | ||
| + | #include <execution> | ||
| + | #include <tbb/tbb.h> | ||
| + | |||
| + | const size_t testSize = 10'000'000; | ||
| + | const int iterationCount = 5; | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | void print_results(const char* const tag, const std::vector<int>& result, | ||
| + | std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point startTime, | ||
| + | std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point endTime) { | ||
| + | printf("%s: %fms\n", tag, | ||
| + | std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>>(endTime - startTime).count()); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | int main() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | std::uniform_int_distribution<int> dis(1, 10); | ||
| + | std::random_device rd; | ||
| + | std::vector<int> data(testSize); | ||
| + | |||
| + | //generating data | ||
| + | for (auto& d : data) { | ||
| + | d = dis(rd); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | //Serial inclusive sum | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | std::vector<int> result(data); | ||
| + | const auto startTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | std::inclusive_scan(std::execution::seq, data.begin(), data.end(), result.begin()); | ||
| + | |||
| + | const auto endTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); | ||
| + | print_results("STL Serial Inclusive sum", result, startTime, endTime); | ||
| + | std::cout << "Scan result: " << result[testSize - 1] << "\n"; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | //Inclusive sum parallel unseq | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | std::vector<int> result(data); | ||
| + | const auto startTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | std::inclusive_scan(std::execution::par_unseq, data.begin(), data.end(), result.begin()); | ||
| + | |||
| + | const auto endTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); | ||
| + | print_results("STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq", result, startTime, endTime); | ||
| + | std::cout << "Scan result: " << result[testSize - 1] << "\n"; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | //Inclusive sum parallel | ||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | std::vector<int> result(data); | ||
| + | const auto startTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | std::inclusive_scan(std::execution::par, data.begin(), data.end(), result.begin()); | ||
| + | |||
| + | const auto endTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); | ||
| + | print_results("STL Inclusive sum parallel", result, startTime, endTime); | ||
| + | std::cout << "Scan result: " << result[testSize - 1] << "\n"; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i) | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | std::vector<int> result(data); | ||
| + | auto body = [&](const tbb::blocked_range<int>& r, int sum, bool is_final_scan)->int { | ||
| + | int temp = sum; | ||
| + | for (int i = r.begin(); i < r.end(); ++i) { | ||
| + | temp = temp + data[i]; | ||
| + | if (is_final_scan) | ||
| + | result[i] = temp; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | return temp; | ||
| + | }; | ||
| + | |||
| + | const auto startTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); | ||
| + | tbb::parallel_scan(tbb::blocked_range<int>(0, testSize),0, body, [](int left, int right) { | ||
| + | return left + right; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | ); | ||
| + | const auto endTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now(); | ||
| + | print_results("TBB Inclusive sum parallel", result, startTime, endTime); | ||
| + | std::cout << "Scan result: " << result[testSize - 1] << "\n"; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | </pre> | ||
| + | Results on an intel i7-3770k, average of 5 runs: | ||
| + | [[File:scancomparison.PNG |thumb|center|600px| Results of STL vs TBB scan algorithms]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | Raw Results: | ||
| + | <pre> | ||
| + | STL Serial Inclusive sum: 9.695900ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Serial Inclusive sum: 13.188200ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Serial Inclusive sum: 9.139700ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Serial Inclusive sum: 10.686900ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Serial Inclusive sum: 7.812900ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq: 39.005100ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq: 29.428300ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq: 30.756500ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq: 26.180600ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq: 28.135300ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Inclusive sum parallel: 28.015000ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Inclusive sum parallel: 30.922700ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Inclusive sum parallel: 38.238000ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Inclusive sum parallel: 29.686100ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | STL Inclusive sum parallel: 28.986200ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | TBB Inclusive sum parallel: 59.180100ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | TBB Inclusive sum parallel: 13.341900ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | TBB Inclusive sum parallel: 13.508600ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | TBB Inclusive sum parallel: 10.201700ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | TBB Inclusive sum parallel: 9.710400ms | ||
| + | Scan result: 55000150 | ||
| + | </pre> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:57, 4 December 2020
GPU621/DPS921 | Participants | Groups and Projects | Resources | Glossary
Contents
C++11 STL Comparison to TBB - Case Studies
C++ has a standard template library (STL) that has over 100,000 algorithms for different jobs. Within these algorithms there are ones that provide the capability of parallelising work. TBB is the Threading Building Block template library that also allows for parallel programming. TBB breaks down work into tasks that can run in parallel. For our project, we will look into the completion of different use cases using both the TBB library as well as the STL library, analyzing differences in the code, as well as run times for these algorithms.
Group Members
What we aim to display
Throughout this wiki, differences between C++11’s and C++17’s standard template library and Intel’s Thread Building Blocks template library look to be addressed. This will include C++11 multitasking capabilities vs Threaded Building Block parallelism and how they are setup within the IDE and ran. We will also investigate the more recent C++17 and its support for true parallelism, and how that compares to Intel’s Threaded Building Block library.
C++ 11 Standard Template Library
C++11 was released in September of 2011, approved by the International Organization for Standardization[1]. C++ has a long history dating back to 1997, and for that reason some concepts may be outdated which is why we will be talking about C++11 and C++17. STL is the standard template library that allows for users to leverage data structures without the hassle of implementation. A simple function call or object instantiation is all that is needed. Although STL simplifies a lot, it still requires a working knowledge of Template Classes to work with. STL provides three main components: Algorithms, Iterators, and containers.
Containers
STL includes containers such as unordered_map, and forward_list, a singly-linked list, vectors, and queues. The list of containers introduced is expansive and was done for performance reasons.
Iterators
A way to access data stored within the containers above. It is almost like a pointer to a large container of items and helps iterate through the container. Iterators also allow for dereferencing the iterator to access the data within the pointer.
Algorithms
Operations to be performed on a range of elements using Containers and Iterators. The algorithms act directly on the iterator and has nothing to do with the structure of the container. This means you will only be working with the elements and cannot change the size or structure of the container. Algorithms such as remove_if, reverse, and fill are common algorithms.
Multitasking in C++11
C++ 11 introduced the ability to code using multitasking, a form of parallelism on shared memory instead of serial. This is known as “virtual parallelism” as it is not true parallelism (see figure 1). Every task created through “virtual parallelism” or multitasking in the Standard Template Library runs on one available core. If multiple tasks are created, they are split into minor tasks, and then split into an order of when they should be running. This means that you can have two tasks in progress at the same time, but they are never working at the same time.
What is provided?
Threads
Each thread represents a single thread of execution. If you plan on running two tasks through multi tasking, you will need two threads created. Once a new thread object is created the thread will execute. Note that a thread object being created with no passed arguments in the constructor will lead to a thread object being created, but no thread.
Threads will accept Function Pointers, and if the function requires parameters, then the parameters required, function objects, and even lambda functions.
To identify each thread object there is ``` std::thread::get_id() ``` which will provide the ide of the thread object, and ```std::this_thread::get_id()``` to get the id of the current thread in use.
All Threads created must be joined using ```std::thread::join(). If this is not in place, a run time error will occur as the main thread will complete its executing leaving the other threads running.
//Source: https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/thread/thread/thread
#include <thread>
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
void f1(int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
std::cout << "Thread 1 executing\n";
++n;
}
}
void f2(int& n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
std::cout << "Thread 2 executing\n";
++n;
}
}
class foo
{
public:
void bar()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
std::cout << "Thread 3 executing\n";
++n;
}
}
int n = 0;
};
class baz
{
public:
void operator()()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
std::cout << "Thread 4 executing\n";
++n;
}
}
int n = 0;
};
int main()
{
int n = 0;
foo f;
baz b;
std::thread t1; // t1 is not a thread
std::thread t2(f1, n + 1); // pass by value
std::thread t3(f2, std::ref(n)); // pass by reference. Must use std::ref()
std::thread t4(std::move(t3)); // t4 is now running f2(). t3 is no longer a thread
std::thread t5(&foo::bar, &f); // t5 runs foo::bar() on object f
std::thread t6(b); // t6 runs baz::operator() on object b. Function Object
t2.join();
t4.join();
t5.join();
t6.join();
std::cout << "Final value of n is " << n << '\n';
std::cout << "Final value of foo::n is " << f.n << '\n';
}
Result:
Thread 1 executing Thread 1 executing Thread 2 executing Thread 3 executing Thread 3 executing Thread 3 executing Thread 3 executing Thread 3 executing Thread 1 executing Thread 1 executing Thread 1 executing Thread 4 executing Thread 4 executing Thread 4 executing Thread 4 executing Thread 4 executing Thread 2 executing Thread 2 executing Thread 2 executing Thread 2 executing Final value of n is 5 Final value of foo::n is 5
Race Conditions and Mutual Exclusion
Race conditions occur when two or more threads perform operations on the same memory location and modify the data at said memory location, causing unexpected results. To fix this issue, lock mechanisms must be introduced.
Mutex’s are the lock mechanism mentioned above. The purpose of a mutex is to make an area of memory accessible only to the thread that has accessed it. Once a thread is done with its changes to the memory, the thread will unlock it, move on, and allow the next thread to make its changes.
Mutex’s in C++ are introduced with the <Mutex> header file from the std::mutex class. A mutex has two main functions, std::mutex::lock() and std::mutex::unlock().
Mutex code example:
// mutex example
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <thread> // std::thread
#include <mutex> // std::mutex
#include <vector>
// THIS IS THE MUTEX LOCK EXAMPLE
std::mutex mtx; // mutex for critical section
void print_block(int n, char c) {
// critical section (exclusive access to std::cout signaled by locking mtx):
mtx.lock();//comment out these lines to remove mutex
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) { std::cout << c; }
std::cout << '\n';
mtx.unlock();//comment out these lines to remove mutex
}
int main()
{
std::thread th1(print_block, 50, '*');
std::thread th2(print_block, 50, '$');
th1.join();
th2.join();
return 0;
}
Results with the mutexes in place:
$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$ **************************************************
If the locks are removed, the output will change every run. The results will look similar to:
$$$$$$$************************************************** $$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$$
Atomicity
The Atomic operations library throws out the concept of using locks and allows for lockless concurrent programming. The atomic class handles everything for you when it comes to making sure the memory space does not encounter bugs when running between multiple threads.
Atomic code example:
#include <iostream> // std::cout
#include <thread> // std::thread
#include <mutex> // std::mutex
#include <vector>
#include <atomic>
//THIS IS THE ATOMIC CODE //Result is the same as if you were to use mutex locks. Wallet will contain 5000
class Wallet
{
std::atomic<int> mMoney;
public:
Wallet() :mMoney(0) {}
int getMoney() { return mMoney; }
void addMoney(int money)
{
for (int i = 0; i < money; ++i)
{
mMoney++;
}
}
};
int testMultithreadedWallet()
{
Wallet walletObject;
std::vector<std::thread> threads;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
threads.push_back(std::thread(&Wallet::addMoney, &walletObject, 1000));
}
for (int i = 0; i < threads.size(); i++)
{
threads.at(i).join();
}
return walletObject.getMoney();
}
int main()
{
int val = 0;
for (int k = 0; k < 1000; k++)
{
if ((val = testMultithreadedWallet()) != 5000)
{
std::cout << "Error at count = " << k << " Money in Wallet = " << val << std::endl;
//break;
}
}
std::cout << "Money in Wallet is: " << val << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Results:
Money in Wallet is: 5000
Intel Threading Building Blocks
Overview of TBB
Intel TBB is a library which provides features for parallel programming.It is used for task-based parallelism and requires no special compiler support. TBB has features such as Parallel Algorithms, memory allocation, threads and synchronization. Along side these features are similar features that were talked about in C++11. Naturally, TBB supports features such as containers and iterators, but with additional features to support the parallel nature of the library. Finally, TBB allows for generic programming which removes type requirements.
Containers
Containers within TBB allow for multiple threads to alter the same container at once. These containers are known as concurrent containers. Examples of these containers are:
- concurrent_unordered_map
- concurrent_hash_map
- concurrent_queue or concurrent_vector
Iterators
Parallel algorithms within Intel TBB are generic, This allows for the use of iterators and STL algorithms within parallel algorithms.
Algorithms
Algorithms within the TBB library are created for a similar reason that the algorithms in the Standard Template Library are, to allow for easier use and improve on performance. Algorithms within the library include:
- parallel_for
- parallel_reduce
- parallel_scan
Mutual Exclusion
A TBB mutex is created by access tbb::mutex from the <tbb/mutex.h> file. To lock a mutex you call tbb::mutex::lock() and to unlock, tbb::mutex::unlock(). Different mutexes in TBB have a combination of different flavors, or attributes. These attributes have tradeoffs depending on which one is chosen.
- Scalable - Is a mutex that does not do worse than limiting one execution to a thread. It is generally slow.
- Fair/Unfair: Allows for threads to move forward in the program in the order that they arrive. Unfair threads are potentially faster as they will allow for running threads to cut the line over threads that are waiting.
- Recursive: Allows for a thread with a lock on the mutex to acquire another lock on the mutex.
- Yield or Block: If there is a long wait, a decision will be made if progress can continue, and if it can then yield the processor. If it cannot be made it will block otherwise.
Taken from threadingbuildingblocks.org is a table displaying different mutexes and the flavors they possess.
|
Mutex |
Scalable |
Fair |
Recursive |
Long Wait |
Size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
mutex |
OS dependent |
OS dependent |
no |
blocks |
≥ 3 words |
|
recursive_mutex |
OS dependent |
OS dependent |
✓ |
blocks |
≥ 3 words |
|
spin_mutex |
no |
no |
no |
yields |
1 byte |
|
speculative_spin_mutex |
HW dependent |
no |
no |
yields |
2 cache lines |
|
queuing_mutex |
✓ |
✓ |
no |
yields |
1 word |
|
spin_rw_mutex |
no |
no |
no |
yields |
1 word |
|
speculative_spin_rw_mutex |
HW dependent |
no |
no |
yields |
3 cache lines |
|
queuing_rw_mutex |
✓ |
✓ |
no |
yields |
1 word |
|
null_mutex |
moot |
✓ |
✓ |
never |
empty |
|
null_rw_mutex |
moot |
✓ |
✓ |
never |
empty |
Figure 2. https://www.threadingbuildingblocks.org/docs/help/tbb_userguide/Mutex_Flavors.html
Atomics
Virtually the same compared to the Standard Template library. An atomic variable is declared with atomic<Type> variableName. A thread can perform actions on the atomic variable without the need for locks. This is potentially quicker but comes with the downside of having less operations available to perform.
What was added in C++17 STL
C++ 17 introduces parallel algorithms and execution policies, and the reduce, inclusive_scan, and exclusive_scan algorithms. This allows for true parallelization to occur, not multitasking. The execution policies that were created in C++17 are what allow for the distinction between running a program sequentially or in parallel. The algorithms inclusive_scan and exclusive_scan do not require an execution_policy and can simply be called with arguments containing the an iterator pointing to the beginning of a container, and an iterator pointing to the end
Case Studies between STL & TBB
Comparison of TBB parallel sort, STL sort
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <chrono>
#include <random>
#include <ratio>
#include <vector>
#include <execution>
#include <tbb/tbb.h>
using std::chrono::duration;
using std::chrono::duration_cast;
using std::chrono::high_resolution_clock;
using std::milli;
using std::random_device;
using std::sort;
using std::transform;
using std::vector;
const size_t testSize = 10'000'000;
const int iterationCount = 5;
void print_results(const char* const tag, const vector<double>& sorted,
high_resolution_clock::time_point startTime,
high_resolution_clock::time_point endTime) {
printf("%s: Lowest: %g Highest: %g Time: %fms\n", tag, sorted.front(),
sorted.back(),
duration_cast<duration<double, milli>>(endTime - startTime).count());
}
int main() {
random_device rd;
// generate some random doubles:
printf("Testing with %zu doubles...\n", testSize);
vector<double> doubles(testSize);
for (auto& d : doubles) {
d = static_cast<double>(rd());
}
//serial stl sort
for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i)
{
vector<double> sorted(doubles);
const auto startTime = high_resolution_clock::now();
sort(sorted.begin(), sorted.end());
const auto endTime = high_resolution_clock::now();
print_results("Serial STL", sorted, startTime, endTime);
}
//parallel stl sort
for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i)
{
vector<double> sorted(doubles);
const auto startTime = high_resolution_clock::now();
// same sort call as above, but with par_unseq:
sort(std::execution::par_unseq, sorted.begin(), sorted.end());
const auto endTime = high_resolution_clock::now();
// in our output, note that these are the parallel results:
print_results("Parallel STL", sorted, startTime, endTime);
}
//parallel TBB sort
for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i)
{
vector<double> sorted(doubles);
const auto startTime = high_resolution_clock::now();
// same sort call as above, but with par_unseq:
tbb::parallel_sort(sorted);
const auto endTime = high_resolution_clock::now();
// in our output, note that these are the parallel results:
print_results("Parallel TBB", sorted, startTime, endTime);
}
}
Results on an intel i7-3770k, average of 5 runs:
STL parallel sort performed similarly to TBB parallel sort
Comparison of TBB inclusive scan, STL inclusive scan
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <iterator>
#include <numeric>
#include <vector>
#include <random>
#include <chrono>
#include <execution>
#include <tbb/tbb.h>
const size_t testSize = 10'000'000;
const int iterationCount = 5;
void print_results(const char* const tag, const std::vector<int>& result,
std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point startTime,
std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::time_point endTime) {
printf("%s: %fms\n", tag,
std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::duration<double, std::milli>>(endTime - startTime).count());
}
int main()
{
std::uniform_int_distribution<int> dis(1, 10);
std::random_device rd;
std::vector<int> data(testSize);
//generating data
for (auto& d : data) {
d = dis(rd);
}
//Serial inclusive sum
for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i)
{
std::vector<int> result(data);
const auto startTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
std::inclusive_scan(std::execution::seq, data.begin(), data.end(), result.begin());
const auto endTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
print_results("STL Serial Inclusive sum", result, startTime, endTime);
std::cout << "Scan result: " << result[testSize - 1] << "\n";
}
//Inclusive sum parallel unseq
for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i)
{
std::vector<int> result(data);
const auto startTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
std::inclusive_scan(std::execution::par_unseq, data.begin(), data.end(), result.begin());
const auto endTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
print_results("STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq", result, startTime, endTime);
std::cout << "Scan result: " << result[testSize - 1] << "\n";
}
//Inclusive sum parallel
for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i)
{
std::vector<int> result(data);
const auto startTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
std::inclusive_scan(std::execution::par, data.begin(), data.end(), result.begin());
const auto endTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
print_results("STL Inclusive sum parallel", result, startTime, endTime);
std::cout << "Scan result: " << result[testSize - 1] << "\n";
}
for (int i = 0; i < iterationCount; ++i)
{
std::vector<int> result(data);
auto body = [&](const tbb::blocked_range<int>& r, int sum, bool is_final_scan)->int {
int temp = sum;
for (int i = r.begin(); i < r.end(); ++i) {
temp = temp + data[i];
if (is_final_scan)
result[i] = temp;
}
return temp;
};
const auto startTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
tbb::parallel_scan(tbb::blocked_range<int>(0, testSize),0, body, [](int left, int right) {
return left + right;
}
);
const auto endTime = std::chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
print_results("TBB Inclusive sum parallel", result, startTime, endTime);
std::cout << "Scan result: " << result[testSize - 1] << "\n";
}
}
Results on an intel i7-3770k, average of 5 runs:
Raw Results:
STL Serial Inclusive sum: 9.695900ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Serial Inclusive sum: 13.188200ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Serial Inclusive sum: 9.139700ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Serial Inclusive sum: 10.686900ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Serial Inclusive sum: 7.812900ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq: 39.005100ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq: 29.428300ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq: 30.756500ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq: 26.180600ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Inclusive sum parallel unseq: 28.135300ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Inclusive sum parallel: 28.015000ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Inclusive sum parallel: 30.922700ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Inclusive sum parallel: 38.238000ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Inclusive sum parallel: 29.686100ms Scan result: 55000150 STL Inclusive sum parallel: 28.986200ms Scan result: 55000150 TBB Inclusive sum parallel: 59.180100ms Scan result: 55000150 TBB Inclusive sum parallel: 13.341900ms Scan result: 55000150 TBB Inclusive sum parallel: 13.508600ms Scan result: 55000150 TBB Inclusive sum parallel: 10.201700ms Scan result: 55000150 TBB Inclusive sum parallel: 9.710400ms Scan result: 55000150