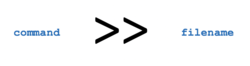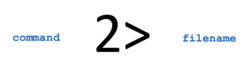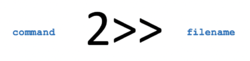Difference between revisions of "Tutorial5: Redirection"
(→Main Objectives of this Practice Tutorial) |
(→KEY CONCEPTS) |
||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
===Redirection (Standard Input, Standard Output, Standard Error)=== | ===Redirection (Standard Input, Standard Output, Standard Error)=== | ||
| − | ''... '''standard streams''' are preconnected input and output communication channels between a computer program and its environment when it begins execution. The three input/output (I/O) connections are called '''standard input''' ('''stdin'''), '''standard output''' ('''stdout''') and '''standard error''' ('''stderr'''). Originally I/O happened via a physically connected system console (input via keyboard, output via monitor), but standard streams '''abstract''' this. When a command is executed via an interactive shell, the streams are typically connected to the text terminal on which the shell is running, but can be changed with '''redirection''' or a '''pipeline'''. '' | + | ===Additional File Manipulation Commands=== |
| + | |||
| + | Before proceeding, there are some additional regular file manipulation commands that you can use with redirection<br>(in addition to the other regular file manipulation commands introduced in week 2). | ||
| + | |||
| + | These commands are displayed in the table below: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <table cellpadding="5" width="55%"><tr><th style="border-bottom: 1px solid black;text-align:left;">Linux Command</th><th style="border-bottom: 1px solid black;text-align:left;">Purpose</th></tr><tr valign="top"><td>'''cut'''</td><td>Used to '''extract''' fields and characters from records. The option '''-c''' option is used to cut by a character or a range of characters. The '''-f''' option indicates the field number or field range to display (this may require using the '''-d''' option to indicate the field separator (delimiter) which is tab by default).<br><br>''Examples:''<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">cut -f2 filename</span> - extract 2nd field from all records in file<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">cut -d' ' -f2,5 filename</span> - extract 2nd and 5th field<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">cut -d' ' -f1-3,5 filename</span> - extract 1st to 3rd and 5th fields<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">cut -c3-5 filename</span> - extract 3rd to 5th characters</td></tr><tr valign="top"><td>'''tr'''</td><td>Used to '''translate''' characters to different characters.<br><br>''Examples:''<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">tr "[a-z]" "[A-Z]" < filename</span> - translate lower to upper case<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">tr "a-z" "A-Z" < filename</span> - same as above (non-System V servers)<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">tr ':' ' ' < filename</span> - translate all colons to spaces<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">tr ' ' '\n' < filename</span> - translate all spaces to newline characters<br><br></td></tr><tr valign="top"><td><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">wc</span></td><td>Displays various '''counts''' of the contents of a file.<br><br>''Examples:''<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">wc -l filename</span> - displays number of lines in file<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">wc -c filename</span> - displays number of characters in file<br><span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold;">wc -w filename</span> - displays number of words in fil<br></td></tr></table> | ||
| + | <br><br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ''... '''standard streams''' are preconnected '''input and output communication channels''' between a computer program and its environment when it begins execution. The three input/output (I/O) connections are called '''standard input''' ('''stdin'''), '''standard output''' ('''stdout''') and '''standard error''' ('''stderr'''). Originally I/O happened via a physically connected system console (input via keyboard, output via monitor), but standard streams '''abstract''' this. When a command is executed via an interactive shell, the streams are typically connected to the text terminal on which the shell is running, but can be changed with '''redirection''' or a '''pipeline'''. '' | ||
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_streams | Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_streams | ||
[[Image:stdin-symbol.png|thumb|right|250px|The '''standard input''' ('''stdin''') symbol that describes where a Unix/Linux command receives '''input''']] | [[Image:stdin-symbol.png|thumb|right|250px|The '''standard input''' ('''stdin''') symbol that describes where a Unix/Linux command receives '''input''']] | ||
| − | '''Standard input''' ('''stdin''') is a term which describes from where a command receives input.<br> | + | '''Standard input''' ('''stdin''') is a term which describes from where a command receives '''input'''.<br> |
This would apply only to Unix/Linux commands that accept stdin input (like ''cat'', ''more'', ''less'', ''sort'', ''grep'', ''head'', ''tail'', etc.).<br> | This would apply only to Unix/Linux commands that accept stdin input (like ''cat'', ''more'', ''less'', ''sort'', ''grep'', ''head'', ''tail'', etc.).<br> | ||
| − | |||
''Examples:'' | ''Examples:'' | ||
| Line 75: | Line 84: | ||
| − | <table align="right"><tr><td>[[Image:stdout-symbol-1.png|thumb|right|250px|The '''standard input''' ('''stdin''') symbol with one greater than sign overwrites existing file content with command output]]</td><td>[[Image:stdout-symbol-2.png|thumb|right|250px|The '''standard input''' ('''stdin''') symbol with two greater than signs add command's output to bottom of existing file's contents.]]</td></tr></table> | + | <table align="right"><tr><td>[[Image:stdout-symbol-1.png|thumb|right|250px|The '''standard input''' ('''stdin''') symbol with one greater than sign '''overwrites''' existing file content with command output]]</td><td>[[Image:stdout-symbol-2.png|thumb|right|250px|The '''standard input''' ('''stdin''') symbol with two greater than signs '''add''' command's output to '''bottom''' of existing file's contents.]]</td></tr></table> |
| − | '''Standard output''' ('''stdout''') describes where a command sends | + | '''Standard output''' ('''stdout''') describes where a command sends its '''output'''.<br>In the examples below, output from a command is sent to the '''monitor''', unless it is sent to a '''text file'''. |
| Line 84: | Line 93: | ||
| − | <table align="right"><tr><td>[[Image:stderr-symbol-1.png|thumb|right|250px|The '''standard error''' ('''sterr''') symbol with one greater than sign overwrites existing file content with command's error message.]]</td><td>[[Image:stderr-symbol-2.png|thumb|right|250px|The '''standard error''' ('''stderr''') symbol with two greater than signs add command's error message to bottom of existing file's contents.]]</td></tr></table> | + | <table align="right"><tr><td>[[Image:stderr-symbol-1.png|thumb|right|250px|The '''standard error''' ('''sterr''') symbol with one greater than sign '''overwrites''' existing file content with command's '''error message'''.]]</td><td>[[Image:stderr-symbol-2.png|thumb|right|250px|The '''standard error''' ('''stderr''') symbol with two greater than signs '''add''' command's error message to '''bottom''' of existing file's contents.]]</td></tr></table> |
'''Standard Error''' ('''stderr''') describes where a command sends it's error messages. In the examples below we issue the pwd in capitals on purpose to generate an error message, which can be redirected to a '''text file'''. | '''Standard Error''' ('''stderr''') describes where a command sends it's error messages. In the examples below we issue the pwd in capitals on purpose to generate an error message, which can be redirected to a '''text file'''. | ||
| Line 92: | Line 101: | ||
<span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold">PWD<br>PWD 2> error-message.txt<br>PWD 2 >> error-messages.txt<br>PWD 2> /dev/null</span> | <span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold">PWD<br>PWD 2> error-message.txt<br>PWD 2 >> error-messages.txt<br>PWD 2> /dev/null</span> | ||
| − | The '''/dev/null''' file (sometimes called the '''bit bucket''' or '''black hole''') is a special system file<br>that | + | The '''/dev/null''' file (sometimes called the '''bit bucket''' or '''black hole''') is a special system file<br>that '''discard''' all data written into it. This is useful to discard unwanted command output. |
| Line 100: | Line 109: | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | [[Image:Here Document.png|thumb|right|175px|The '''Here Document''' allows a user to redirect stdin from within the command itself.]] | + | [[Image:Here Document.png|thumb|right|175px|The '''Here Document''' allows a user to redirect stdin from <u>within</u> the command itself.]] |
In Linux, the '''Here Document''' allows a user to redirect stdin from within the command itself. | In Linux, the '''Here Document''' allows a user to redirect stdin from within the command itself. | ||
| Line 107: | Line 116: | ||
<span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold">cat <<+<br>Line 1<br>Line 2<br>Line 3<br>+<br><br> | <span style="font-family:courier;font-weight:bold">cat <<+<br>Line 1<br>Line 2<br>Line 3<br>+<br><br> | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Piping (Using Pipes)=== | ===Piping (Using Pipes)=== | ||
Revision as of 12:54, 31 August 2020
Contents
REDIRECTION: STANDARD INPUT / STANDARD OUTPUT / STANDARD ERROR
Main Objectives of this Practice Tutorial
- Define the terms Standard Input (stdin), Standard Output (stdout), and Standard Error (stderr)
- Understand the purposes of redirection symbols >, >>, 2>, 2>>, and | (pipe)
- Understand the purpose of the following file manipulation commands: cut, tr, and wc
- Define the term pipeline command and explain how a pipeline command functions
- Define the term filter and how it relates to redirection using pipeline commands
- Use the semicolon ";" and grouping "( )" symbols issue multiple Unix / Linux commands in a single line
- Use the backslash "\" symbol to spread-out long Unix/Linux commands over multiple lines
Tutorial Reference Material
| Course Notes |
Linux Command / Shortcut Reference |
YouTube Videos | ||
| Course Notes:
|
Redirection
Multiple Commands |
Redirection Filters | Brauer Instructional Videos: | |
KEY CONCEPTS
Redirection (Standard Input, Standard Output, Standard Error)
Additional File Manipulation Commands
Before proceeding, there are some additional regular file manipulation commands that you can use with redirection
(in addition to the other regular file manipulation commands introduced in week 2).
These commands are displayed in the table below:
| Linux Command | Purpose |
|---|---|
| cut | Used to extract fields and characters from records. The option -c option is used to cut by a character or a range of characters. The -f option indicates the field number or field range to display (this may require using the -d option to indicate the field separator (delimiter) which is tab by default). Examples: cut -f2 filename - extract 2nd field from all records in file cut -d' ' -f2,5 filename - extract 2nd and 5th field cut -d' ' -f1-3,5 filename - extract 1st to 3rd and 5th fields cut -c3-5 filename - extract 3rd to 5th characters |
| tr | Used to translate characters to different characters. Examples: tr "[a-z]" "[A-Z]" < filename - translate lower to upper case tr "a-z" "A-Z" < filename - same as above (non-System V servers) tr ':' ' ' < filename - translate all colons to spaces tr ' ' '\n' < filename - translate all spaces to newline characters |
| wc | Displays various counts of the contents of a file. Examples: wc -l filename - displays number of lines in file wc -c filename - displays number of characters in file wc -w filename - displays number of words in fil |
... standard streams are preconnected input and output communication channels between a computer program and its environment when it begins execution. The three input/output (I/O) connections are called standard input (stdin), standard output (stdout) and standard error (stderr). Originally I/O happened via a physically connected system console (input via keyboard, output via monitor), but standard streams abstract this. When a command is executed via an interactive shell, the streams are typically connected to the text terminal on which the shell is running, but can be changed with redirection or a pipeline.
Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_streams
Standard input (stdin) is a term which describes from where a command receives input.
This would apply only to Unix/Linux commands that accept stdin input (like cat, more, less, sort, grep, head, tail, etc.).
Examples:
tr 'a-z' 'A-Z' < words.txt
cat < abc.txt
sort < xyz.txt
Standard output (stdout) describes where a command sends its output.
In the examples below, output from a command is sent to the monitor, unless it is sent to a text file.
Examples:
ls -l
ls -l > detailed-listing.txt
ls /bin >> output.txt
Standard Error (stderr) describes where a command sends it's error messages. In the examples below we issue the pwd in capitals on purpose to generate an error message, which can be redirected to a text file.
Examples:
PWD
PWD 2> error-message.txt
PWD 2 >> error-messages.txt
PWD 2> /dev/null
The /dev/null file (sometimes called the bit bucket or black hole) is a special system file
that discard all data written into it. This is useful to discard unwanted command output.
Examples:
LS 2> /dev/null
ls > /dev/null
find / -name "tempfile" 2> /dev/null
In Linux, the Here Document allows a user to redirect stdin from within the command itself.
Example:
cat <<+
Line 1
Line 2
Line 3
+
Piping (Using Pipes)
Pipeline Command: Having commands send their standard output directly to standard input of other commands WITHOUT having to use temporary files.
A few simple commands can be combined to form a more powerful command line.
Pipes that are used in a pipeline command are represented by the pipe "|" symbol.
Commands to the right of the pipe symbol are referred to as filters. They are referred to as filters since those commands are used to modify the stdin that was sent from the previous command. Many commands can be "piped" together, but these commands (filters) must be chained in a specific order, depending on what you wish to accomplish
Examples:
ls -al | more
ls | sort -r
ls | sort | more
ls -l | cut -d" " -f2 | tr 'a-z' 'A-z"
ls | grep Linux | head -5
head -7 filename | tail -2
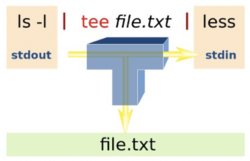
(Image licensed under cc)
The tee utility can be used to split the flow of information. The tee option -a can be used to add content to the bottom of an existing file as opposed to overwriting the file's previous contents.
The reason for the name "tee" is that the splitting of the flow of information resembles a capital T.
Examples:
ls | tee unsorted.txt | sort
ls | grep Linux | tee matched.txt | more
ls | head -5 | tee -a listing.txt
Multiple Commands Using Semicolon, Grouping, and Backquotes
Besides piping, there are other ways that multiple commands may be placed in one line:
commands may be separated by semi-colons.
Example:
sleep 5; ls (Note: each command will be executed when the previous command has terminated)
Multiple commands can also be grouped by using parentheses.
Example:
(echo "Who is on:"; w) > whoson
Commands may also be spread-out over multiple lines, making it easier (for humans) to interpret a long command.
You can add a backslash symbol "\" at the end of a line, to get rid of the special meaning
of newline (to end a command line)
Example:
echo "This will be split over multiple \
lines. Note that the shell will realize \
that a pipe requires another command, so \
it will automatically go to the next line" |tr '[a-z]' '[A-Z]'
INVESTIGATION 1: BASICS OF REDIRECTION
In this section, you will learn how to redirect standard input, standard output and standard error when issuing Unix / Linux commands.
Perform the Following Steps:
- Login your matrix account and issue a command to confirm you are located in your home directory.
- Issue the following Linux command to create the directory: mkdir ~/redirect
- Change to the ~/redirect directory and confirm that you changed to that directory.
- Use a text editor to create a file in your current directory called data.txt and enter the following text displayed below:
This is line 1
This is line 2
This is line 3 - Save editing changes and exit the text editor.
- Issue the following Linux command: tr 'a-z' 'A-Z' < data.txt
What this command do? - Issue the following Linux command: tr 'a-z' 'A-Z' < data.txt > output.txt
What this command do? What are the contents of the file output.txt? - Issue the following Linux command: tr 'a-z' 'A-Z' > output.txt < data.txt
What this command do? Is there any difference in terms of this command and the previous command issued? - Issue the following Linux command: tr 'a-z' 'A-Z' >> output.txt < data.txt
What happens to the content of the output.txt file? Why? - Issue the following Linux command: tail -2 < data.txt > output.txt
What does this command do? Check the contents of the output.txt file to confirm. - Issue the following Linux command: tail -2 > output2.txt < data.txt
Why does this command render the same results as the previous command?
Try explaining how the command works in terms of stdin and then stdout. - Issue the following Linux command to create a file: cat > output3.txt
- Enter the follow text displayed below:
This is the file output3.txt - Press ctrl-d to exit the command.
- Issue the cat command to view the contents of the file: output3.txt
- Issue the following Linux command: cp ~murray.saul/uli101/cars .
- Issue the cat command to view the contents of the cars file.
- Issue the following Linux command: cut -c1-10 cars
What did this command do? - Issue the following Linux command: cut -f5 cars > field5.txt
What did this command do? - Issue the following Linux command: cut -f1-3 cars > field123.txt
What did this command do? - Issue the following Linux command: cut -f1,5 cars > field15.txt
What did this command do? - Issue the following Linux command: wc cars > count1.txt
What information does the count1.txt file contain? - Issue the following Linux command: wc cars > count2.txt
What information does the count2.txt file contain? - Issue the following Linux command: ls -l > listing.txt
What information does the count2.txt file contain? - Issue the following Linux command: pwd > listing.txt
What happenned to the original contents of the file called listing.txt? - Issue the following Linux command (use 2 greater-than signs): date >> listing.txt
What information does the listing.txt file contain? - Issue the following Linux command: cat listing.txt cars > combined.txt
What information does the combined.txt file contain?
NOTE: The cat command stands for "concatenate" which means to combine contents of multiple files into a single file. This is why the command is called "cat". - Issue the following Linux command: cat listing.txt cars murray 2> result.txt
What information does the result.txt file contain? - Issue the following Linux command: cat listing.txt cars murray > myoutput.txt 2> result.txt
What is displayed on the monitor? what do those files contain?
The Here Document allows you to redirect stdin from with the Linux command itself. Let's get some practice using the Here Document. - Issue the following Linux command:
cat <<+
line 1
line 2
line 3
+
What do you notice? - Issue the following Linux command:
grep 2 <<+
line 1
line 2
line 3
+
What do you notice? How does this differ from the previous command? Why?
- The problem with using redirection to create files, you have these files taking up space, which requires you remove them. In the next investigation, you will be learning how to issue pipeline commands which can provide information by issuing several Linux commands without creating temporary files.
INVESTIGATION 2: REDIRECTION USING PIPES
In this section, you will learn to issue pipeline commands and learn how to perform tasks
using Linux commands with or without the generation of temporary files.
Perform the Following Steps:
- Change to your home directory and confirm that you are now in your home directory.
- Issue the ls command to view the contents of your ~/redirect directory.
These are all temporary files that you created in your previous investigation.
The problem with creating temporary files, is that they take up space on your server,
and should be removed. - Issue the following Linux command to remove all files in your redirect directory: rm -r ~/redirect
and confirm that you have removed this directory and its contents.
NOTE: You will be issuing a pipeline command which will use the pipe symbol "|"
that will send the stdout from a command as stdin into another command. - Issue the follow Linux pipeline command: ls /bin | more
What happened? - Issue the following Linux pipeline command: ls /bin | who
What happened? Why is the result different than antipated?
NOTE: When issuing pipeline commands, commands to the right of the pipe symbol must be designed to accept stdin. Since the who command does not, you did NOT see the contents of the /bin directory but only information relating to the who command. Therefore, the order of which you build your pipeline command and the type of command that is used as a filter is extremely important! - Issue the following Linux command: cp /bin/?? > listing.txt
- Issue the following Linux command: sort -r listing.txt
- Issue the following Linux command to remove the listing file: rm listing.txt
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command: ls /bin/?? | sort -r
You should notice that the output from this pipeline command is the same output
from the command you issued in step #6 - Issue the following Linux pipeline command: ls /bin/?? | sort -r | more
What is different with this pipeline command as opposed to the previous pipeline command? - Issue the ls command.
You should notice that no files have been created. Let's get practice issuing more pipeline commands
using commands (previously learned or new) to be used as filters. - Issue the following Linux pipeline command: ls /bin/?? | sort -r | head -5
What did you notice? - Issue the following Linux pipeline command: ls /bin/???? | sort -r | grep r | tail -2
What did you notice? - Issue the following Linux pipeline command: ls /bin/???? | sort -r | grep r | cut -c1-3
- Issue the following Linux pipeline command:
ls /bin/???? | tee unsorted.txt | sort -r | tee sorted.txt | tee unmatched.txt | grep r | tail -2
What did you notice? - Check the files that were created to see how the tee command was used in the previous pipeline command.
- Change to your home directory.
- Issue the rm command to only remove the files unsorted.txt , sorted.txt , and unmatched.txt
- In the next investigation, you will learn various techniques to issue multiple Linux commands on the same line, or long Linux commands over multiple lines.
INVESTIGATION 3: ISSUING MULTIPLE UNIX/LINUX COMMANDS
In this section, you will learn how to issue multiple Unix / Linux commands in a single line or over multiple lines.
Perform the Following Steps:
- Confirm you are located in your home directory.
- Issue the following Linux commands (using semicolon to separate each command): cal;pwd;date
Note the from the output the order of how each of those commands were processed. - Issue the following Linux commands: (cal;pwd;date)
Was there any difference in the output of this command as opposed to the previous command? - Issue the following Linux pipeline command (using \ at the end of most lines):
echo "This will be split over multiple \
lines. Note that the shell will realize \
that a pipe requires another command, so \
it will automatically go to the next line" |tr '[a-z]' '[A-Z]'
Did the command work? What does this command do? - After you complete the Review Questions sections to get additional practice, then work on your online assignment 2 and complete section3 labelled: Redirection and Pipes.
LINUX PRACTICE QUESTIONS
The purpose of this section is to obtain extra practice to help with quizzes, your midterm, and your final exam.
Here is a link to the MS Word Document of ALL of the questions displayed below but with extra room to answer on the document to simulate a quiz:
https://ict.senecacollege.ca/~murray.saul/uli101/uli101_week5_practice.docx
Your instructor may take-up these questions during class. It is up to the student to attend classes in order to obtain the answers to the following questions. Your instructor will NOT provide these answers in any other form (eg. e-mail, etc).
When answering Linux command questions, refer to the following Inverted Tree diagram. The linux directory is contained in your home directory. Assume that you just logged into your Matrix account. Directories are underlined.
Review Questions:
- Write a single Linux command to provide a detailed listing of all files in the /bin directory, sending the output to a file called listing.txt in the “projects” directory (append output to existing file and use a relative pathname)
- Write a single Linux command to redirect the stderr from the command:
cat a.txt b.txt c.txt to a file called error.txt contained in the “assignments” directory. (overwrite previous file’s contents and use only relative pathnames) - Write a single Linux command: cat ~/a.txt ~/b.txt ~/c.txt and redirect stdout to a file called “good.txt” to the “tests” directory and stderr to a file called “bad.txt” to the “tests” directory. (overwrite previous contents for both files and use only relative-to-home pathnames).
- Write a single Linux command to redirect the stdout from the command:
cat a.txt b.txt c.txt to a file called wrong.txt contained in the “projects” directory and throw-out any standard error messages so they don’t appear on the screen (append output to existing file and use only relative pathnames). - Write a single Linux pipeline command to display a detailed listing of the “projects “directory but pause one screen at a time to view and navigate through all of the directory contents. Use a relative-to-home pathname.
- Write a single Linux pipeline command to display the sorted contents (in reverse alphabetical order) of the “linux” directory. Use a relative pathname.
- Assume that the text file called “.answers.txt” contains 10 lines. Write a single Linux pipeline command to only displays lines 5 through 8 for this file. Use only relative pathnames.
- Write a single Linux pipeline command to only display the contents of the “assignments” directory whose filenames match the pattern “murray” (both upper or lowercase). Use an absolute pathname.
- Write a single Linux pipeline command to display the number of characters contained in the file called “.answers.txt”. Use a relative-to-home pathname.
- Write a single Linux pipeline command to display the number of lines contained in the file called “questions.txt”. Use a relative pathname.
- Write a single Linux pipeline command to display only the first 10 characters of each filename contained in your current directory. Also, there is will be a lot of output, so also pause at each screenful so you can navigate throughout the display contents. Use a relative pathname.
- Create a table listing each Linux command, useful options that were mentioned in this tutorial for the following Linux commands: cut , tr , wc , and tee.