Difference between revisions of "Abstract Factory"
(→Definition) |
(→UML Class Diagram) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
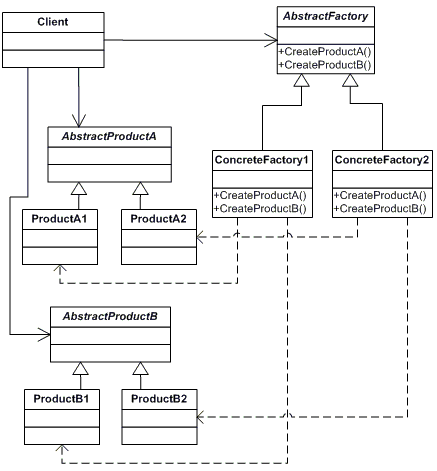
A software design pattern, the Abstract Factory Pattern provides a way to encapsulate a group of individual factories that have a common theme. In normal usage, the client software would create a concrete implementation of the abstract factory and then use the generic interfaces to create the concrete objects that are part of the theme. The client does not know (nor care) about which concrete objects it gets from each of these internal factories since it uses only the generic interfaces of their products. This pattern separates the details of implementation of a set of objects from its general usage. | A software design pattern, the Abstract Factory Pattern provides a way to encapsulate a group of individual factories that have a common theme. In normal usage, the client software would create a concrete implementation of the abstract factory and then use the generic interfaces to create the concrete objects that are part of the theme. The client does not know (nor care) about which concrete objects it gets from each of these internal factories since it uses only the generic interfaces of their products. This pattern separates the details of implementation of a set of objects from its general usage. | ||
| − | ===UML | + | ===UML Diagram=== |
| + | |||
[[Image:Abstract_factory_uml.gif]] | [[Image:Abstract_factory_uml.gif]] | ||
| + | |||
Picture Source:[http://www.dofactory.com/Patterns/PatternAbstract.aspx] | Picture Source:[http://www.dofactory.com/Patterns/PatternAbstract.aspx] | ||
Revision as of 19:09, 18 February 2007
Definition
A software design pattern, the Abstract Factory Pattern provides a way to encapsulate a group of individual factories that have a common theme. In normal usage, the client software would create a concrete implementation of the abstract factory and then use the generic interfaces to create the concrete objects that are part of the theme. The client does not know (nor care) about which concrete objects it gets from each of these internal factories since it uses only the generic interfaces of their products. This pattern separates the details of implementation of a set of objects from its general usage.
UML Diagram
Picture Source:[1]