Difference between revisions of "UnknownX"
(→V2 -- One array) |
(→Assignment 2 - V1 Parallelization) |
||
| (17 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
[[File:Pycpu.PNG]]<br /> | [[File:Pycpu.PNG]]<br /> | ||
| + | Here is the code to calculate each pixel. It is good to use GPU to calculate them because each pixel is independent. | ||
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) { | for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) { | ||
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) { | for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) { | ||
| Line 422: | Line 423: | ||
| − | == Assignment 2 - Parallelization== | + | == Assignment 2 - V1 Parallelization== |
| + | |||
| + | Output result(converted to PNG formate): | ||
| + | |||
[[File:GpuassOutput.PNG]] | [[File:GpuassOutput.PNG]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Run time graph: | ||
[[File:Pygpu2.PNG]] | [[File:Pygpu2.PNG]] | ||
CPU code: | CPU code: | ||
| + | |||
| + | The most expensive part in the program. | ||
| + | |||
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) { | for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) { | ||
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) { | for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) { | ||
| Line 440: | Line 449: | ||
clamp255(pix_col); | clamp255(pix_col); | ||
} | } | ||
| − | pixs[3 * (y * N + x)] = (int)pix_col.x; | + | //Store RGB to array |
| + | pixs[3 * (y * N + x)] = (int)pix_col.x; | ||
pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 1] = (int)pix_col.y; | pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 1] = (int)pix_col.y; | ||
pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 2] = (int)pix_col.z; | pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 2] = (int)pix_col.z; | ||
| Line 446: | Line 456: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | + | Main code on .cu: | |
| + | |||
| + | 1. Allocate memory on device. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 2. run kunal. ntpb = 1024. | ||
| + | |||
| + | 3. copy the key data out. | ||
| + | |||
int size = N * N; | int size = N * N; | ||
int nblocks = (size + ntpb - 1) / ntpb; | int nblocks = (size + ntpb - 1) / ntpb; | ||
| Line 464: | Line 481: | ||
| − | Kernel | + | Kernel: |
| + | |||
| + | before: | ||
| + | for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) | ||
| + | for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) | ||
| + | after: | ||
| + | int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; | ||
| + | int x = idx / N; | ||
| + | int y = idx % N; | ||
__global__ void kernel_tray(Vec3 pix_col, int N, int* pixs_x, int* pixs_y, int* pixs_z) { | __global__ void kernel_tray(Vec3 pix_col, int N, int* pixs_x, int* pixs_y, int* pixs_z) { | ||
| Line 486: | Line 511: | ||
clamp255(pix_col); | clamp255(pix_col); | ||
} | } | ||
| + | //Store RGB to arrays | ||
pixs_x[y * N + x] = (int)pix_col.x; | pixs_x[y * N + x] = (int)pix_col.x; | ||
pixs_y[y * N + x] = (int)pix_col.y; | pixs_y[y * N + x] = (int)pix_col.y; | ||
pixs_z[y * N + x] = (int)pix_col.z; | pixs_z[y * N + x] = (int)pix_col.z; | ||
} | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | Profile on nvvp: | ||
| + | [[File:matrix.senecac.on.ca/~zzha1/Capture.PNG]] | ||
== Assignment 3 - Optimization == | == Assignment 3 - Optimization == | ||
| Line 530: | Line 559: | ||
=== V3 -- Occupancy === | === V3 -- Occupancy === | ||
| + | If we use 1024 threads, we only get 50%. However, if we change it to 640, we can get 60%. <br /> | ||
before: | before: | ||
const int ntpb = 1024; | const int ntpb = 1024; | ||
| Line 542: | Line 572: | ||
=== V4 -- Coalescence === | === V4 -- Coalescence === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Before this modification, here is our array. | ||
| + | R1 G1 B1 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ R2 G2 B2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ | ||
| + | After we modify switch the x and y. | ||
| + | R1 G1 B1 R1 G1 B1 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Before | Before | ||
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; | int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; | ||
| Line 575: | Line 612: | ||
'''What problems does it solve?''' <br /> | '''What problems does it solve?''' <br /> | ||
1. Using too many registers | 1. Using too many registers | ||
| + | To get 100%, we have to use less than 32 registers. If we change it from double to float, it reduces from 44 to 29. | ||
[[File:Pyoccu2.PNG]] | [[File:Pyoccu2.PNG]] | ||
| − | 2. Calculating in double | + | 2. Calculating in double is very slow on Geforce device. |
| + | |||
[[File:pyfloat.PNG]] | [[File:pyfloat.PNG]] | ||
| − | == | + | ==Links== |
| − | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ARn_yhgk7aE | + | Referances: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ARn_yhgk7aE |
| + | |||
| + | PPT: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/10Cr_zIDUultkQLzdyC3_3B-GKO_bl6RJFHpWNg72tRk/edit#slide=id.g20678afd80_0_1313 | ||
Latest revision as of 04:50, 13 April 2017
Contents
Ray Tracing
Team Member
eMail All
Progress
Assignment 1 - FileCompressor
FileCompressor
Environment:
System: Windows 10
CPU: i5-6400 2.70GHz
RAM: 8GB 2444Hz
Video card: NVIDIA GTX 1060 3GB
The size of file before compressing is 128MB After:65.2MB (Depend on the file)
Here is the major code to compress a file :
The following image shows that the CompressCore function takes 99.55% of the time to compress a 128MB file.
As the size of file increase, the time that this program spend on compressing a file will increase.
Assignment 1 Ray Tracing v2
Environment:
System: Windows 10
CPU: i5-6400 2.70GHz
RAM: 8GB 2444Hz
Video card: NVIDIA GTX 1060 3GB
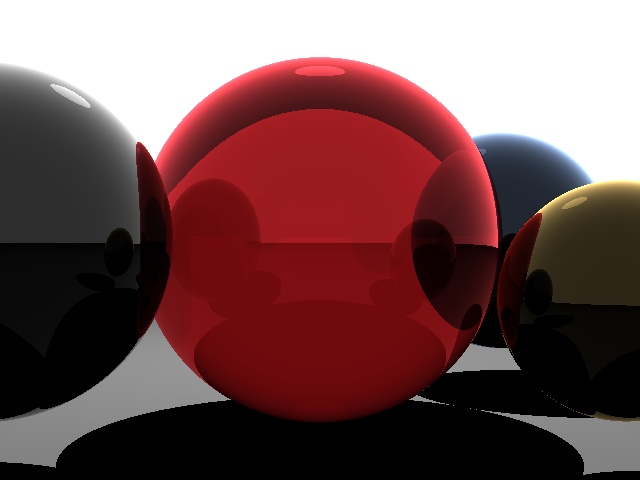
Output:
Here is the code to calculate each pixel. It is good to use GPU to calculate them because each pixel is independent.
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) {
pix_col = black;
const Ray ray(Vec3(x, y, 0), Vec3(0, 0, 1));
if (sphere.intersect(ray, t)) {
const Vec3 pi = ray.o + ray.d*t;
const Vec3 L = light.c - pi;
const Vec3 N = sphere.getNormal(pi);
const double dt = dot(L.normalize(), N.normalize());
pix_col = (red + white*dt) * 0.5;
clamp255(pix_col);
}
pixs[3 * (y * N + x)] = (int)pix_col.x;
pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 1] = (int)pix_col.y;
pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 2] = (int)pix_col.z;
}
}
Assignment 1 Ray Tracing
Environment:
System: Windows 10
CPU: i7-6700HQ 2.60GHz
RAM: 16GB 21337Hz
Video card: NVIDIA GTX 1060 6GB
Program: raytracing.cpp from scratchpixel.com tutorial on basic raytracing. website along with source code location: [1]
Compilation
Unix -
g++ -O2 -o raytrace raytracer.cpp
raytrace
OSX -
clang++ -O2 -o raytrace raytracer.cpp
raytrace
From the compilation it creates this ppm file
Running the Flat Profile: gprof -p -b raytrace > raytrace.flt
gives us this :
Flat profile:
Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds.
% cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls us/call us/call name 87.76 0.43 0.43 307200 1.40 1.40 trace(Vec3<float> const&, Vec3<float> const&, std::vector<Sphere, std::allocator<Sphere> > const&, int const&) 12.24 0.49 0.06 render(std::vector<Sphere, std::allocator<Sphere> > const&) 0.00 0.49 0.00 4 0.00 0.00 std::vector<Sphere, std::allocator<Sphere> >::_M_insert_aux(__gnu_cxx::__normal_iterator<Sphere*, std::vector<Sphere, std::allocator<Sphere> > >, Sphere const&) 0.00 0.49 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__Z3mixRKfS0_S0_
Observation:
From looking at the result of the flat profile we can see that the trace and the render functions take the most time to run.
Running the call graph: gprof -q -b raytrace > raytrace.clg
Observation: From looking at both the flat profile and the call graph we can see that both the trace and the render functions are the hot spots of the program.
Possible Parallelizations:
When looking at both the Trace Function and the render function.
Render Function :
void render(const std::vector<Sphere> &spheres) {
unsigned width = 640, height = 480;
Vec3f *image = new Vec3f[width * height], *pixel = image;
float invWidth = 1 / float(width), invHeight = 1 / float(height);
float fov = 30, aspectratio = width / float(height);
float angle = tan(M_PI * 0.5 * fov / 180.);
// Trace rays
for (unsigned y = 0; y < height; ++y) { Possible Parallelization spot
for (unsigned x = 0; x < width; ++x, ++pixel) {
float xx = (2 * ((x + 0.5) * invWidth) - 1) * angle * aspectratio;
float yy = (1 - 2 * ((y + 0.5) * invHeight)) * angle;
Vec3f raydir(xx, yy, -1);
raydir.normalize();
*pixel = trace(Vec3f(0), raydir, spheres, 0);
}
}
// Save result to a PPM image (keep these flags if you compile under Windows)
std::ofstream ofs("./untitled.ppm", std::ios::out | std::ios::binary);
ofs << "P6\n" << width << " " << height << "\n255\n";
for (unsigned i = 0; i < width * height; ++i) {
ofs << (unsigned char)(std::min(float(1), image[i].x) * 255) <<
(unsigned char)(std::min(float(1), image[i].y) * 255) <<
(unsigned char)(std::min(float(1), image[i].z) * 255);
}
ofs.close();
delete [] image;
}
In the render function it has a runtime speed of T(n) = o^2.
Trace Function:
Vec3f trace(
const Vec3f &rayorig, const Vec3f &raydir, const std::vector<Sphere> &spheres, const int &depth)
{
//if (raydir.length() != 1) std::cerr << "Error " << raydir << std::endl;
float tnear = INFINITY;
const Sphere* sphere = NULL;
// find intersection of this ray with the sphere in the scene
for (unsigned i = 0; i < spheres.size(); ++i) {
float t0 = INFINITY, t1 = INFINITY;
if (spheres[i].intersect(rayorig, raydir, t0, t1)) {
if (t0 < 0) t0 = t1;
if (t0 < tnear) {
tnear = t0;
sphere = &spheres[i];
}
}
}
// if there's no intersection return black or background color
if (!sphere) return Vec3f(2);
Vec3f surfaceColor = 0; // color of the ray/surfaceof the object intersected by the ray
Vec3f phit = rayorig + raydir * tnear; // point of intersection
Vec3f nhit = phit - sphere->center; // normal at the intersection point
nhit.normalize(); // normalize normal direction
// If the normal and the view direction are not opposite to each other
// reverse the normal direction. That also means we are inside the sphere so set
// the inside bool to true. Finally reverse the sign of IdotN which we want
// positive.
float bias = 1e-4; // add some bias to the point from which we will be tracing
bool inside = false;
if (raydir.dot(nhit) > 0) nhit = -nhit, inside = true;
if ((sphere->transparency > 0 || sphere->reflection > 0) && depth < MAX_RAY_DEPTH) {
float facingratio = -raydir.dot(nhit);
// change the mix value to tweak the effect
float fresneleffect = mix(pow(1 - facingratio, 3), 1, 0.1);
// compute reflection direction (not need to normalize because all vectors
// are already normalized)
Vec3f refldir = raydir - nhit * 2 * raydir.dot(nhit);
refldir.normalize();
Vec3f reflection = trace(phit + nhit * bias, refldir, spheres, depth + 1);
Vec3f refraction = 0;
// if the sphere is also transparent compute refraction ray (transmission)
if (sphere->transparency) {
float ior = 1.1, eta = (inside) ? ior : 1 / ior; // are we inside or outside the surface?
float cosi = -nhit.dot(raydir);
float k = 1 - eta * eta * (1 - cosi * cosi);
Vec3f refrdir = raydir * eta + nhit * (eta * cosi - sqrt(k));
refrdir.normalize();
refraction = trace(phit - nhit * bias, refrdir, spheres, depth + 1);
}
// the result is a mix of reflection and refraction (if the sphere is transparent)
surfaceColor = (
reflection * fresneleffect +
refraction * (1 - fresneleffect) * sphere->transparency) * sphere->surfaceColor;
}
else {
// it's a diffuse object, no need to raytrace any further
for (unsigned i = 0; i < spheres.size(); ++i) {
if (spheres[i].emissionColor.x > 0) {
// this is a light
Vec3f transmission = 1;
Vec3f lightDirection = spheres[i].center - phit;
lightDirection.normalize();
for (unsigned j = 0; j < spheres.size(); ++j) {
if (i != j) {
float t0, t1;
if (spheres[j].intersect(phit + nhit * bias, lightDirection, t0, t1)) {
transmission = 0;
break;
}
}
}
surfaceColor += sphere->surfaceColor * transmission *
std::max(float(0), nhit.dot(lightDirection)) * spheres[i].emissionColor;
}
}
}
return surfaceColor + sphere->emissionColor;
}
Within this trace function the possible parallelization points would be here :
{
for (unsigned i = 0; i < spheres.size(); ++i) {
float t0 = INFINITY, t1 = INFINITY;
if (spheres[i].intersect(rayorig, raydir, t0, t1)) {
if (t0 < 0) t0 = t1;
if (t0 < tnear) {
tnear = t0;
sphere = &spheres[i];
}
}
}
} {
else {
// it's a diffuse object, no need to raytrace any further
for (unsigned i = 0; i < spheres.size(); ++i) {
if (spheres[i].emissionColor.x > 0) {
// this is a light
Vec3f transmission = 1;
Vec3f lightDirection = spheres[i].center - phit;
lightDirection.normalize();
for (unsigned j = 0; j < spheres.size(); ++j) {
if (i != j) {
float t0, t1;
if (spheres[j].intersect(phit + nhit * bias, lightDirection, t0, t1)) {
transmission = 0;
break;
}
}
}
surfaceColor += sphere->surfaceColor * transmission *
std::max(float(0), nhit.dot(lightDirection)) * spheres[i].emissionColor;
}
}
}
return surfaceColor + sphere->emissionColor;
}
In this function it has a runtime speed of T(n) = O^2.
Presentation
What is Ray Tracing?
Ray tracing is the technique of generating an image by tracing the paths light would travel through pixels in an image plane and simulating the effects it encounters with virtual objects.
Code
struct Vec3 {
double x, y, z;
Vec3(double x, double y, double z) : x(x), y(y), z(z) {}
Vec3 operator + (const Vec3& v) const { return Vec3(x + v.x, y + v.y, z + v.z); }
Vec3 operator - (const Vec3& v) const { return Vec3(x - v.x, y - v.y, z - v.z); }
Vec3 operator * (double d) const { return Vec3(x*d, y*d, z*d); }
Vec3 operator / (double d) const { return Vec3(x / d, y / d, z / d); }
Vec3 normalize() const {
double mg = sqrt(x*x + y*y + z*z);
return Vec3(x / mg, y / mg, z / mg);
}
};
inline double dot(const Vec3& a, const Vec3& b) {
return (a.x*b.x + a.y*b.y + a.z*b.z);
}
struct Ray {
Vec3 o, d;
Ray(const Vec3& o, const Vec3& d) : o(o), d(d) {}
};
struct Sphere {
Vec3 c;
double r;
Sphere(const Vec3& c, double r) : c(c), r(r) {}
Vec3 getNormal(const Vec3& pi) const { return (pi - c) / r; }
bool intersect(const Ray& ray, double &t) const {
const Vec3 o = ray.o;
const Vec3 d = ray.d;
const Vec3 oc = o - c;
const double b = 2 * dot(oc, d);
const double c = dot(oc, oc) - r*r;
double disc = b*b - 4 * c;
if (disc < 1e-4) return false;
disc = sqrt(disc);
const double t0 = -b - disc;
const double t1 = -b + disc;
t = (t0 < t1) ? t0 : t1;
return true;
}
};
int main() {
steady_clock::time_point ts, te,tm;
ts = steady_clock::now();
const int N = 500;
const Vec3 white(255, 255, 255);
const Vec3 black(0, 0, 0);
const Vec3 red(0, 255, 0);
const Sphere sphere(Vec3(N*0.5, N*0.5, 50), 50);
const Sphere light(Vec3(0, 0, 50), 1);
std::ofstream out("out.ppm");
out << "P3\n" << N << ' ' << N << ' ' << "255\n";
double t;
Vec3 pix_col(black);
int* pixs = new int[N * N * 3];
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) {
pix_col = black;
const Ray ray(Vec3(x, y, 0), Vec3(0, 0, 1));
if (sphere.intersect(ray, t)) {
const Vec3 pi = ray.o + ray.d*t;
const Vec3 L = light.c - pi;
const Vec3 N = sphere.getNormal(pi);
const double dt = dot(L.normalize(), N.normalize());
pix_col = (red + white*dt) * 0.5;
clamp255(pix_col);
}
pixs[3 * (y * N + x)] = (int)pix_col.x;
pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 1] = (int)pix_col.y;
pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 2] = (int)pix_col.z;
}
}
te = steady_clock::now();
reportTime("matrix-matrix multiplication", te - ts);
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) {
out << pixs[3 * (y * N + x)] << ' '
<< pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 1] << ' '
<< pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 2] << '\n';
}
}
tm = steady_clock::now();
reportTime("matrix-matrix multiplication", tm - ts);
delete[] pixs;
}
Points of possible Parallelization
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) {
pix_col = black;
const Ray ray(Vec3(x, y, 0), Vec3(0, 0, 1));
if (sphere.intersect(ray, t)) {
const Vec3 pi = ray.o + ray.d*t;
const Vec3 L = light.c - pi;
const Vec3 N = sphere.getNormal(pi);
const double dt = dot(L.normalize(), N.normalize());
pix_col = (red + white*dt) * 0.5;
clamp255(pix_col);
}
pixs[3 * (y * N + x)] = (int)pix_col.x;
pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 1] = (int)pix_col.y;
pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 2] = (int)pix_col.z;
}
}
Graph
Assignment 2 - V1 Parallelization
Output result(converted to PNG formate):
Run time graph:
CPU code:
The most expensive part in the program.
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y) {
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x) {
pix_col = black;
const Ray ray(Vec3(x, y, 0), Vec3(0, 0, 1));
if (sphere.intersect(ray, t)) {
const Vec3 pi = ray.o + ray.d*t;
const Vec3 L = light.c - pi;
const Vec3 N = sphere.getNormal(pi);
const double dt = dot(L.normalize(), N.normalize());
pix_col = (red + white*dt) * 0.5;
clamp255(pix_col);
}
//Store RGB to array
pixs[3 * (y * N + x)] = (int)pix_col.x;
pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 1] = (int)pix_col.y;
pixs[3 * (y * N + x) + 2] = (int)pix_col.z;
}
}
Main code on .cu:
1. Allocate memory on device.
2. run kunal. ntpb = 1024.
3. copy the key data out.
int size = N * N; int nblocks = (size + ntpb - 1) / ntpb; int* h_pixs_x = new int[N * N]; int* h_pixs_y = new int[N * N]; int* h_pixs_z = new int[N * N]; int* d_pixs_x; int* d_pixs_y; int* d_pixs_z; cudaMalloc((void**)&d_pixs_x, N * N * sizeof(int)); cudaMalloc((void**)&d_pixs_y, N * N * sizeof(int)); cudaMalloc((void**)&d_pixs_z, N * N * sizeof(int)); kernel_tray << <nblocks, ntpb >> >(pix_col, N, d_pixs_x, d_pixs_y, d_pixs_z); cudaMemcpy(h_pixs_x, d_pixs_x, N * N * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaMemcpy(h_pixs_y, d_pixs_y, N * N * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaMemcpy(h_pixs_z, d_pixs_z, N * N * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
Kernel:
before:
for (int y = 0; y < N; ++y)
for (int x = 0; x < N; ++x)
after:
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; int x = idx / N; int y = idx % N;
__global__ void kernel_tray(Vec3 pix_col, int N, int* pixs_x, int* pixs_y, int* pixs_z) {
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
int x = idx / N;
int y = idx % N;
const Vec3 white(255, 255, 255);
const Vec3 black(0, 0, 0);
const Vec3 red(255, 0, 0);
const Sphere sphere(Vec3(N*0.5, N*0.5, 50), 50);
const Sphere light(Vec3(0, 0, 50), 1);
double t;
pix_col = black;
const Ray ray(Vec3(x, y, 0), Vec3(0, 0, 1));
if (sphere.intersect(ray, t)) {
const Vec3 pi = ray.o + ray.d*t;
const Vec3 L = light.c - pi;
const Vec3 N = sphere.getNormal(pi);
const double dt = dot(L.normalize(), N.normalize());
pix_col = (red + white*dt) * 0.5;
clamp255(pix_col);
}
//Store RGB to arrays
pixs_x[y * N + x] = (int)pix_col.x;
pixs_y[y * N + x] = (int)pix_col.y;
pixs_z[y * N + x] = (int)pix_col.z;
}
Profile on nvvp: File:Matrix.senecac.on.ca/~zzha1/Capture.PNG
Assignment 3 - Optimization
V2 -- One array
PPM file output:
We allocate three arrays to store the all the results. Each pixel stores in 3 arrys, and it is slow.
Instead of 3 arrays, we allocate a bigger array and store all the pixels in this array.
For the first pixel.
1st: R _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 2nd: G _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 3rd: B _ _ _ _ _ _ _
new array: R G B _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Before
int* d_pixs_x; int* d_pixs_y; int* d_pixs_z; cudaMalloc((void**)&d_pixs_x, N * N * sizeof(int)); cudaMalloc((void**)&d_pixs_y, N * N * sizeof(int)); cudaMalloc((void**)&d_pixs_z, N * N * sizeof(int)); kernel_tray << <nblocks, ntpb >> >(pix_col, N, d_pixs_x, d_pixs_y, d_pixs_z); cudaMemcpy(h_pixs_x, d_pixs_x, N * N * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaMemcpy(h_pixs_y, d_pixs_y, N * N * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); cudaMemcpy(h_pixs_z, d_pixs_z, N * N * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
After
int* d_pixs; cudaMalloc((void**)&d_pixs, N * N * 3 * sizeof(int)); kernel_tray << <nblocks, ntpb >> >(pix_col, N, d_pixs); cudaMemcpy(h_pixs, d_pixs, N * N * 3 * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
V3 -- Occupancy
If we use 1024 threads, we only get 50%. However, if we change it to 640, we can get 60%.
before:
const int ntpb = 1024;
After:
const int ntpb = 640;
V4 -- Coalescence
Before this modification, here is our array.
R1 G1 B1 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ R2 G2 B2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
After we modify switch the x and y.
R1 G1 B1 R1 G1 B1 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
Before
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; int x = idx / N; int y = idx % N;
After
int idx = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; int y = idx / N; int x = idx % N;
V5 -- Double -> float
struct Vec3 {
double x, y, z;
__host__ __device__ Vec3(double x, double y, double z) : x(x), y(y), z(z) {}
__host__ __device__ Vec3 operator + (const Vec3& v) const { return Vec3(x + v.x, y + v.y, z + v.z); }
__host__ __device__ Vec3 operator - (const Vec3& v) const { return Vec3(x - v.x, y - v.y, z - v.z); }
__host__ __device__ Vec3 operator * (double d) const { return Vec3(x*d, y*d, z*d); }
__host__ __device__ Vec3 operator / (double d) const { return Vec3(x / d, y / d, z / d); }
__host__ __device__
Vec3 normalize() const {
double mg = sqrt(x*x + y*y + z*z);
return Vec3(x / mg, y / mg, z / mg);
}
};
What problems does it solve?
1. Using too many registers
To get 100%, we have to use less than 32 registers. If we change it from double to float, it reduces from 44 to 29.
2. Calculating in double is very slow on Geforce device.
Links
Referances: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ARn_yhgk7aE
PPT: https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/10Cr_zIDUultkQLzdyC3_3B-GKO_bl6RJFHpWNg72tRk/edit#slide=id.g20678afd80_0_1313