Difference between revisions of "GPU610 Team Tsubame"
Yanhao Lei (talk | contribs) (→Presentation) |
Yanhao Lei (talk | contribs) (→Presentation) |
||
| Line 940: | Line 940: | ||
[[File:SDiagram.PNG]] | [[File:SDiagram.PNG]] | ||
| − | '''Parallelize''' | + | '''2. Parallelize''' |
*Kernel: | *Kernel: | ||
Revision as of 12:21, 5 April 2017
Contents
Maze
Team Members
- Mark Anthony Villaflor (Leader; Maze)
- Huachen Li (Prime Numbers)
- Yanhao Lei (Wiki; Pi)
eMail All
Progress
- February 10, 2017 - Completed Phase 1 (Select and Assess)
- March 20, 2017 - Added instructions to compile and execute Maze in Visual Studio
- April 4, 2017 - Updated Phase 2 and 3
PHASE 1
Pi
This is a comparison between two programs that calculate Pi.
- Test System Specifications
OS: Windows 7 (64-bit) CPU: Intel Core i3-2350M @ 2.30GHz GPU: GeForce GT 520MX (48 CUDA cores) IDE: Microsoft Visual Studio Enterprise 2015; Version 14.0.25431.01 Update 3
- How To Execute On Linux?
1. Here is the Makefile:
# Change this to "monte-carlo" if needed
VER = leibniz
# Uncomment and modify the following lines to specify a specific version of GCC
#GCC_VERSION = 5.2.0
#PREFIX = /usr/local/gcc/${GCC_VERSION}/bin/
CC = ${PREFIX}gcc
CPP = ${PREFIX}g++
$(VER): $(VER).o ; \
$(CPP) -g -pg -o$(VER) $(VER).o
$(VER).o: $(VER).cpp ; \
$(CPP) -c -O2 -g -pg -std=c++14 $(VER).cpp
# Remember to ">make clean" after ">make" to cleanup if the cleaning does not happen automatically
clean: ; \
rm *\.o
2. Copy leibniz.cpp and/or monte-carlo.cpp and put them into the same directory as the Makefile.
3. Execute the following command (in the same directory as the Makefile):
> make
4. Execute the binary with:
> ./leibniz [ n ]
OR
> ./monte-carlo [ n ]
Where n is the number of iterations.
Leibniz formula implementation:
leibniz.cpp
00 #include <iostream> 01 #include <iomanip> 02 #include <string> 03 04 #include <chrono> 05 06 // Function duplicated from Workshop 2 - BLAS 07 void reportTime(const char* msg, std::chrono::steady_clock::duration span) { 08 auto ms = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(span); 09 std::cout << msg << " - took - " 10 << ms.count() << " millisecs" << std::endl; 11 } 12 13 // Arctangent of 1; execute for ~n iterations to refine the result 14 long double arctan1( unsigned long long int it ) { 15 long double r = 0.0; // 1 op. (=) runs 1 time 16 17 // v0.25; due to performing the operations in a different order, there are rounding issues... 18 for ( long double d = 0.0; d < it; d++ ) { // 1 op. (=) runs 1 time; 2 op.s (<, ++) run n times 19 long double de = d * 4.0 + 1.0; // 3 op.s (=, *, +) run n times 20 r += (1.0 / de) - (1.0 / (de + 2.0)); // 6 op.s (+ & =, /, -, /, +) run n times 21 } 22 23 return r; // 1 op. (return) runs 1 time 24 } 25 26 int main( int argc, char* argv[] ) { 27 unsigned long long int n = std::stoull(argv[1], 0); 28 29 std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point ts, te; 30 ts = std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); 31 long double pi = 4.0 * arctan1( n ); 32 te = std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); 33 reportTime("Arctangent(1) ", te - ts); 34 35 // Maximum length of a long double is 64 digits; minus "3." gives 62 digits. 36 std::cout.precision(62); 37 std::cout << "Pi: " << std::fixed << pi << std::endl; 40 }
- STAGE 1 - Big-O:
There is only one for loop in this program (on line 18); it executes d times, where d is the first argument provided to the program on the command line. Summing up the operations in the (predicted) hotspot, T(n) = 11n + 3; therefore O(n) runtime.
- STAGE 2 - Potential Speedup
Using Amdahl's Law:
P = 1708ms / 1725ms (using the third test data from below...) P = 0.99014 n = 48 (processors reported by deviceQuery.exe) Sn = 1 / ( 1 - P + P / n ) S48 = 1 / ( 1 - 0.99014 + 0.99014 / 48 ) S48 = 32.79988
The maximum speedup on the test system is approximately 33 times.
- STAGE 3 - Test Runs
The following tests were done on the Matrix server:
4 digits are correct at 10K iterations:
> time ./leibniz 10000 Arctangent(1) - took - 0 millisecs Pi: 3.14154265358982449354505184224706226814305409789085388183593750 real 0m0.016s user 0m0.004s sys 0m0.008s
7 digits are correct at 10M iterations:
> time ./leibniz 10000000 Arctangent(1) - took - 171 millisecs Pi: 3.14159260358979321929411010483335076060029678046703338623046875 real 0m0.187s user 0m0.172s sys 0m0.012s
No difference at 100M iterations:
> time ./leibniz 100000000 Arctangent(1) - took - 1708 millisecs Pi: 3.14159264858979533105269588144636827564681880176067352294921875 real 0m1.725s user 0m1.704s sys 0m0.008s
The following tests were done on the test system; these results will be used for the comparison between the serial and parallel versions.
n = 10,000
Arctangent(1) - took - 0 millisecs Pi: 3.14154265358982032196877298702020198106765747070312500000000000
n = 10,000,000
Arctangent(1) - took - 199 millisecs Pi: 3.14159260358809833135751432564575225114822387695312500000000000
n = 100,000,000
Arctangent(1) - took - 2087 millisecs Pi: 3.14159264457621567601108836242929100990295410156250000000000000
Monte-Carlo algorithm implementation:
monte-carlo.cpp
00 #include <iostream> 01 #include <random> 02 #include <string> 03 04 #include <chrono> 05 06 // Duplicated from Workshop 2 - BLAS 07 void reportTime(const char* msg, std::chrono::steady_clock::duration span) { 08 auto ms = std::chrono::duration_cast<std::chrono::milliseconds>(span); 09 std::cout << msg << " - took - " << 10 ms.count() << " millisecs" << std::endl; 11 } 12 13 int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { 14 std::chrono::steady_clock::time_point ts, te; 15 16 ts = std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); 17 unsigned long long int n = std::stoull(argv[1], 0), 18 totalCircle = 0; 19 20 int stride = 1000, 21 circleSize = n / stride; 22 23 unsigned int* circle = new unsigned int[circleSize]; 24 25 for (int i = 0; i < circleSize; i++) 26 circle[i] = 0; 27 28 std::random_device rd; 29 std::mt19937 mt(rd()); 30 std::uniform_real_distribution<long double> dist(0.0, 1.0); 31 te = std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); 32 reportTime("Init. ", te - ts); 33 34 ts = std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); 35 for (unsigned long long int i = 0; i < circleSize; i++) { 36 for (int j = 0; j < stride; j++) { 37 long double x = dist(mt), 38 y = dist(mt); 39 // if position is inside the circle... 40 if (x * x + y * y < 1.0) { 41 circle[i]++; 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 46 for (int i = 0; i < circleSize; i++) 47 totalCircle += circle[i]; 48 49 long double pi = 4.0 * ((long double) totalCircle) / ((long double) n); 50 te = std::chrono::steady_clock::now(); 51 reportTime("Drop points ", te - ts); 52 53 std::cout.precision(62); 54 std::cout << "Pi: " << std::fixed << pi << std::endl; 55 56 delete [] circle; 57 }
- STAGE 1 - Big-O:
The (predicted) hotspot begins from line 35 and ends at line 44. Although there are two for loops, the outer for loop executes n / stride times while the inner for loop executes stride times; the actual iteration is just n ( O(n) runtime ).
- STAGE 2 - Potential Speedup:
Using Amdahl's Law:
P = 10883ms / 10903ms (using the last sample of the third test data from below...) P = 0.99817 n = 48 (processors reported by deviceQuery.exe) Sn = 1 / ( 1 - P + P / n ) S48 = 1 / ( 1 - 0.99817 + 0.99817 / 48 ) S48 = 44.19015
The maximum speedup on the test system is approximately 44 times.
- STAGE 3 - Test Runs
The following tests were done on the Matrix server:
At around 10K iterations, the first decimal is stable.
> time ./monte-carlo 10000 Init. - took - 0 millisecs Drop points - took - 1 millisecs Pi: 3.11679999999999999995940747066214271399076096713542938232421875 real 0m0.019s user 0m0.004s sys 0m0.008s > time ./monte-carlo 10000 Init. - took - 0 millisecs Drop points - took - 1 millisecs Pi: 3.16480000000000000009124645483638005316606722772121429443359375 real 0m0.018s user 0m0.008s sys 0m0.004s > time ./monte-carlo 10000 Init. - took - 0 millisecs Drop points - took - 1 millisecs Pi: 3.16639999999999999995108079797745403993758372962474822998046875 real 0m0.018s user 0m0.004s sys 0m0.008s
The next digit is stable at around 10M iterations
> time ./monte-carlo 10000000 Init. - took - 0 millisecs Drop points - took - 1096 millisecs Pi: 3.14150879999999999990685506379151092914980836212635040283203125 real 0m1.114s user 0m1.092s sys 0m0.008s > time ./monte-carlo 10000000 Init. - took - 0 millisecs Drop points - took - 1097 millisecs Pi: 3.14219679999999999993332000514101309818215668201446533203125000 real 0m1.114s user 0m1.092s sys 0m0.016s > time ./monte-carlo 10000000 Init. - took - 0 millisecs Drop points - took - 1097 millisecs Pi: 3.14158840000000000010696443730751070688711479306221008300781250 real 0m1.115s user 0m1.088s sys 0m0.012s
By 100M, the third digit appears to be stable.
> time ./monte-carlo 100000000 Init. - took - 1 millisecs Drop points - took - 10910 millisecs Pi: 3.14138611999999999989559296142971334120375104248523712158203125 real 0m10.930s user 0m10.881s sys 0m0.012s > time ./monte-carlo 100000000 Init. - took - 1 millisecs Drop points - took - 10847 millisecs Pi: 3.14185203999999999998835042980260823242133483290672302246093750 real 0m10.868s user 0m10.833s sys 0m0.016s > time ./monte-carlo 100000000 Init. - took - 1 millisecs Drop points - took - 10883 millisecs Pi: 3.14160056000000000009896028441147564080893062055110931396484375 real 0m10.903s user 0m10.865s sys 0m0.016s
The following tests were done on the test system; these results will be used for the comparison between the serial and parallel versions.
n = 10,000
Init. - took - 2 millisecs Drop points - took - 1 millisecs Pi: 3.12440000000000006608047442568931728601455688476562500000000000 Init. - took - 1 millisecs Drop points - took - 2 millisecs Pi: 3.14880000000000004334310688136611133813858032226562500000000000 Init. - took - 2 millisecs Drop points - took - 2 millisecs Pi: 3.12760000000000015774048733874224126338958740234375000000000000
n = 10,000,000
Init. - took - 2 millisecs Drop points - took - 2046 millisecs Pi: 3.14098960000000015924115359666757285594940185546875000000000000 Init. - took - 2 millisecs Drop points - took - 2059 millisecs Pi: 3.14231840000000017809611563279759138822555541992187500000000000 Init. - took - 2 millisecs Drop points - took - 2052 millisecs Pi: 3.14155439999999996913970790046732872724533081054687500000000000
n = 100,000,000
Init. - took - 2 millisecs Drop points - took - 21263 millisecs Pi: 3.14143352000000009027758096635807305574417114257812500000000000 Init. - took - 2 millisecs Drop points - took - 21101 millisecs Pi: 3.14146268000000006281879905145615339279174804687500000000000000 Init. - took - 3 millisecs Drop points - took - 20884 millisecs Pi: 3.14172063999999995331791069475002586841583251953125000000000000
Summary
Both programs calculate finite results of Pi, however the Leibniz implementation has higher accuracy and calculates more digits per iteration. Since both algorithms have O(n) runtime, the Leibniz implementation is also superior in terms of speed.
With regards to the hotspots, both programs contain one area that holds over 99% of their total execution time; these areas will be the focus for parallelization. The programs were revised to remove all data dependencies, thus there should be no conflicts between threads when the parallel codes are applied.
Maze
Testing Environment:
- Operating system: Linux
- Compiler: g++ 5.2.0
- Processor: Dual-Core AMD Opteron(tm) Processor 8220
- System memory: 3098088 kB
How to setup:
1. Download source file: https://github.com/corzani/maze
2. Create “Makefile” file:
# Makefile for GPU610/assigment1/maze
#
GCC_VERSION = 5.2.0
PREFIX = /usr/local/gcc/${GCC_VERSION}/bin/
CC = ${PREFIX}gcc
CPP = ${PREFIX}g++
OBJS = Maze.o MazeDebug.o MazePng.o main.o
SOURCE = Maze.cpp MazeDebug.cpp MazePng.cpp main.cpp
LIBS = -lpng
TARGET = maze
$(TARGET): $(OBJS)
$(CPP) -pg -o$(TARGET) $(OBJS) $(LIBS)
$(OBJS): $(SOURCE)
$(CPP) -c -O2 -g -pg -std=c++14 $(SOURCE)
#all: $(TARGET)
clean:
rm *.o
3. Complile and run:
> make > maze <maze x axes> <maze y axes>
Example:
> maze 5000 5000
Update (03.20.2017) - How to setup in Visual Studio 2015
1. Download source files from https://github.com/corzani/maze
2. Create a new Visual Studio project
3. Copy all header and cpp files from the downloaded maze directory to the project directory (not the solution directory)
4. In VS, right click on the project in the Solution explorer and Add -> Existing Item; pick the copied files from the previous step
5. In VS, go to menu Tools -> NuGet Package Manager -> Package Manager Console; in the new console (at the bottom of the screen in default configuration), execute:
PM> Install-Package libpng
6. In VS, Open MazePng.cpp, remove the following line:
#include <unistd.h>
7. In VS, change the Configuration from Debug to Release and Platform from x86 to x64
8. In VS, go to menu Build -> Build Solution
Analysis:
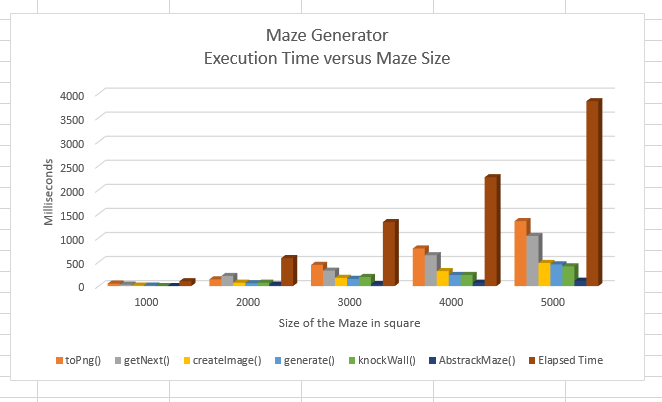
The program function named toPng() takes up an average of 42% (min: 35%; max: 50%) of the execution time. The reason for toPng() to take so much runtime is because of the for loop that building the walls of the maze.
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i) {
row_pointers[i] = new png_byte[width * 3];
for (int j = 0; j < width * 3; j += 3) {
row_pointers[i][j] = WALL;
row_pointers[i][j + 1] = WALL;
row_pointers[i][j + 2] = WALL;
}
}
The function also has a runtime of O(n^2).
For n = 1000
Flat profile: Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls ms/call ms/call name 50.00 0.05 0.05 MazePng::toPng(unsigned int) 30.00 0.08 0.03 1999978 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::getNext(unsigned int, short*, unsigned int*) 10.00 0.09 0.01 1 10.00 10.00 MazePng::createImage(unsigned char**, unsigned int) 10.00 0.10 0.01 AbstractMaze::generate(int) 0.00 0.10 0.00 999999 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::knockWall(unsigned int, unsigned int, AbstractMaze::directions) 0.00 0.10 0.00 7798 0.00 0.00 _ZNSt5dequeIjSaIjEE16_M_push_back_auxIJjEEEvDpOT_ 0.00 0.10 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 std::_Deque_base<unsigned int, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::_M_initialize_map(unsigned int) 0.00 0.10 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 std::_Deque_base<unsigned int, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::~_Deque_base() 0.00 0.10 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN12AbstractMaze3mapE 0.00 0.10 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN7MazePngC2Ejj 0.00 0.10 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN9MazeDebugC2Ejj 0.00 0.10 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I_main 0.00 0.10 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::AbstractMaze(unsigned int, unsigned int)
For n = 2000
Flat profile: Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls ms/call ms/call name 36.21 0.21 0.21 7999992 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::getNext(unsigned int, short*, unsigned int*) 24.14 0.35 0.14 MazePng::toPng(unsigned int) 12.07 0.42 0.07 3999999 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::knockWall(unsigned int, unsigned int, AbstractMaze::directions) 12.07 0.49 0.07 1 70.00 70.00 MazePng::createImage(unsigned char**, unsigned int) 10.34 0.55 0.06 AbstractMaze::generate(int) 5.17 0.58 0.03 1 30.00 30.00 AbstractMaze::AbstractMaze(unsigned int, unsigned int) 0.00 0.58 0.00 31113 0.00 0.00 _ZNSt5dequeIjSaIjEE16_M_push_back_auxIJjEEEvDpOT_ 0.00 0.58 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 std::_Deque_base<unsigned int, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::_M_initialize_map(unsigned int) 0.00 0.58 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 std::_Deque_base<unsigned int, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::~_Deque_base() 0.00 0.58 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN12AbstractMaze3mapE 0.00 0.58 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN7MazePngC2Ejj 0.00 0.58 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN9MazeDebugC2Ejj 0.00 0.58 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I_main
For n = 3000
Flat profile: Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls ms/call ms/call name 33.08 0.44 0.44 MazePng::toPng(unsigned int) 24.06 0.76 0.32 17999970 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::getNext(unsigned int, short*, unsigned int*) 14.29 0.95 0.19 8999999 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::knockWall(unsigned int, unsigned int, AbstractMaze::directions) 12.78 1.12 0.17 1 170.00 170.00 MazePng::createImage(unsigned char**, unsigned int) 11.28 1.27 0.15 AbstractMaze::generate(int) 3.01 1.31 0.04 1 40.00 40.00 AbstractMaze::AbstractMaze(unsigned int, unsigned int) 1.50 1.33 0.02 70076 0.00 0.00 _ZNSt5dequeIjSaIjEE16_M_push_back_auxIJjEEEvDpOT_ 0.00 1.33 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 std::_Deque_base<unsigned int, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::_M_initialize_map(unsigned int) 0.00 1.33 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 std::_Deque_base<unsigned int, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::~_Deque_base() 0.00 1.33 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN12AbstractMaze3mapE 0.00 1.33 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN7MazePngC2Ejj 0.00 1.33 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN9MazeDebugC2Ejj 0.00 1.33 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I_main
For n = 4000
Flat profile: Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls ms/call ms/call name 34.51 0.78 0.78 MazePng::toPng(unsigned int) 28.32 1.42 0.64 31999957 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::getNext(unsigned int, short*, unsigned int*) 13.72 1.73 0.31 1 310.00 310.00 MazePng::createImage(unsigned char**, unsigned int) 10.18 1.96 0.23 15999999 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::knockWall(unsigned int, unsigned int, AbstractMaze::directions) 10.18 2.19 0.23 AbstractMaze::generate(int) 3.10 2.26 0.07 1 70.00 70.00 AbstractMaze::AbstractMaze(unsigned int, unsigned int) 0.00 2.26 0.00 124808 0.00 0.00 _ZNSt5dequeIjSaIjEE16_M_push_back_auxIJjEEEvDpOT_ 0.00 2.26 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 std::_Deque_base<unsigned int, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::_M_initialize_map(unsigned int) 0.00 2.26 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 std::_Deque_base<unsigned int, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::~_Deque_base() 0.00 2.26 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN12AbstractMaze3mapE 0.00 2.26 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN7MazePngC2Ejj 0.00 2.26 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN9MazeDebugC2Ejj 0.00 2.26 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I_main
For n = 5000
Flat profile: Each sample counts as 0.01 seconds. % cumulative self self total time seconds seconds calls ms/call ms/call name 35.16 1.35 1.35 MazePng::toPng(unsigned int) 27.08 2.39 1.04 49999831 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::getNext(unsigned int, short*, unsigned int*) 12.50 2.87 0.48 1 480.00 480.00 MazePng::createImage(unsigned char**, unsigned int) 11.72 3.32 0.45 AbstractMaze::generate(int) 10.68 3.73 0.41 24999999 0.00 0.00 AbstractMaze::knockWall(unsigned int, unsigned int, AbstractMaze::directions) 2.86 3.84 0.11 1 110.00 110.00 AbstractMaze::AbstractMaze(unsigned int, unsigned int) 0.00 3.84 0.00 195749 0.00 0.00 _ZNSt5dequeIjSaIjEE16_M_push_back_auxIJjEEEvDpOT_ 0.00 3.84 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 std::_Deque_base<unsigned int, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::_M_initialize_map(unsigned int) 0.00 3.84 0.00 2 0.00 0.00 std::_Deque_base<unsigned int, std::allocator<unsigned int> >::~_Deque_base() 0.00 3.84 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN12AbstractMaze3mapE 0.00 3.84 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN7MazePngC2Ejj 0.00 3.84 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I__ZN9MazeDebugC2Ejj 0.00 3.84 0.00 1 0.00 0.00 _GLOBAL__sub_I_main
Summary:
Function toPng() has an average of 42% execution time. It also has O(n^2) runtime.
Prime Numbers
Script started on Fri 10 Feb 2017 12:21:37 AM EST
hli206@matrix:~/GPU610/Assignment/primeNum> cat primeNum.custom.cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<chrono>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<math.h> // Math.h For sqrt function
using namespace std;
using namespace std::chrono;
void init(float* a, int n) {
const float randf = 1.0f / (float) RAND_MAX;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
a[i] = std::rand() * randf;
}
void reportTime(const char* msg, steady_clock::duration span) {
auto ms = duration_cast<milliseconds>(span);
std::cout << msg << " - took - " <<
ms.count() << " millisecs" << std::endl;
}
void primeFinder(int num, int bn) {
for (int i=2; i<num; i++)
for (int j=2; j*j<=i; j++)
{
if (i % j == 0)
break;
else if (j+1 > sqrt(i)) {
if(bn == 1)
cout << i << endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
int n, boolN;
steady_clock::time_point ts, te;
cout<<"Enter the Number :";
cin>>n;
cout<<"Show result?(1/0)"<<endl;
cin>>boolN;
cout<<"List Of Prime Numbers Below "<<n<<endl;
std::srand(std::time(nullptr));
ts = steady_clock::now();
primeFinder(n, boolN);
te = steady_clock::now();
reportTime("Prime Number(); ", te - ts);
return 0;
}
hli206@matrix:~/GPU610/Assignment/primeNum> cat Makefile
# Makefile for Assignment1
#
VER=custom
GCC_VERSION = 5.2.0
PREFIX = /usr/local/gcc/${GCC_VERSION}/bin/
CC = ${PREFIX}gcc
CPP = ${PREFIX}g++
primeNum.${VER}: primeNum.${VER}.o
$(CPP) -oprimeNum.${VER} primeNum.${VER}.o
primeNum.${VER}.o: primeNum.${VER}.cpp
$(CPP) -c -O2 -std=c++14 primeNum.${VER}.cpp
clean:
rm *.o
hli206@matrix:~/GPU610/Assignment/primeNum> make
make: `primeNum.custom' is up to date.
hli206@matrix:~/GPU610/Assignment/primeNum> primeNum.custom
Enter the Number :50
Show result?(1/0)
1
List Of Prime Numbers Below 50
5
7
11
13
17
19
23
29
31
37
41
43
47
Prime Number(); - took - 0 millisecs
hli206@matrix:~/GPU610/Assignment/primeNum> primeNum.custom
Enter the Number :100000
Show result?(1/0)
0
List Of Prime Numbers Below 100000
Prime Number(); - took - 84 millisecs
hli206@matrix:~/GPU610/Assignment/primeNum> primeNum.custom
Enter the Number :1000000
Show result?(1/0)
0
List Of Prime Numbers Below 1000000
Prime Number(); - took - 2065 millisecs
hli206@matrix:~/GPU610/Assignment/primeNum> primNum.custom
If 'primNum.custom' is not a typo you can use command-not-found to lookup the package that contains it, like this:
cnf primNum.custom
hli206@matrix:~/GPU610/Assignment/primeNum> primeNum.custom
Enter the Number :10000000
Show result?(1/0)
0
List Of Prime Numbers Below 10000000
Prime Number(); - took - 53504 millisecs
hli206@matrix:~/GPU610/Assignment/primeNum> exit
exit
Script done on Fri 10 Feb 2017 12:25:53 AM EST
Analysis
This is a simple c++ program for finding any prime number within range. The program function primeFinder () is the only function in the program so it takes up to nearly 100% of the execution time. Moreover, primeFinder() has a runtime of O(n^2).
primeFinder() function:
void primeFinder(int num, int bn) {
for (int i=2; i<num; i++)
for (int j=2; j*j<=i; j++)
{
if (i % j == 0)
break;
else if (j+1 > sqrt(i)) {
if(bn == 1)
cout << i << endl;
}
}
}
Recommendation
Maze.
Although Pi may have more potential, its calculated results are too limited. On the other hand, Maze has a higher limit which will enable us to do better testing.
PHASE 2
Maze
Testing Environment:
- Operating system: Windows 8.1 Enterprise 64-bit (6.3, Build 9600) (9600.winblue_ltsb.160812-0914)
- Compiler: Visual Studio 2015
- Processor: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-4790 CPU @ 3.60GHz (8 CPUs), ~3.6GHz
- System memory: 16384MB RAM
How to setup in Visual Studio 2015 in Cuda:
1. Download source files from https://github.com/corzani/maze
2. Create a new Cuda project
3. Copy all header and cpp files from the downloaded maze directory to the project directory (not the solution directory)
4. In VS, right click on the project in the Solution explorer and Add -> Existing Item; pick the copied files from the previous step
5. In VS, go to menu Tools -> NuGet Package Manager -> Package Manager Console; in the new console (at the bottom of the screen in default configuration), execute:
PM> Install-Package libpng
6. In VS, replace the entire MazePng.cpp file with the following code:
/*
* MazePng.cpp
*
* Created on: 12 Jul 2013
* Author: yac
*/
#include "MazePng.h"
// Include the parallel code...
#include "MazePng.cuh"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
MazePng::MazePng(const unsigned int width, const unsigned int height) : AbstractMaze(width, height) { }
MazePng::~MazePng() { }
void MazePng::toPng(unsigned int scale) {
png_byte color_type;
png_byte bit_depth;
png_structp png_ptr;
png_infop info_ptr;
png_bytep *row_pointers;
int height, width;
FILE *fp;
width = (this->width * 2) + 1;
height = (this->height * 2) + 1;
color_type = PNG_COLOR_TYPE_RGB;
bit_depth = 8;
row_pointers = new png_bytep[height];
// Call the kernel wrapper...
kw_drawWalls(row_pointers, this->cells, this->width, this->height, width, height, WALL, start);
fp = fopen("out.png", "wb");
png_ptr = png_create_write_struct(PNG_LIBPNG_VER_STRING, NULL, NULL, NULL);
info_ptr = png_create_info_struct(png_ptr);
png_init_io(png_ptr, fp);
png_set_IHDR(png_ptr, info_ptr, width, height, bit_depth, color_type,
PNG_INTERLACE_NONE, PNG_COMPRESSION_TYPE_BASE,
PNG_FILTER_TYPE_BASE);
png_write_info(png_ptr, info_ptr);
png_write_image(png_ptr, row_pointers);
png_write_end(png_ptr, NULL);
png_destroy_write_struct(&png_ptr, &info_ptr);
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i) {
delete[] row_pointers[i];
}
delete[] row_pointers;
fclose(fp);
}
7. In VS, right click on the project in the Solution explorer and Add -> New Item; Add a new Cuda c++ header file, name it "MazePng.cuh"
8. Copy and paste the following code into "MazePng.cuh":
// MazePng.cuh #ifndef MAZEPNG_CUH_ #define MAZEPNG_CUH_ #include "MazePng.h" #include <cuda_runtime.h> const int ntpb = 1024; void kw_drawWalls(png_bytep*& row_pointers, const short* cells, const int width, const int height, const int pixWidth, const int pixHeight, const png_byte WALL, const int start); #endif
9. In VS, right click on the project in the Solution explorer and Add -> New Item; Add a new Cuda c++ file, name it "MazePng.cu"
10. Copy and paste the following code into "MazePng.cu":
// MazePng.cu
#include "MazePng.cuh"
__global__ void k_drawWalls(png_byte* rows, const short* cells, const int width, const int height, const int len, const int size) {
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < size) {
rows[i] = WALL;
__syncthreads();
int px = i % len;
int py = i / len;
int x = (px - 1) / 2;
int y = (py - 1) / 2;
if (px > 0 && py > 0 && x < width && y < height) {
int c = (cells[y * width + x] & 0xC0) >> 6;
int idx = py * len + 3 * px;
if (c == 2) {
if (py % 2 > 0 && px % 2 == 0) {
rows[idx] = rows[idx + 1] = rows[idx + 2] = PATH;
}
}
else if (c == 1) {
if (py % 2 == 0 && px % 2 > 0) {
rows[idx] = rows[idx + 1] = rows[idx + 2] = PATH;
}
}
else if (c == 0) {
if ((py % 2 > 0 && px % 2 == 0) || (py % 2 == 0 && px % 2 > 0)) {
rows[idx] = rows[idx + 1] = rows[idx + 2] = PATH;
}
}
if (py % 2 > 0 && px % 2 > 0) {
rows[idx] = rows[idx + 1] = rows[idx + 2] = PATH;
}
}
}
}
// Kernel wrapper...
void kw_drawWalls(png_bytep*& row_pointers, const short* cells, const int width, const int height, const int pixWidth, const int pixHeight, const png_byte WALL, const int start) {
int rowLen = pixWidth * 3;
for (int i = 0; i < pixHeight; ++i) {
row_pointers[i] = new png_byte[rowLen];
}
png_byte* d_rows;
short* d_cells;
int nblks = (pixHeight * rowLen + ntpb - 1) / ntpb;
int szRows = pixHeight * rowLen * sizeof(png_byte);
int szCells = height * width * sizeof(short);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_rows, szRows);
cudaMalloc((void**)&d_cells, szCells);
cudaMemcpy(d_cells, cells, szCells, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
k_drawWalls << <nblks, ntpb >> > (d_rows, d_cells, width, height, rowLen, szRows);
cudaDeviceSynchronize();
cudaStream_t* stream = new cudaStream_t[pixHeight];
for (int i = 0; i < pixHeight; i++) {
cudaStreamCreate(&stream[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < pixHeight; i++) {
cudaMemcpyAsync(row_pointers[i], d_rows + (i * rowLen), rowLen * sizeof(png_byte), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost, stream[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < pixHeight; i++) {
cudaStreamDestroy(stream[i]);
}
if (start < width) {
int x = start * 2 + 1;
row_pointers[0][3 * x] = row_pointers[0][3 * x + 1] = row_pointers[0][3 * x + 2] = PATH;
}
delete[] stream;
cudaFree(d_cells);
cudaFree(d_rows);
}
11. In VS, change the Configuration from Debug to Release and Platform from x86 to x64
12. In VS, go to menu Build -> Build Solution
PHASE 3
Presentation
1. Introduction
- Maze
The program generates a maze in png file. It takes 2 arguments: the height and the width of the maze.
- Maze image
- Analysis:
Parallelizable?
The program function named toPng() has a runtime of O(n^2); it takes up an average of 42% (min: 35%; max: 50%) of the program's execution time.
for (int i = 0; i < height; ++i) {
row_pointers[i] = new png_byte[width * 3];
for (int j = 0; j < width * 3; j += 3) {
row_pointers[i][j] = WALL;
row_pointers[i][j + 1] = WALL;
row_pointers[i][j + 2] = WALL;
}
}
- Profiling:
2. Parallelize
- Kernel:
__global__ void k_drawWalls(png_byte* rows, const short* cells, const int width, const int height, const int len, const int size) {
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < size) {
rows[i] = WALL;
__syncthreads();
int px = i % len;
int py = i / len;
int x = (px - 1) / 2;
int y = (py - 1) / 2;
if (px > 0 && py > 0 && x < width && y < height) {
int c = (cells[y * width + x] & 0xC0) >> 6;
int idx = py * len + 3 * px;
if (c == 2) {
if (py % 2 > 0 && px % 2 == 0) {
rows[idx] = rows[idx + 1] = rows[idx + 2] = PATH;
}
}
else if (c == 1) {
if (py % 2 == 0 && px % 2 > 0) {
rows[idx] = rows[idx + 1] = rows[idx + 2] = PATH;
}
}
else if (c == 0) {
if ((py % 2 > 0 && px % 2 == 0) || (py % 2 == 0 && px % 2 > 0)) {
rows[idx] = rows[idx + 1] = rows[idx + 2] = PATH;
}
}
if (py % 2 > 0 && px % 2 > 0) {
rows[idx] = rows[idx + 1] = rows[idx + 2] = PATH;
}
}
}
}
- Profiling:
- Sum up:
- Maze size < 1500 * 1500
- Maze size > 1500 * 1500
3. Optimize
- New Kernel
__global__ void k_drawWalls(png_byte* rows, const short* cells, const int width, const int height, const int len, const int size) {
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < size) {
rows[i] = WALL;
__syncthreads();
}
}
__global__ void k_drawPaths(png_byte* rows, const short* cells, const int width, const int height, const int len) {
int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
if (i < width * height) {
int x = i % width;
int y = i / width;
int cas = (cells[i] & 0xC0) >> 6;
int oddY = (2 * y + 1) * len;
int evenY = (2 * y + 2) * len;
int oddX = (2 * x + 1) * 3;
int evenX = (2 * x + 2) * 3;
if (cas == 2) {
rows[oddY + evenX] = rows[oddY + evenX + 1] = rows[oddY + evenX + 2] = PATH;
}
else if (cas == 1) {
rows[evenY + oddX] = rows[evenY + oddX + 1] = rows[evenY + oddX + 2] = PATH;
}
else if (cas == 0) {
rows[oddY + evenX] = rows[oddY + evenX + 1] = rows[oddY + evenX + 2] = PATH;
rows[evenY + oddX] = rows[evenY + oddX + 1] = rows[evenY + oddX + 2] = PATH;
}
rows[oddY + oddX] = rows[oddY + oddX + 1] = rows[oddY + oddX + 2] = PATH;
}
}
Because there was too many else if condition in the old Kernel, we rewrite the Kernel to avoid divergent.
- Sum up:
- Still too many if statement in the Kernel
- Almost the same section as the serial