Difference between revisions of "OPS335 FTP Lab"
(→Build your VM) |
m (Clarifying instructions) |
||
| (40 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
[[Category:OPS335]][[Category:OPS335 Labs]] | [[Category:OPS335]][[Category:OPS335 Labs]] | ||
==VSFTP Setup== | ==VSFTP Setup== | ||
| − | This lab will show you how to set up an FTP server | + | This lab will show you how to set up an FTP server and provide you with experience identifying configuration parameters that meet your requirements. |
| − | + | You'll be using your Centos host as the FTP server and connecting to it from your VMs and from other machines. | |
===Background Information:=== | ===Background Information:=== | ||
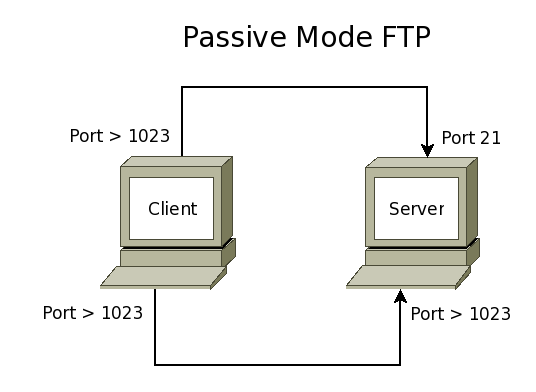
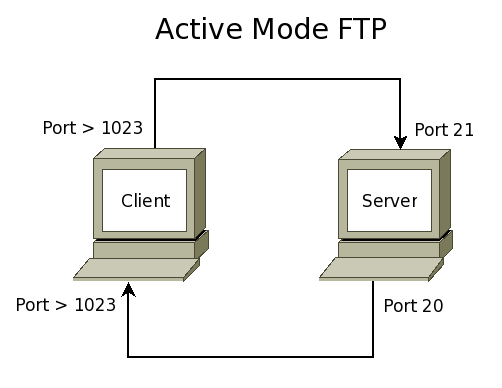
| − | FTP uses 2 TCP ports. The first, usually port 21, is used to send commands to the server (ls, cd, get, put, etc.) and to receive command replies from the server. The second, | + | FTP uses 2 TCP ports. The first, usually port 21, is used to send commands to the server (ls, cd, get, put, etc.) and to receive command replies from the server. The second, sometimes port 20, is used to send a file to the server during an upload or to receive a file from the server during a download. |
*FTP can work in 2 modes: Active or Passive. | *FTP can work in 2 modes: Active or Passive. | ||
**In active mode the client connects to the server on port 21. The server then connects back to the client from port 20. In both connections, the ports used on the client are insecure high-numbered ports ( greater than 1023 ). | **In active mode the client connects to the server on port 21. The server then connects back to the client from port 20. In both connections, the ports used on the client are insecure high-numbered ports ( greater than 1023 ). | ||
**In passive mode the client first connects to the server on port 21 and makes a second connection to a high-numbered port. As with active mode, the ports used on the client are insecure high-numbered ports ( greater than 1023 ). | **In passive mode the client first connects to the server on port 21 and makes a second connection to a high-numbered port. As with active mode, the ports used on the client are insecure high-numbered ports ( greater than 1023 ). | ||
| − | FTP can be set up so that anonymous users (users without accounts on the server) may download and possibly upload files. | + | FTP can be set up so that anonymous users (users without accounts on the server) may download and possibly upload files.<br /> |
| + | [[Image:Passive-ftp.png]][[Image:Active-ftp.png]] | ||
| − | === | + | ===Configure your VM=== |
| − | *Power up your PC (the gateway with host name | + | *Power up your PC (the gateway with host name host), login as your user-id, open a terminal window and "su" to root. |
| − | * | + | *Check the settings on your firewall. Ensure that you can still use the services you have configured in previous labs. |
| − | + | *Now make sure you are connected to the Internet. Start Firefox and authenticate yourself into the network. | |
| − | + | *Login to your VM1 and ensure you have the firewall set up to allow the services you have previously configured (e.g. DNS, apache). If those services are not functioning, fix them (or your firewall) now. | |
| − | + | Before preceeding to the next part ensure your gateway is working properly and that your server has access to the Internet. Try some of these commands on your VM/guest: | |
| − | *Now make sure you are connected to the Internet. Start Firefox and authenticate yourself | + | ping 192.168.X.1 |
| − | |||
| − | *Login to your | ||
| − | Before preceeding to the next part ensure your gateway is working properly and that your server has | ||
| − | ping 192.168. | ||
host cbc.ca | host cbc.ca | ||
| − | also | + | also use lynx from your vm to ensure you can view internal and external web sites. |
===Set up your FTP Server (Passive Mode)=== | ===Set up your FTP Server (Passive Mode)=== | ||
| − | + | *On your Centos host you should not need to install vsftpd. If it is not present, install it. | |
| − | #*Anonymous users should be able to login and download any files (permissions allowing) from the /var/ftp/pub. | + | yum install vsftpd |
| + | #Edit the config file (/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf) to implement the following: | ||
| + | #*Anonymous users should be able to login and download any files (permissions allowing) from the directory /var/ftp/pub. | ||
#*Anonymous uploading should not be allowed. | #*Anonymous uploading should not be allowed. | ||
| − | #* | + | #*Prevent local accounts from logging in. |
| − | #The FTP Greeting Banner should be set to "Welcome to OPS335 FTP Server". | + | #*The FTP Greeting Banner should be set to "Welcome to my OPS335 FTP Server". |
| − | #Set the maximum number of concurrent client connections to | + | #*Set the server to listen on IPv4 sockets, not IPv6. |
| − | #Set the maximum transfer rate for anonymous users to | + | #*Set the maximum number of concurrent client connections to 30. |
| − | #Set the connection timeout for | + | #*Set the maximum transfer rate for anonymous users to 140300 bytes per second. |
| − | #Enable file transfer logging. | + | #*Set the connection timeout for idle clients to two minutes. |
| − | #You'll now have to modify your | + | #*Enable file transfer logging. |
| − | # | + | #*Limit the range of ports passive mode is allowed to use to 14335 to 14935. |
| − | + | #You'll now have to modify your firewall to allow NEW tcp connections on port 21, and tcp connections on the same ports vsftp is will use for data connections. | |
| − | #At this point you should test your FTP server from hosts within your intranet. It should | + | #Verify that the ftp connection tracking module is installed in your kernel with the "lsmod" command. If it is not, you'll have to install it with the command: "modprobe nf_conntrack_ftp". |
| − | #*ftp | + | #Start your ftp server. |
| − | #* | + | #From the command line of your server, create a new file (or several) in /var/ftp/pub. |
| − | === | + | #Change the ownership of the /var/ftp/pub directory to the user ftp. |
| − | *Now configure your firewall (using iptables) on the gateway to allow FTP clients | + | #At this point you should test your FTP server from other hosts within your intranet. It should allow anonymous users to retrieve files. From one of your VMs try these activities: |
| − | + | #*ftp using the login 'ftp' to your host, then list and get the file you created. | |
| − | *Test your firewall by logging into a second PC (try both Windows and Linux) and attempt an FTP connection to your gateway PC. Test | + | #*Try logging is as a user that exists on that machine. |
| + | |||
| + | ===Connecting from outside your intranet=== | ||
| + | *Now configure your firewall (using iptables) on the gateway machine to allow FTP clients from outside your network (if you did not already do so). | ||
| + | *Test your firewall by logging into a second PC (try both Windows and Linux) and attempt an FTP connection to your gateway PC. Test the anonymous user's ability to list and get files again. | ||
| + | |||
===Set up your FTP Server (Active Mode)=== | ===Set up your FTP Server (Active Mode)=== | ||
| − | #Edit /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf and disable Passive mode | + | #Edit /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf and disable Passive mode, ensure active mode is enabled, and then restart vsftpd. |
| + | #Add any iptables rules necessary to allow active connections. | ||
#Test your firewall by logging into a second PC (try both Windows and Linux) and attempt an FTP connection to your gateway PC. Test both local user as well as anonymous connections. | #Test your firewall by logging into a second PC (try both Windows and Linux) and attempt an FTP connection to your gateway PC. Test both local user as well as anonymous connections. | ||
| − | ===Log Packets with | + | |
| − | #On the firewall/gateway add iptables log rules to monitor ftp traffic (control and data) | + | ===Log Packets with iptables=== |
| − | + | #On the firewall/gateway add iptables log rules to monitor ftp traffic (control and data) from outside your network in both of the following. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
#*INPUT chain of filter table | #*INPUT chain of filter table | ||
#*OUTPUT chain of filter table | #*OUTPUT chain of filter table | ||
| − | # | + | #While monitoring your packets using "tail -f /var/log/messages" - test your firewall logs by connecting from one of your VMs, and then by logging into a second PC (try both Windows and Linux) and attempt an FTP connection to your gateway PC. Test both local user as well as anonymous connections. |
| − | + | ||
==Completing the Lab== | ==Completing the Lab== | ||
| − | + | In completing this lab you have gained experience using a service that has multiple modes. You have practiced researching configuration parameters to find the ones you need. This will be an invaluable skill, as you will not usually have anyone telling you specifically which parameters to set, or what values to set them to. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | # | + | Exploration questions: |
| − | # | + | #What parameters did you use to force vsftp to use active mode only. |
| − | # | + | #What version number of vsftpd are you using. |
| − | # | + | #What parameters would you set to configure vsftp to use ssl for authentication. |
| − | + | #If you wanted to allow your local users to access their files through ftp, what parameters would you set, and what would you set them to? | |
| − | |||
Latest revision as of 17:02, 30 November 2015
Contents
VSFTP Setup
This lab will show you how to set up an FTP server and provide you with experience identifying configuration parameters that meet your requirements. You'll be using your Centos host as the FTP server and connecting to it from your VMs and from other machines.
Background Information:
FTP uses 2 TCP ports. The first, usually port 21, is used to send commands to the server (ls, cd, get, put, etc.) and to receive command replies from the server. The second, sometimes port 20, is used to send a file to the server during an upload or to receive a file from the server during a download.
- FTP can work in 2 modes: Active or Passive.
- In active mode the client connects to the server on port 21. The server then connects back to the client from port 20. In both connections, the ports used on the client are insecure high-numbered ports ( greater than 1023 ).
- In passive mode the client first connects to the server on port 21 and makes a second connection to a high-numbered port. As with active mode, the ports used on the client are insecure high-numbered ports ( greater than 1023 ).
FTP can be set up so that anonymous users (users without accounts on the server) may download and possibly upload files.
Configure your VM
- Power up your PC (the gateway with host name host), login as your user-id, open a terminal window and "su" to root.
- Check the settings on your firewall. Ensure that you can still use the services you have configured in previous labs.
- Now make sure you are connected to the Internet. Start Firefox and authenticate yourself into the network.
- Login to your VM1 and ensure you have the firewall set up to allow the services you have previously configured (e.g. DNS, apache). If those services are not functioning, fix them (or your firewall) now.
Before preceeding to the next part ensure your gateway is working properly and that your server has access to the Internet. Try some of these commands on your VM/guest:
ping 192.168.X.1 host cbc.ca
also use lynx from your vm to ensure you can view internal and external web sites.
Set up your FTP Server (Passive Mode)
- On your Centos host you should not need to install vsftpd. If it is not present, install it.
yum install vsftpd
- Edit the config file (/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf) to implement the following:
- Anonymous users should be able to login and download any files (permissions allowing) from the directory /var/ftp/pub.
- Anonymous uploading should not be allowed.
- Prevent local accounts from logging in.
- The FTP Greeting Banner should be set to "Welcome to my OPS335 FTP Server".
- Set the server to listen on IPv4 sockets, not IPv6.
- Set the maximum number of concurrent client connections to 30.
- Set the maximum transfer rate for anonymous users to 140300 bytes per second.
- Set the connection timeout for idle clients to two minutes.
- Enable file transfer logging.
- Limit the range of ports passive mode is allowed to use to 14335 to 14935.
- You'll now have to modify your firewall to allow NEW tcp connections on port 21, and tcp connections on the same ports vsftp is will use for data connections.
- Verify that the ftp connection tracking module is installed in your kernel with the "lsmod" command. If it is not, you'll have to install it with the command: "modprobe nf_conntrack_ftp".
- Start your ftp server.
- From the command line of your server, create a new file (or several) in /var/ftp/pub.
- Change the ownership of the /var/ftp/pub directory to the user ftp.
- At this point you should test your FTP server from other hosts within your intranet. It should allow anonymous users to retrieve files. From one of your VMs try these activities:
- ftp using the login 'ftp' to your host, then list and get the file you created.
- Try logging is as a user that exists on that machine.
Connecting from outside your intranet
- Now configure your firewall (using iptables) on the gateway machine to allow FTP clients from outside your network (if you did not already do so).
- Test your firewall by logging into a second PC (try both Windows and Linux) and attempt an FTP connection to your gateway PC. Test the anonymous user's ability to list and get files again.
Set up your FTP Server (Active Mode)
- Edit /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf and disable Passive mode, ensure active mode is enabled, and then restart vsftpd.
- Add any iptables rules necessary to allow active connections.
- Test your firewall by logging into a second PC (try both Windows and Linux) and attempt an FTP connection to your gateway PC. Test both local user as well as anonymous connections.
Log Packets with iptables
- On the firewall/gateway add iptables log rules to monitor ftp traffic (control and data) from outside your network in both of the following.
- INPUT chain of filter table
- OUTPUT chain of filter table
- While monitoring your packets using "tail -f /var/log/messages" - test your firewall logs by connecting from one of your VMs, and then by logging into a second PC (try both Windows and Linux) and attempt an FTP connection to your gateway PC. Test both local user as well as anonymous connections.
Completing the Lab
In completing this lab you have gained experience using a service that has multiple modes. You have practiced researching configuration parameters to find the ones you need. This will be an invaluable skill, as you will not usually have anyone telling you specifically which parameters to set, or what values to set them to.
Exploration questions:
- What parameters did you use to force vsftp to use active mode only.
- What version number of vsftpd are you using.
- What parameters would you set to configure vsftp to use ssl for authentication.
- If you wanted to allow your local users to access their files through ftp, what parameters would you set, and what would you set them to?